Artificial Intelligence Certification Course
- 19k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend
- Live Class
With the advancement in Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence has taken a high road. Deep Learning is considered to be the most advanced technology built to solve complex problems that use massive data sets. This blog on what is a Neural Networks will introduce you to the basic concepts of Neural Networks and how they can solve complex data-driven problems.
Here’s a list of topics that will be covered in this blog:
Modeled in accordance with the human brain, a Neural Network was built to mimic the functionality of a human brain. The human brain is a neural network made up of multiple neurons, similarly, an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is made up of multiple perceptrons (explained later).
A neural network consists of three important layers:
Check out this Artificial Intelligence Course by Edureka to upgrade your AI skills to the next level. Before we get into the depths of how a Neural Network functions, let’s understand what Deep Learning is.
Deep Learning is an advanced field of Machine Learning that uses the concepts of Neural Networks to solve highly-computational use cases that involve the analysis of multi-dimensional data. It automates the process of feature extraction, making sure that very minimal human intervention is needed.

So what exactly is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is an advanced sub-field of Machine Learning that uses algorithms inspired by the structure and function of the brain called Artificial Neural Networks.
People often tend to think that Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are the same since they have common applications. For example, Siri is an application of AI, Machine learning and Deep learning.
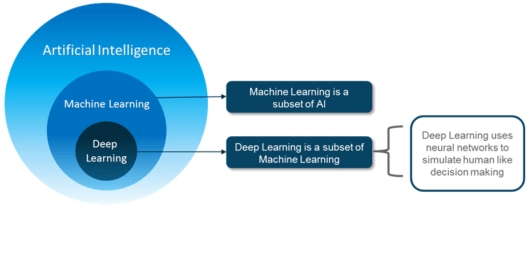
So how are these technologies related?
To sum it up AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning are interconnected fields. Machine Learning and Deep learning aids Artificial Intelligence by providing a set of algorithms and neural networks to solve data-driven problems.
Now that you’re familiar with the basics, let’s understand what led to the need for Deep Learning.
Machine Learning was a major breakthrough in the technical world, it led to the automation of monotonous and time-consuming tasks, it helped in solving complex problems and making smarter decisions. However, there were a few drawbacks in Machine learning that led to the emergence of Deep Learning.
Here are some limitations of Machine Learning:
Before we get into the depths of Neural Networks, let’s consider a real-world use case where Deep Learning is implemented.
Did you know that PayPal processes over $235 billion in payments from four billion transactions by its more than 170 million customers? It uses this vast amount of data to identify possible fraudulent activities among other reasons.
With the help of Deep Learning algorithms, PayPal mined data from their customer’s purchasing history in addition to reviewing patterns of likely fraud stored in its databases to predict whether a particular transaction is fraudulent or not.
