To use Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) in a GAN for generating graph-based data (e.g., for social network modeling), you can follow the following steps:
- Generator: Use a GNN architecture to generate graph structures (nodes and edges) based on a latent vector. The generator can create new graphs while preserving the topological properties such as degree distribution and connectivity.
- Discriminator: Use another GNN to evaluate the generated graph by comparing its structural properties (e.g., node relationships) with real graph data.
- Graph-Level Loss: Use graph-specific loss functions such as graph classification loss or graph reconstruction loss to ensure that the generated graphs have meaningful connectivity patterns and node features.
Here is the code snippet you can refer to:
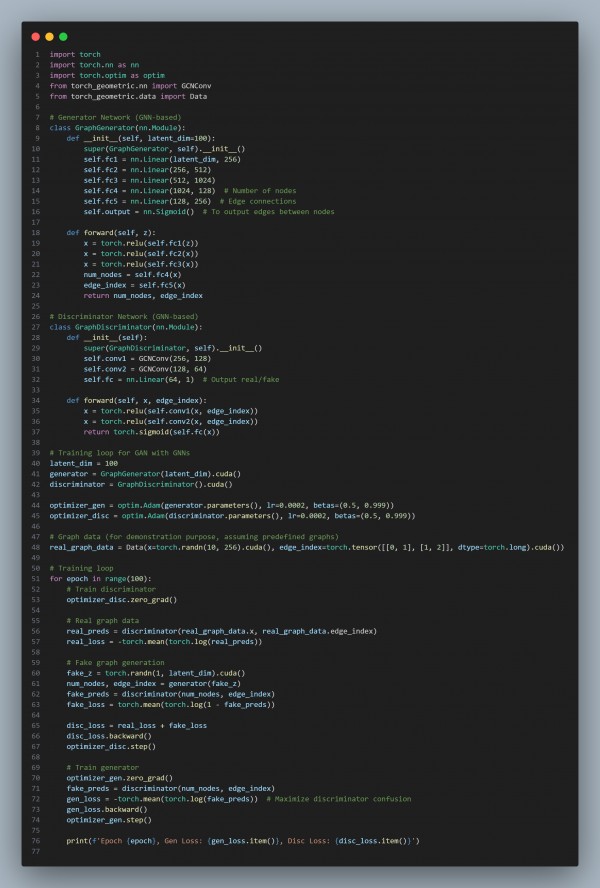
In the above code, we are using the following key strategies:
- GNN-based Generator: The generator uses a fully connected network followed by graph generation layers to produce node features and edge connections.
- GNN-based Discriminator: The discriminator uses graph convolutions (GCNConv) to capture structural patterns and relationships in the graph.
- Graph Loss: The generator and discriminator are trained using graph-specific loss functions to ensure realistic graph generation.
- Latent Space to Graph: The latent vector is mapped to a graph structure, where node features and edges are learned to represent relationships in the graph data.
Hence, by referring to the above, you can use graph neural networks in a GAN to generate graph-based data for social network modeling.
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
X
 Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering
Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month
JOIN MEETUP GROUP