Tools like Git are very heavily used for tracking changes, managing history and collaboration of the teams around infrastructure code. With an IaC project such as Terraform or Ansible, with every modification or update a commit on a shared GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket repo is made. This way not only collaboration takes place and rolling back becomes possible and the changes are clearly defined in the time series change in the infra.
Some important practices when it comes to managing version control on infrastructure code include:
Modularize Code: The infrastructure code is broken down into smaller modules that can be reused. This allows teams to have different versions and updates on specific parts without affecting the entire codebase.
Branching Strategy: Branches can be used for development, testing, and production environments. A common branching strategy involves using feature, dev, stage, and main. This allows isolated environments for testing before deploying it into production.
Commit Frequently and Track Changes: It lets one track the incremental upgrades; the meaningful commit message makes changes in the infrastructures easier to understand
Pull Requests: With a pull request, the team codes get reviewed and approved before implementation to prevent the possible occurrence of errors.
Automation via CI/CD Pipelines: CI/CD pipelines can be used to automatically validate and deploy changes to infrastructure. For instance, a CI/CD pipeline might validate Terraform configurations using the terraform plan and terraform validate commands before pushing the changes.
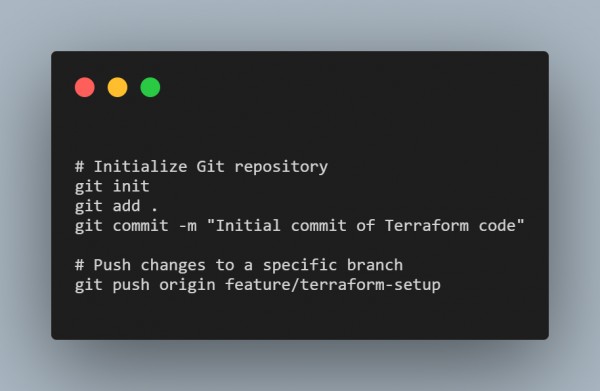
Example: Use the Git to create a new repository. Then, initiate a simple Terraform setup by committing your code change and finally pushing to the remote branch.
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
 Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP