A general script automation choice in CI/CD pipelines includes Bash, Python, and Groovy. They cover everything in CI/CD: versatile, widely supported, and perfect for more common CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI. Adding DevOps training to your skill set can help you master these scripting languages and optimize automation in your workflows.Here's why these languages are so popular in a nutshell:
- Bash: Fit for tiny scripts that run natively on Unix-like operating systems. Fits well for making aliases for functions, moving and renaming files, updating your system to the latest packages, or integrating with other CLI tools.
- Python: Highly readable with an incredibly broad set of libraries, Python is ideal for heavier tasks, such as API integration, data manipulation or when you need cross-platform compatibility.
- Groovy: This is quite commonly used with Jenkins, but its use would be to script in the Jenkins environment, especially to set up and manage Jenkins jobs.
Here’s a simple example of a Bash script to automate a CI/CD pipeline task, such as deploying an application:
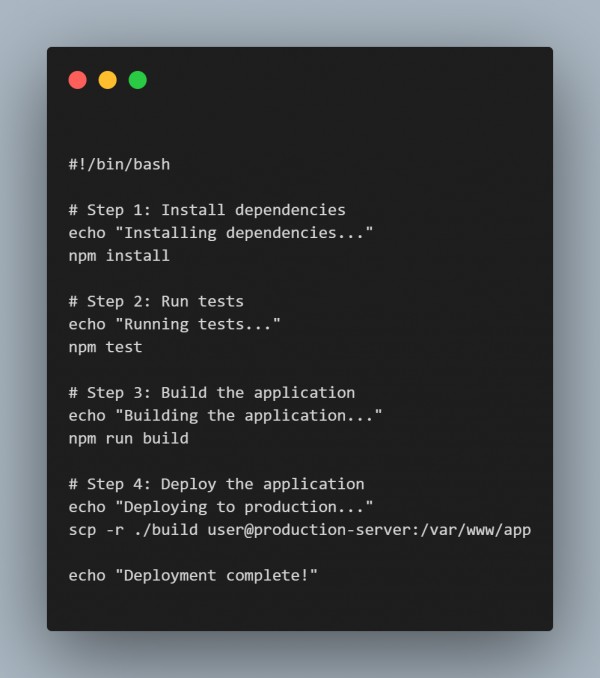
This is a very basic example of CI/CD flow. It installs dependencies there, runs tests, builds an app, and then it is deployed to a server on production.
I have found combining languages on a task-by-task basis according to the requirements of the task at hand to be flexible and effective in CI/CD pipelines.
If you're looking for a better career, I personally suggest you take the DevOps Post Graduate Program!
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
 Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP