Ensuring high availability in applications has multifaceted approaches, coding techniques, and tools. I approach it as follows:
1. Load Balancing
Techniques/Tools: I use tools such as Nginx, HAProxy, or AWS Elastic Load Balancer that can help me distribute traffic very evenly across multiple servers. It minimizes the chance of a point of failure.
Coding Example (Nginx configuration snippet):

2. Replication and Redundancy
Techniques/Tools: Databases like MySQL replication or multi-AZ deployments at AWS are known to make use of master-slave replication. This leaves open the possibility for always accessing data, such as in the case of one node crashing.
Coding Example (MySQL Replication):

3. Auto-Scaling
Techniques/Tools: Instances running by AWS Auto Scaling or Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler scale up or down based on traffic.
Coding Example (Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler):

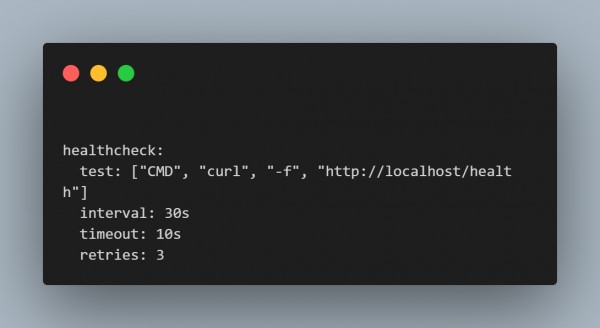
4. Health Checks and Failover Mechanisms
Techniques/Tools: Health checks can be done with Docker Swarm or Kubernetes to monitor the state of the application. Automated failover will also take place so if there are instances of failures, the traffic would automatically be redirected to healthy instances.
Coding Example (Docker Swarm):
5. Caching
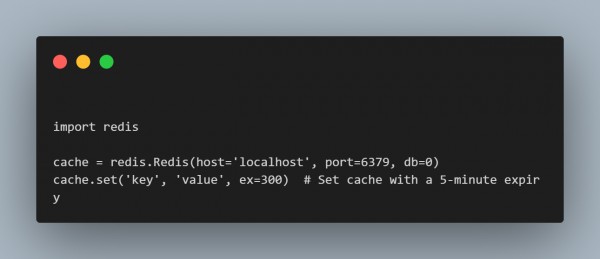
Techniques/Tools: Redis or Memcached can be used to cache frequently accessed data mechanisms on the primary application servers, offloading, and therefore decongesting the load, which in turn quickens the response times.
Coding Example (Redis setup for caching):
With these practices and tools in place, applications become highly available, responsive, even in the presence of heavy traffic, or when hardware has failed.
If you're looking for a better career, I personally suggest you take the PG in DevOps!
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
 Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP