DevOps Certification Training
- 187k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Puppet is the most mature and the most widely used tool for Configuration Management. There is a high possibility that it can be a major point of discussion in your interview. So here I am with the set of frequently asked Puppet interview questions. Curious to know more about Puppet check out this Puppet blog series.
This Puppet Interview Questions blog is a part of parent blog DevOps Interview Questions. It includes all the DevOps Stages.
No surprise, In this Puppet Interview Questions blog the first question has to be:
I will advise you to first give a small definition of Puppet. Puppet is a Configuration Management tool which is used to automate administration tasks.
| Feature | Description |
| Infrastructure Automation | It defines and continuously enforces the IT configurations no matter where your infrastructure lives. |
| Automated Provisioning | It provides an automated provisioning across your heterogeneous IT infrastructure. |
| Task Management | It can make changes or remediate urgent problems alongside the model-driven automation management. |
| Visualization & Reporting | It gives you an insight into your infrastructure, audit changes, & get rich reporting in a graphical console. |
| Code Management | It manages the infrastructure as code using version control systems to enable continuous delivery. |
| Discovery & Insights | It can quickly discover resources that need automated management and drive change. |
| Orchestration | It lets you orchestrate change with control, visibility, & automated intelligence. |
Now, you should describe how Puppet Master and Agent communicates.
Puppet has a Master-Slave architecture in which the Slave has to first send a Certificate signing request to Master and Master has to sign that Certificate in order to establish a secure connection between Puppet Master and Puppet Slave as shown on the diagram below. Puppet Slave sends a request to Puppet Master and Puppet Master then pushes configuration on Slave.
Refer the diagram below that explains the above description:
For this question just explain Puppet Architecture. Refer the diagram below:
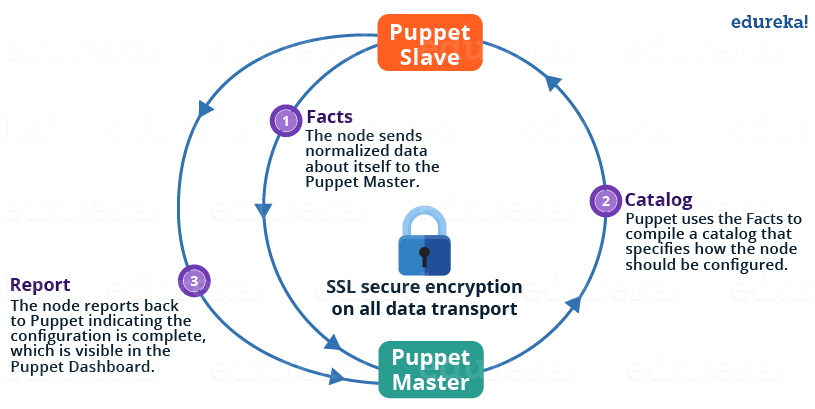
The following functions are performed in the above image:
Now the interviewer might dig in deep, so the next set of Puppet interview questions will test your knowledge about various components of Puppet.
It is a very important question and just make sure you go in a correct flow according to me you should first define Manifests.
Every node (or Puppet Agent) has got its configuration details in Puppet Master, written in the native Puppet language. These details are written in the language which Puppet can understand and are termed as Manifests. Manifests are composed of Puppet code and their filenames use the .pp extension.
Now give an example, you can write a manifest in Puppet Master that creates a file and installs apache on all Puppet Agents (Slaves) connected to the Puppet Master.
For this answer I will prefer the below mentioned explanation:
A Puppet Module is a collection of Manifests and data (such as facts, files, and templates), and they have a specific directory structure. Modules are useful for organizing your Puppet code, because they allow you to split your code into multiple Manifests. It is considered best practice to use Modules to organize almost all of your Puppet Manifests.
Puppet programs are called Manifests. Manifests are composed of Puppet code and their file names use the .pp extension.
You are expected to answer what exactly Facter does in Puppet so, according to me you should start by explaining:
Facter is basically a library that discovers and reports the per-Agent facts to the Puppet Master such as hardware details, network settings, OS type and version, IP addresses, MAC addresses, SSH keys, and more. These facts are then made available in Puppet Master’s Manifests as variables.
I will suggest you to first, tell the uses of Puppet Catalog.
When configuring a node, Puppet Agent uses a document called a catalog, which it downloads from a Puppet Master. The catalog describes the desired state for each resource that should be managed, and may specify dependency information for resources that should be managed in a certain order.
If your interviewer wants to know more about it mention the below points:
Puppet compiles a catalog using three main sources of configuration info:
There is no minimum or maximum organization size that can benefit from Puppet, but there are sizes that are more likely to benefit. Organizations with only a handful of servers are unlikely to consider maintaining those servers to be a real problem, Organizations with many servers are more likely to find, difficult to manage those servers manually so using Puppet is more beneficial for those organizations.
The best way to install and upgrade Puppet and Facter is via your operating system’s package management system, using either your vendor’s repository or one of Puppet Labs’ public repositories.
If you have installed Puppet from source, make sure you remove old versions entirely (including all application and library files) before upgrading. Configuration data (usually located in/etc/puppet or /var/lib/puppet, although the location can vary) can be left in place between installs.
The next set of Puppet Interview Questions will test your experience with Puppet.
According to me you should mention the command first.
To check the list of Certificate signing requests from Puppet Agent to Puppet Master execute puppet cert list command in Puppet Master.
I will advise you to also add:
If you want to sign a particular Certificate execute: puppet cert sign <Hostname of agent>. You can also sign all the Certificates at once by executing: puppet cert sign all.
Answer to this question is pretty direct just tell the uses of the above commands:
I hope you have enjoyed the above set of Puppet interview questions, the next set of questions will be more challenging, so be prepared.
I will advise you to answer this by mentioning the characters:
Class names can contain lowercase letters, numbers, and underscores, and should begin with a lowercase letter. “::” (Scope Resolution Operator) can be used as a namespace separator.
The same rules should be used when naming defined resource types, modules, and parameters, although modules and parameters cannot use the namespace separator.
Variable names can include alphanumeric characters and underscores, and are case-sensitive.
Yes. As of Puppet 2.7.6 basic types and providers do run on Windows, and the test suite is being run on Windows to ensure future compatibility.
I will suggest you to mention the below points in your answer:
Explain about some tools that you have used along with Puppet to do a specific task. You can refer the below example:
Changes and requests are ticketed through Jira and we manage requests through an internal process. Then, we use Git and Puppet’s Code Manager app to manage Puppet code in accordance with best practices. Additionally, we run all of our Puppet changes through our continuous integration pipeline in Jenkins using the beaker testing framework.
Explain them about your past experience of Puppet and how it was useful to resolve conflicts, you can refer the below mention example:
The development team wanted root access on test machines managed by Puppet in order to make specific configuration changes. We responded by meeting with them weekly to agree on a process for developers to communicate configuration changes and to empower them to make many of the changes they needed. Through our joint efforts, we came up with a way for the developers to change specific configuration values themselves via data abstracted through Hiera. In fact, we even taught one of the developers how to write Puppet code in collaboration with us.
I will suggest you to start this answer by saying:
Not directly. However, Facter reads in custom facts from a special subset of environment variables. Any environment variable with a prefix of FACTER_ will be converted into a fact when Facter runs.
Now explain the interviewer with an example:
$ FACTER_FOO=”bar” $ export FACTER_FOO</span> $ facter | grep ‘foo’</span> foo => bar
The value of the FACTER_FOO environment variable would now be available in your Puppet manifests as $foo, and would have a value of ‘bar’. Using shell scripting to export an arbitrary subset of environment variables as facts is left as an exercise for the reader.
First you need to define Virtual Resource.
Virtual Resources specifies a desired state for a resource without necessarily enforcing that state. Although virtual resources can only be declared once, they can be realized any number of times.
I will suggest you to mention the uses of Virtual Resources as well:
Once you are prepared with the above Puppet interview questions your dream job is not far.
I have included the frequently asked Puppet interview questions. If you have more questions in your mind just type it in the comment box below and we will reply you ASAP. Before going for the interview I will suggest you to check out this Puppet blog series.
If you found this blog on Puppet Interview Questions relevant, check out the DevOps training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. The Edureka DevOps Certification Training course helps learners gain expertise in various DevOps processes and tools such as Puppet, Jenkins, Nagios and GIT for automating multiple steps in SDLC.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
what is the biggest challenge you faced while writing modules?