Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking Internship ...
- 15k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
What is Steganography? It is the practice of concealing information within ordinary files or media, making the hidden data undetectable to anyone unaware of its presence. From ancient techniques like invisible ink to modern digital methods that embed messages in images, audio, or network traffic, it has evolved significantly. While it is widely used for data protection and digital watermarking, cybercriminals also exploit it to hide malware and evade detection.
It is the art of hiding a message in a way that prevents detection. Unlike cryptography, which focuses on encrypting data to make it unreadable to unauthorized users, it hides the very existence of the message itself.
This term comes from the Greek words steganos (meaning covered or concealed) and graphein (meaning writing). The technique has ancient origins, with the Greeks using it to conceal military messages. For instance, Spartan warriors would hide messages on wooden tablets, cover them with wax, and then send them off for retrieval by the intended recipient, who would scrape off the wax to read the hidden message.
Now that we understand what it is and how it functions, let’s explore how it differs from cryptography and obfuscation, two other techniques used to secure information.
Although steganography, cryptography, and obfuscation all aim to protect data, they are distinct techniques:
While steganography, cryptography, and obfuscation each serve different purposes, real-world examples help illustrate how it is actively used across various fields.
It has evolved from simple physical methods to complex digital techniques. Here are some examples:
In the digital realm, steganography has become even more sophisticated, using techniques like the Least Significant Bit (LSB) algorithm, which hides information in image, audio, or video files.
As steganography has evolved, different methods have emerged to hide information across various mediums. Let’s take a closer look at the five major types.
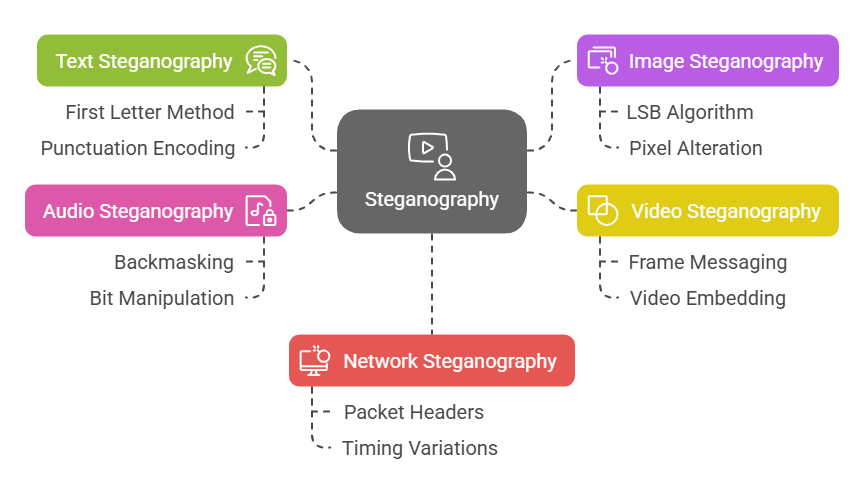
It hides messages within a body of text. Simple methods include using the first letter of each sentence to spell out a hidden message. More complex techniques might involve subtle encoding within punctuation marks or spaces.
In this, information is concealed within digital images. The Least Significant Bit (LSB) algorithm is often used, where the least significant bit of each pixel is altered to encode the hidden message. These changes are generally imperceptible to the human eye, making it an effective form.
Example: A digital photo might seem normal to the viewer, but hidden in the pixels could be a secret message or even another image.
It works similarly to image steganography, but since videos are essentially a sequence of images, entire messages or even videos can be concealed. Each video frame can carry a hidden message, making it a more advanced technique.
Example: An attacker could embed a malicious video inside a seemingly innocuous video clip, with hidden data in each frame.
This involves hiding messages within sound files. One well-known method is backmasking, where a message is played backward, requiring the listener to reverse the audio to hear it. More advanced techniques manipulate the least significant bits of the audio file, just like in images.
It hides data in network traffic, often within the headers or payloads of packets sent over the internet. It can also involve variations in packet timings, allowing data to be covertly transmitted without raising suspicion.
Example: Attackers may use network steganography to hide malware command-and-control communications within normal network activity, bypassing firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
With a clear understanding of the different types of steganography, let’s explore some of the tools and techniques used to implement these methods effectively.
Steganography Tutorial
There are several tools available for those looking to explore steganography:
1. OpenStego: This open-source tool supports image file steganography, allowing users to hide data in images or watermark files.
2. OpenPuff: A more advanced tool, OpenPuff supports hiding data in audio, video, and image files. It even allows messages to be split across multiple files for added security.
3. Steghide: A steganography program that allows users to embed data within audio and image files, specifically supporting formats like JPEG, BMP, WAV, and AU. It offers encryption and compression of embedded data, enhancing security and reducing file size.
4. Xiao Steganography: A free tool that enables users to hide secret files within BMP images or WAV audio files. It supports encryption algorithms such as RC2 and Triple DES, providing an additional layer of security to the hidden data.
5. SilentEye: A cross-platform application (available for Windows and Linux) that facilitates hiding messages within images and audio files. It supports various image formats, including BMP, JPG, and PNG, as well as audio formats like WAV. SilentEye also offers encryption of the hidden data to enhance security.
While steganography can be used for legitimate purposes, it also poses a significant risk when exploited by cybercriminals. Let’s examine how malicious hackers leverage it for nefarious activities.
While steganography has legitimate uses, such as securing confidential communication, it is also exploited by cybercriminals. Hackers often use it to hide malicious code within seemingly harmless files. For instance, a web skimmer can be concealed within the EXIF metadata of an image, enabling it to capture sensitive user data on e-commerce sites without being detected.
In one case, researchers discovered that attackers hid malware code in the metadata of a seemingly innocent image, which was then executed upon viewing the image, compromising the users’ personal information.
Steganography, the art of concealing information within other non-secret data, has a rich history and continues to play a significant role in modern digital communication. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored its various forms, techniques, and applications, highlighting both its legitimate uses and potential for misuse. As technology advances, understanding it becomes increasingly crucial for both protecting sensitive information and recognizing its potential threats in the cybersecurity landscape.
For those eager to deepen their cybersecurity expertise, Edureka’s Cyber Security Training Course offers hands-on experience in key areas such as IAM, network security, and cryptography, preparing you for in-demand roles at top companies.
It is used in various fields such as cybersecurity, digital watermarking, and protecting intellectual property. It allows individuals or organizations to hide sensitive data within seemingly innocuous files.
It is the practice of hiding a secret message within a non-secret medium, like an image, text, or audio file. Common techniques include Least Significant Bit (LSB) in images, backmasking in audio, and encoding hidden messages within video frames.
There are five main types are: text, image, video, audio, and network.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co