Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
One in-demand certification for cybersecurity is the CISSP Certification, which is commonly known as Certified Information Systems Security Professional. CISSP is a globally recognized certification focusing on various aspects of cybersecurity, including risk management and security policies. It is offered by (ISC)², i.e., The International Information System Security Certification Consortium. These CISSP Interview Questions and Answers will help you prepare yourself for security-related interviews and CISSP exam preparation as well.
Cybersecurity is a broad and complex field that involves protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage. Cybersecurity professionals ensure that information is accessible only to those who have the proper authorization and put in place measures to prevent unauthorized alteration, modification, or deletion of information. The growing demand for cybersecurity professionals is likely to persist as organizations strive to strengthen their cyber defenses because of the persistent cyber threats.
Becoming a cybersecurity professional involves a combination of education, hands-on experience, and continuous learning. CISSP Certification is an important milestone for cyber professionals as it validates their skills, opens up career opportunities, provides industry recognition, and contributes to continuous learning and development.
Now, let’s explore the CISSP Interview Questions and Answers in according to the eight domains of CISSP. We have more than 30 CISSP interview questions and answers line up below.
1. Explain the CIA triad.
The CIA triad consists of three core principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These principles form the basis for designing and implementing security measures to protect information assets.
Confidentiality: Confidentiality means that information is only available to authorized individuals, entities, or processes. It deals with safeguarding data against unauthorized access and disclosure.
Integrity: Integrity ensures that information remains accurate, complete, and reliable throughout its lifecycle. It involves protecting data from unauthorized modification, alteration, or corruption.
Availability: Availability ensures that data is accessible when needed by authorized users. It involves ensuring that systems, networks, and data remain operational and accessible, even in the face of disruptions, failures, or attacks.
2. What are the steps you need to take for risk management in your organization?
There are five main steps involved in risk management. They are
Identify Risks: This step includes Identifying potential risks that could affect the objectives of the organization. This deals with identifying internal and external factors that may lead to threats.
Assess Risks: Evaluate the impact of identified risks. This step involves analyzing the probability of each risk occurring and estimating the severity of its impact. Risk assessment techniques such as qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis can be employed.
Risk Prioritization: It deals with ranking risks according to their impact to determine which ones require immediate attention for mitigation. Consider factors such as the organization’s risk tolerance and available resources when prioritizing risks.
Risk Mitigation: This step involves developing and implementing strategies to reduce identified risks by taking preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of risks. Common risk mitigation strategies include risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk reduction, and risk acceptance.
Risk Monitoring: This step deals with continuously monitoring the effectiveness of risk management measures. This step involves monitoring key risk indicators (KRIs) and performance metrics to track the status of identified risks.
3. What is Privacy? What are the OECD privacy guidelines?
Privacy is the ability of individuals to control access to their personal data and to make decisions about how that information is collected, used, shared, and stored by others. Personal data must be well protected to comply with current privacy laws and to protect the value of the information and of the organization itself.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an international organization dedicated to establishing international standards and policies, as well as finding solutions to social, economic, and environmental challenges.
OECD guidelines are based on these following principles:
4. Can you suggest some methods to enforce personnel security policies and procedures in your organization?
5. Explain Data Classification Roles.
6. Explain the Information life cycle.
The information life cycle refers to the stages through which information passes from its creation or acquisition to its disposal. This is commonly used in information management to understand and manage the flow of information within organizations.

7. What are some methods to protect data in transit?
Data in transit refers to information that is actively being transferred or transmitted between systems, networks, or devices. This can include various types of data, such as emails, files, messages, or streaming media, as it travels from a source to a destination over a network.
8. What are some methods for Information Obfuscation?
Information obfuscation methods are techniques that obscure or conceal sensitive or confidential information, which is employed to protect data privacy, intellectual property, or sensitive information.
9. Explain any five secure design principles.
10. What are Security models? Explain any one security model.
Security models are conceptual frameworks used to enforce security policies and access controls within a computing environment. These models provide a structured approach to managing security requirements. There are several security models. One such security model is the Bell-LaPadula model.
The Bell-LaPadula model is a security model used primarily for confidentiality enforcement in computer systems. This model has become a foundational concept in the field of computer security. The model is based on the principle of mandatory access control (MAC), where access to resources is determined by security labels associated with subjects and objects. In the Bell-LaPadula model, Each piece of information and each user in the system is assigned a security label that indicates its security level.
Some Properties of Bell-LaPadula model include:
11. Explain TCSEC and ITSEC.
TCSEC and ITSEC are two Evaluation criteria systems for measuring security architectures.
Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC)
Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria, also known as The Orange Book, is a well-known framework for evaluating computer system security features. It was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) in the 1980s.
The classification levels under this evaluation criteria are:
Class A – Verified Protection
Class B – Mandatory Security Protection
Class C – Discretionary Security Protection
Class D – Minimal Protection
The Orange Book only measures the confidentiality of single-box architectures. Because of these limitations, Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (ITSEC) was designed.
Related Post : CISM vs CISSP
Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (ITSEC)
The Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria is a security evaluation framework Developed in the late 1980s by several European countries to provide a standardized methodology for evaluating the security features and capabilities of computer systems. ITSEC had ‘E’ levels of assurance. E levels range from E0 to E6.
12. How to reduce risk in mobile-based systems?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Mobile Application Management (MAM) solutions help organizations secure mobile devices and applications. Some ways to reduce risk in mobile-based systems are:
13. What are the steps you followed to set up Wi-Fi in your home?
Step 1: Choose a Wi-Fi Router
Select a Wi-Fi router that meets your internet usage needs.
Step 2: Connect the Router
Connect the router to your internet modem via Ethernet cable. Most routers have a WAN port where you’ll connect the modem.
Step 3: Access Router Settings
Connect a device to the router’s default Wi-Fi network or connect directly via an Ethernet cable. Open a web browser and type the router’s IP address in the address bar. Log in to the router’s administration interface using the username and password provided in the router’s documentation.
Step 4: Configure Wi-Fi Settings
You can configure the Wi-Fi network name, security settings, and Wi-Fi password.
Step 5: Test and Troubleshoot
Test your Wi-Fi network to ensure that devices can connect and access the internet reliably.
Step 6: Secure Your Network
Enable additional security features such as guest networks, MAC address filtering, and firmware updates to improve the security of your Wi-Fi network.
14. What is the OSI model?
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. The OSI model is a framework that standardizes the functions of a computing system into seven distinct layers. Each layer serves a specific purpose and interacts with subsequent layers to facilitate communication between devices and systems. The seven layers are:
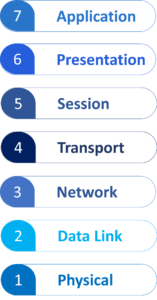
15. What are the Network attack phases?
Network attacks typically involve multiple phases, each designed to achieve specific objectives in compromising the target network or system.
Any successful attack will have the following phases:

16. What are DoS and DDoS attacks?
In a DoS (Denial-of-Service) attack, a single attacker or a small group of attackers targets a server, network, or application by flooding it with a high volume of traffic. This flood of traffic consumes the target’s resources, causing it to become unresponsive.
In a DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attack, multiple devices, known as botnets, are coordinated to launch simultaneous attacks against a single target. These devices could be infected computers, smartphones, IoT devices, or servers controlled by the attacker. The coordinated attack amplifies the impact of the attack.
17. What are Access control services?
Access control services refer to the set of mechanisms and policies implemented to regulate and manage access to resources, systems, and data within an organization’s IT environment.

18. What are the three types of authentication?
Two-factor authentication requires users to ensure any of the above two factors of authentication to verify their Identity.
Multi-factor authentication uses two or more authentication methods to verify a user’s Identity.
19. What are the potential risks related to IDaaS?
IDaaS stands for Identity as a Service. It is a cloud-based service that provides identity and access management capabilities to organizations.
20. How often should access reviews be performed?
Access reviews should be performed regularly to ensure that users’ access rights and permissions remain appropriate with their roles and responsibilities. Access of an employee should be reviewed and approved by the owner at the change of role. Any access that is not needed should be removed. When an employee leaves the company, their access should be reviewed, and all access should be removed.
21. What is the role of security professionals?
22. What is the difference between Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing?
| Vulnerability Assessment | Penetration Testing |
| Automated | Manual |
| Performed in minutes/hours | Performed in several days |
| Non-intrusive | Intrusive |
| Using Standard scanners | Using advanced techniques |
23. What is the difference between Key Performance Indicators and Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)?
| Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) |
| Lagging Indicators | Leading Indicators |
| Tracks Internal Performance | Tracks Internal and External Risks |
| Measured Monthly/Quarterly | Measured Weekly/Daily/Hourly |
| Non-Financial Measures | Financial and Non-Financial Measures |
24. What is Banner grabbing and OS fingerprinting?
Banner grabbing involves retrieving information from network services or applications by connecting to open ports on target systems and capturing the response messages sent by the services upon connection.
OS fingerprinting involves analyzing network packets or responses from target systems to identify unique characteristics or patterns that can be used to determine the operating system.
25. What are the steps included in the forensic investigation process?
Forensic investigation is a systematic process used to collect, preserve, analyze, and present digital evidence related to cybercrimes or security incidents.
26. What are Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are comprehensive solutions that provide organizations with real-time visibility into their IT infrastructure and network security by collecting, analyzing, and correlating security event data from various sources.
SIEM Steps:
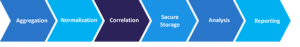
27. What is Malware?
Malware refers to any type of software or code designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. Malware is created by cybercriminals with malicious intent and can take various forms, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and rootkits. Once introduced into a system, malware may replicate itself or exploit vulnerabilities to infect other systems within the same network or organization.
28. What is Patch management?
Patch management is the process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and applying patches or updates to software, operating systems, firmware, and hardware devices to address security vulnerabilities.
Steps included in Patch management:

Related Post : CISSP Endorsement
29. What is DevOps security?
DevOps security, also known as DevSecOps, is a set of practices, methodologies, and tools that integrate security principles and practices into the DevOps (Development and Operations) process. It aims to foster collaboration between development, operations, and security teams to build, deploy, and manage software applications and IT infrastructure securely throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
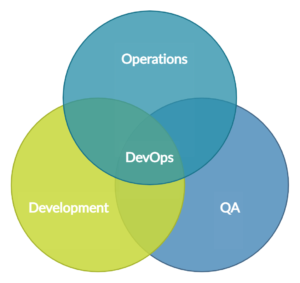
30. What is Code obfuscation? Explain its types.
Code obfuscation is a technique used to conceal the source code of a software application, making it more difficult for attackers to understand, analyze, and reverse engineer.
The three main types of obfuscation are:
31. What is the difference between REST and SOAP APIs?
REST (Representational State Transfer) and SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) are two different architectural styles used for designing web services and APIs.
Here are the key differences between REST and SOAP APIs:
| REST | SOAP |
| Representational State Transfer | Simple Object Access Protocol |
| Flexible | Rigid |
| Based on HTTP | Based on XML |
| Mostly Used in Web Applications | Used in Web Applications and Non-Web Applications |
32. Why do Software development vulnerabilities occur?
Software development vulnerabilities occur due to a variety of factors, including human error, programming mistakes, insecure coding practices, design flaws, inefficient testing, and lack of security Awareness.
The CISSP certification exam focuses on assessing a candidate’s expertise across a broad range of cybersecurity principles. CISSP interview questions can range from theoretical concepts to practical problem-solving scenarios. Candidates may be asked about security policies, risk management strategies, incident response procedures, cryptography, network security measures, and legal or regulatory issues related to information security. The goal is to evaluate the candidate’s comprehensive understanding of information security practices and principles with the CISSP interview questions.
The 8 domains of the CISSP Certification are:
These domains are significant in CISSP interview questions as they represent the core knowledge areas that candidates are expected to be proficient in. Interview questions may delve into any of these domains to assess a candidate’s abilities and understanding of information security within these critical areas.
The passing ratio for the CISSP Certification exam can vary from year to year. Generally, the CISSP exam has a pass rate of around 20% to 30%. This low pass rate underscores the exam’s difficulty level and the comprehensive understanding required across all eight domains. Success in the CISSP exam is indicative of a candidate’s deep knowledge and expertise in the field of information security, which is assessed by CISSP interview questions and how the candidate answers them.
To get the perfect score to ace all CISSP interview questions, focus on mastering the eight CISSP domains through study and practical application, enhance your communication and problem-solving skills, practice with mock CISSP interview questions, and stay updated on the latest cybersecurity trends.
Related Post : How to pass CISSP
This brings us to the end of the ‘CISSP Interview Questions and Answers blog. This blog covers the most common CISSP Interview questions broken down according to the eight domains. I hope you are clear with all the questions and answers. Make sure to go through this blog for your next Cybersecurity Interview. All the best!
Have a query for us? Kindly let us know in the comments section, and we’ll get in touch with you.
Edureka’s CISSP Training offers the best-in-class training experience to help you obtain the CISSP certification, along with helping you upskill and enabling you to secure well-suited leadership roles in the cybersecurity industry. Earning the CISSP Certification validates your extensive technical and managerial expertise as an information security specialist, enabling you to proficiently create, implement, and administer your organization’s security framework. Enroll today and take your career to greater heights in the cybersecurity domain!
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co