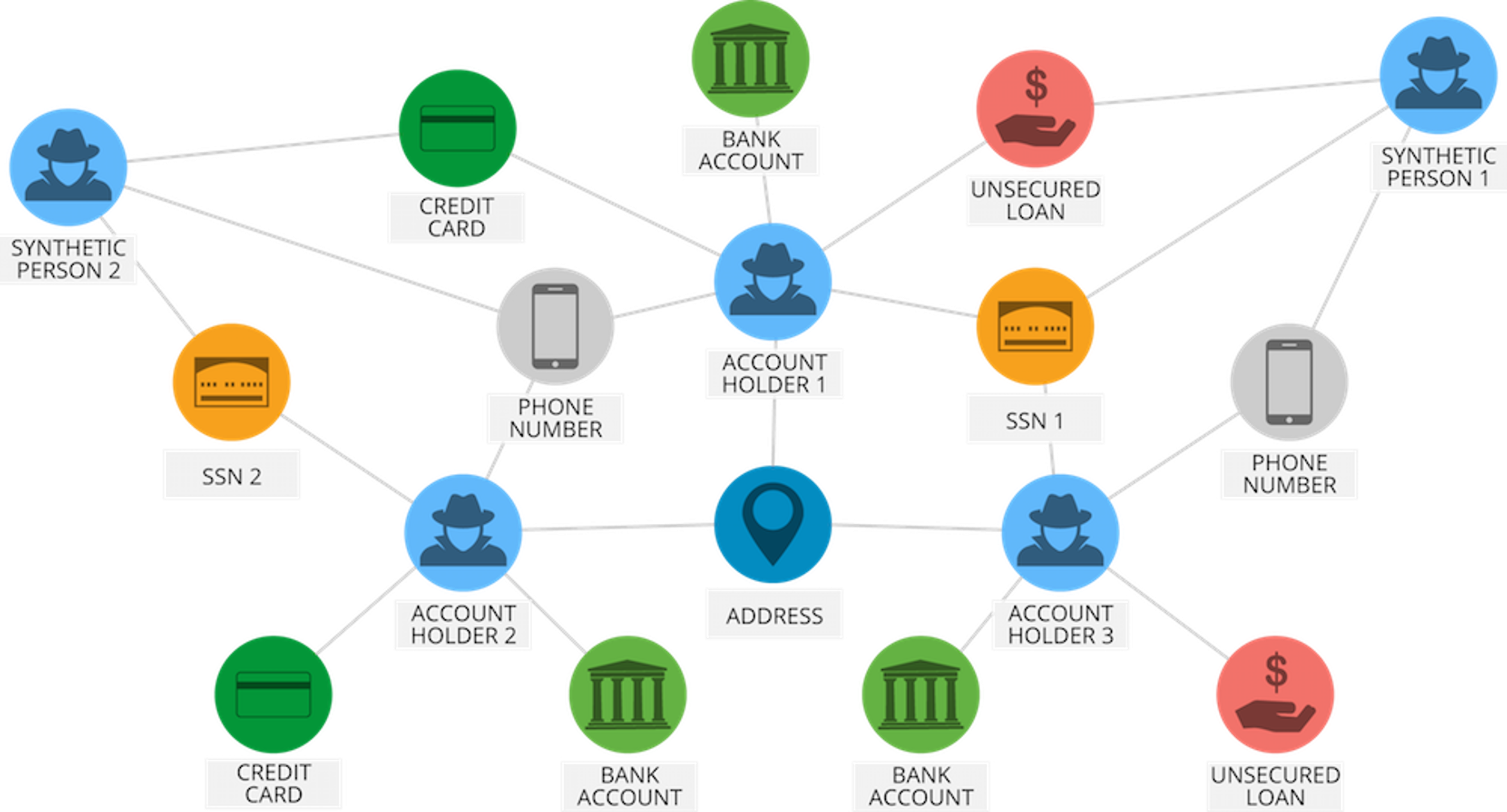
The company has been relying on Deep Learning & Machine Learning technology for around 10 years. Initially, the fraud monitoring team used simple, linear models. But over the years the company switched to a more advanced Machine Learning technology called, Deep Learning.
Fraud risk manager and Data Scientist at PayPal, Ke Wang, quoted:
“What we enjoy from more modern, advanced machine learning is its ability to consume a lot more data, handle layers and layers of abstraction and be able to ‘see’ things that a simpler technology would not be able to see, even human beings might not be able to see.”
A simple linear model is capable of consuming around 20 variables. However, with Deep Learning technology one can run thousands of data points. Therefore, by implementing Deep Learning technology, PayPal can finally analyze millions of transactions to identify any fraudulent activity.
Now let’s go into the depths of a Neural Network and understand how they work.
To understand neural networks, we need to break it down and understand the most basic unit of a Neural Network, i.e. a Perceptron.
A Perceptron is a single layer neural network that is used to classify linear data. It has 4 important components:
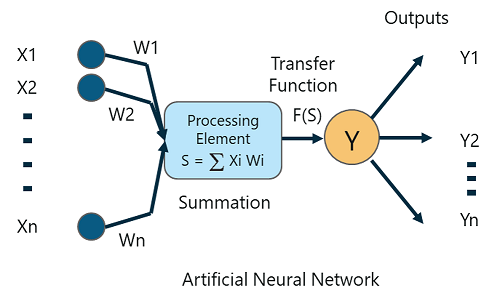
The basic logic behind a Perceptron is as follows:
The inputs (x) received from the input layer are multiplied with their assigned weights w. The multiplied values are then added to form the Weighted Sum. The weighted sum of the inputs and their respective weights are then applied to a relevant Activation Function. The activation function maps the input to the respective output.
Why do we have to assign weights to each input?
Once an input variable is fed to the network, a randomly chosen value is assigned as the weight of that input. The weight of each input data point indicates how important that input is in predicting the outcome.
The bias parameter, on the other hand, allows you to adjust the activation function curve in such a way that a precise output is achieved.
Once the inputs are assigned some weight, the product of the respective input and weight is taken. Adding all these products gives us the Weighted Sum. This is done by the summation function.
The main aim of the activation functions is to map the weighted sum to the output. Activation functions such as tanh, ReLU, sigmoid and so on are examples of transformation functions.
To learn more about the functions of Perceptrons, you can go through this Deep Learning: Perceptron Learning Algorithm blog.
Before we wrap up this blog, let’s take a simple example to understand how a Neural Network operates.
Consider a scenario where you are to build an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) that classifies images into two classes:
So how do you create a Neural network that classifies the leaves into diseased and non-diseased crops?
The process always begins with processing and transforming the input in such a way that it can be easily processed. In our case, each leaf image will be broken down into pixels depending on the dimension of the image.
For example, if the image is composed of 30 by 30 pixels, then the total number of pixels will be 900. These pixels are represented as matrices, which are then fed into the input layer of the Neural Network.
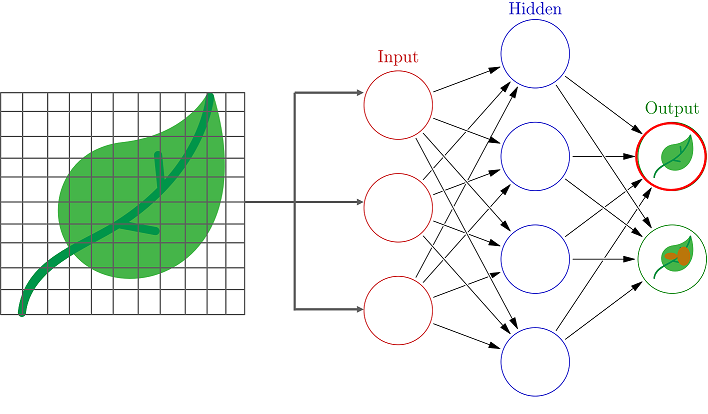
Just like how our brains have neurons that help in building and connecting thoughts, an ANN has perceptrons that accept inputs and process them by passing them on from the input layer to the hidden and finally the output layer.
As the input is passed from the input layer to the hidden layer, an initial random weight is assigned to each input. The inputs are then multiplied with their corresponding weights and their sum is sent as input to the next hidden layer.
Here, a numerical value called bias is assigned to each perceptron, which is associated with the weightage of each input. Further, each perceptron is passed through activation or a transformation function that determines whether a particular perceptron gets activated or not.
An activated perceptron is used to transmit data to the next layer. In this manner, the data is propagated (Forward propagation) through the neural network until the perceptrons reach the output layer.
At the output layer, a probability is derived which decides whether the data belongs to class A or class B.
Sounds simple, doesn’t it? Well, the concept behind Neural Networks is purely based on the functioning of the human brain. You require in-depth knowledge of various mathematical concepts and algorithms. Here’s a list of blogs to get you started:
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co