Data Science and Machine Learning Internship ...
- 22k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
With the release of Python 3.8, there is a lot of curiosity to understand what major changes were made to the Python programming language. In this article, we will learn what’s new in Python 3.8, the new features, new modules, etc. The following topics are covered in this blog.
Python 3.8 was released on October 14th, 2019. With the release of Python 3.8, there is a lot to catch up on regarding the new features that came with the release. Developers must understand how the new features will impact the outcome of their projects and what all modifications were made to the older modules as well as new modules added to the programming language to be on the right track.
With the new release, there is a need to understand how porting might work and what all changes are required to make the code efficient even after the porting is done. With this in mind, let us take a look at the new features that were introduced with the new release of Python 3.8.
Python 3.8 has released a new feature in the form of a walrus operator, the name resembles the eyes and tusk of a walrus.

It is an assignment operator “:=” that is used to assign values to a variable as a larger part of the expression. Let us take a look at an example to understand how it works.
if (n := len(a)) > 10:
print(f"List is too long ({n} elements, expected <= 10)")
The walrus operator is useful in while loops that need a value for the loop termination and then the same value again in the body of the loop. It can also be used in the list comprehensions, where a value needed in the filtering conditions are is also needed in the expression body.
While loop example
# Loop over fixed length blocks
while (block := f.read(256)) != '':
process(block)
List comprehension example
[clean_name.title() for name in names
if (clean_name := normalize('NFC', name)) in allowed_names]
Since the walrus operator is an expression, it can be used for lambda functions and comprehensions where statements are illegal. There are a few limitations with the walrus operator listed down below.
Multiple targets are not directly supported
Single assignment targets other than a single NAME are not supported
Priority around commas are different
Iterable packing and unpacking are not supported
Inline type annotations are not supported
Augmented assignment is not supported
Let us also take a look at an example to see how it improves the code.
if self._is_special:
ans = self._check_nans(context=context)
if ans:
return ans
if self._is_special and (ans := self._check_nans(context=context)):
return ans
There is a new function parameter syntax “/”, It is used to indicate that some parameters can be used positionally and cannot be used as keywords.
Let us take a look at an example to understand how it works.
def f(a, b, /, c, d, *, e, f):
print(a, b, c, d, e, f)
f(10, 20, 30, d=40, e=50, f=60)
It allows pure python functions to fully emulate the existing C coded functions. The pow() function cannot use positional arguments.
One more benefit of making arguments positional only is that it allows the parameter name to be changed in the future without the risk of breaking the code. Positional only arguments greatly solve the implementation of functions and methods that need to accept arbitrary keyword arguments.
There is a new PYTHONPYCACHEPREFIX setting in python 3.8, it configures the implicit bytecode cache to use a separate parallel filesystem tree.
The location of the cache is reported in sys.pycache_prefix and none indicates the default location in __pycache__ directories.
PYTHONPYCACHEPREFIX is also available as -X pycache_prefix in Python 3.8.
With Python 3.8, the same ABI is used whether it is built in debug mode or in release mode. When Python used UNIX in debug mode, it is now possible to load the C extensions that are built in release mode and the extensions build using the stable ABI.
Release build and Debug build have become ABI compatible with Python 3.8. On UNIX, C extensions no longer have to be linked to libpython except for android and Cygwin. We can load the C extensions easily using the shared library python.
Now, when the UNIX is built in debug mode, import also looks for C extensions compiled in release mode and stable ABI.
Python 3.8 has added a = specifier for f-strings. Let us take an example to understand this.
user = 'eric_idle'
member_since = date(1975, 7, 31)
f'{user=} {member_since=}'
Output: "user='eric_idle' member_since=datetime.date(1975, 7, 31)"
The usual f-strings specifier allows more control over how the result is displayed, but the = specifier displays the whole expression so the calculations can be displayed.
The new python release has added an audit hook and a verified open hook, they allow applications and frameworks written in pure Python code to take advantage of extra notifications. They also allow system administrators or embedders to deploy builds of python where auditing is always available.
Audit Hook
An audit hook in an application is an exit point that allows the auditor to add the modules subsequently. This happens by activating the hook to transfer control to an audit module.
Verified Open Hook
The verified open hook allows python embedders to integrate with operating system support when launching scripts or importing Python code.
Python 3.8 adds new C API to configure the initialization for finer control and better error reporting. The following new structures are added.
Following is a list of functions that were added.
It is a fast calling protocol for CPython, It is added to the Python/C API. It is basically meant to formalize the existing optimizations that were already made for various classes. The vector call only deals with Python/C API and does not make any changes to the Python language and standard libraries.
Any extension type that implements a callable can use this protocol in Python 3.8.
Although it has been added in the current release, it is still provisional and will be made fully public in the next release with Python 3.9.
The process in which a Python object hierarchy is converted to byte stream is known as “pickling”. It is also known as serialization, marshalling, etc.
When pickle is used to transfer large data transfers between the python processes in order to take full advantage of multi-core or multi-machine processing, it is important to optimize the transfer by reducing memory copies.
The pickle 5 protocol introduces support for out-of-band buffers where data can be transmitted separately from the main pickle stream.
It covers the extra metadata needed for out-of-band data buffers
Pickle 5 has a new PickleBuffer type for __reduce_ex__ implementations to return out-of-band data buffers
It has a new buffer_callback parameter when pickling, to handle out-of-band data buffers
It also has a new buffers parameter when unpickling to provide out-of-band data buffers.
There has been an addition of a new module in Python 3.8, the new importlib.metadata module provides provisional support for reading metadata from third party packages. Let us take a look at an example in which it is used to extract an installed package’s version number, list of entry points, etc.
from importlib.metadata import version, requires, files
version('requests')
Output: '2.22.0'
list(requires('requests'))
Output: ['chardet (<3.1.0,>=3.0.2)']
list(files('requests'))[:5]
[PackagePath('requests-2.22.0.dist-info/INSTALLER'),PackagePath('requests-2.22.0.dist-info/LICENSE'),PackagePath('requests-2.22.0.dist-info/METADATA'),PackagePath('requests-2.22.0.dist-info/RECORD'),PackagePath('requests-2.22.0.dist-info/WHEEL')]
Here are a few other language changes that are going to be very useful while working with Python 3.8.
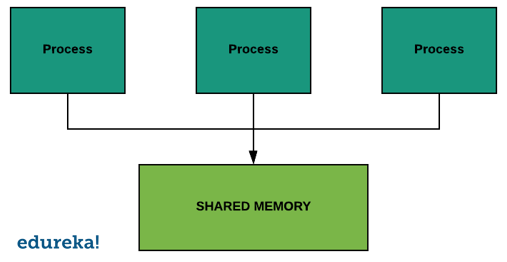
Multiprocessing Shared Memory
With python 3.8, in the multiprocessing module, there is a new SharedMemory class that allows regions of memory to be created and shared between different python processes.
Typing Module Improvements
Python 3.8 has made new changes to the typing module to make robust checks possible.
The Final type annotation and final keyword indicate that the objects should not be overridden, subclassed, or reassigned at any point.
The Literal type restricts expressions to a specific value or list of values.
The TypeDict type lets you create dictionaries where the value associated are restricted to one or more types.
Reversible Dictionaries
Python 3.8 allows reversed() with dictionaries. Here is a simple example to show how it works
my_dict = {a: 'edureka', b: 'python'}
list(reversed(my_dict.items()))
Output: [(b, 'python'), (a, 'edureka')]
Syntax Warnings
With the release of Python 3.8, the Python interpreter throws SyntaxWarnings if you make syntax errors in the python code. It is more clear with the warnings to identify what is missing really.
This brings us to the end of this article where we have learned what’s new in Python 3.8. I hope you are clear with all that has been shared with you in this tutorial.
If you found this article on “What’s New In Python 3.8” relevant, check out the Edureka Python Certification Training, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe.
We are here to help you with every step on your journey and come up with a curriculum that is designed for students and professionals who want to be a Python developer. The course is designed to give you a head start into Python programming and train you for both core and advanced Python concepts along with various Python frameworks like Django.
If you come across any questions, feel free to ask all your questions in the comments section of “What’s New In Python 3.8” and our team will be glad to answer.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co