DevOps Certification Training Course with Gen ...
- 194k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Continuous Integration is the most important part of DevOps that is used to integrate various DevOps stages. Jenkins is the most famous Continuous Integration tool, I know you are curious to know the reason behind the popularity of Jenkins, and if Jenkins is easy to learn. I am pretty sure after reading this What is Jenkins blog, all your questions will get answered.

Let us understand what is Jenkins in simple words.
Jenkins is an open-source automation tool written in Java with plugins built for continuous integration. Jenkins is used to build and test your software projects continuously making it easier for developers to integrate changes to the project, and making it easier for users to obtain a fresh build. It also allows you to continuously deliver your software by integrating with a large number of testing and deployment technologies.
With Jenkins, organizations can accelerate the software development process through automation. Jenkins integrates development life-cycle processes of all kinds, including build, document, test, package, stage, deploy, static analysis, and much more.
Jenkins achieves Continuous Integration with the help of plugins. Plugins allow the integration of Various DevOps stages. If you want to integrate a particular tool, you need to install the plugins for that tool. For example Git, Maven 2 project, Amazon EC2, HTML publisher etc.
The image below depicts that Jenkins is integrating various DevOps stages:
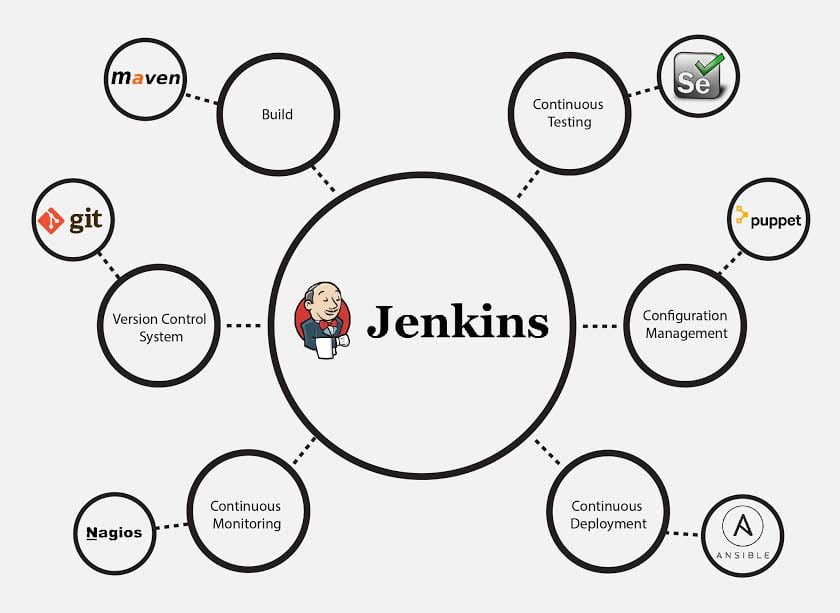
There are certain things about Jenkins that separates it from other the Continuous Integration tool. Let us take a look on those points.
The following are some facts about Jenkins that makes it better than other Continuous Integration tools:
It is evident from the above points that Jenkins has a very high demand globally. Before we dive into Jenkins it is important to know what is Continuous Integration and why it was introduced.
Continuous Integration is a development practice in which the developers are required to commit changes to the source code in a shared repository several times a day or more frequently. Every commit made in the repository is then built. This allows the teams to detect the problems early. Apart from this, depending on the Continuous Integration tool, there are several other functions like deploying the build application on the test server, providing the concerned teams with the build and test results, etc.
Let us understand its importance with a use-case.
I am pretty sure you all have used Nokia phones at some point in your life. In a software product development project at Nokia, there was a process called Nightly builds. Nightly builds can be thought of as a predecessor to Continuous Integration. It means that every night an automated system pulls the code added to the shared repository throughout the day and builds that code. The idea is quite similar to Continuous Integration, but since the code that was built at night was quite large, locating and fixing of bugs was a real pain. Due to this, Nokia adopted Continuous Integration (CI). As a result, every commit made to the source code in the repository was built. If the build result shows that there is a bug in the code, then the developers only need to check that particular commit. This significantly reduced the time required to release new software.
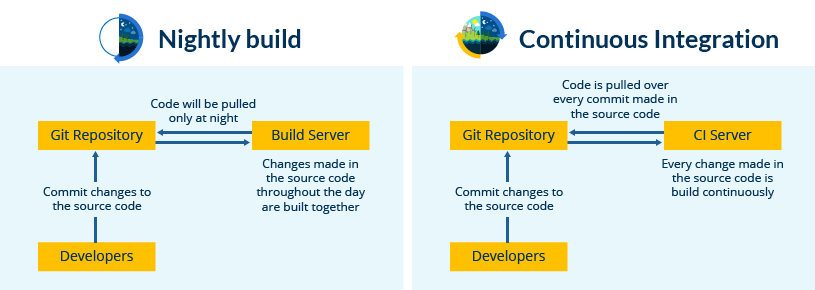
Now is the correct time to understand how Jenkins achieves Continuous Integration.
Let us imagine a scenario where the complete source code of the application was built and then deployed on test server for testing. It sounds like a perfect way to develop software, but, this process has many flaws. I will try to explain them one by one:
It is evident from the above-stated problems that not only the software delivery process became slow but the quality of software also went down. This leads to customer dissatisfaction. So to overcome such chaos there was a dire need for a system to exist where developers can continuously trigger a build and test for every change made in the source code. This is what CI is all about. Jenkins is the most mature CI tool available so let us see how Continuous Integration with Jenkins overcame the above shortcomings.
I will first explain to you a generic flow diagram of Continuous Integration with Jenkins so that it becomes self-explanatory, how Jenkins overcomes the above shortcomings. This will help you in understanding how does Jenkins work.
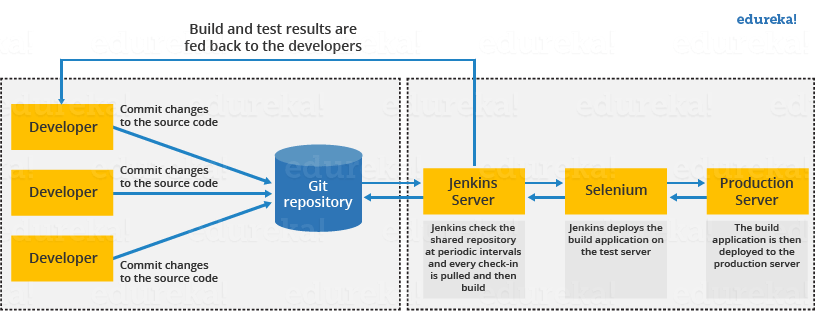
The above diagram is depicting the following functions:
You now know how Jenkins overcomes the traditional SDLC shortcomings. The table below shows the comparison between “Before and After Jenkins”.
| Before Jenkins | After Jenkins |
|---|---|
| The entire source code was built and then tested. Locating and fixing bugs in the event of build and test failure was difficult and time-consuming, which in turn slows the software delivery process. | Every commit made in the source code is built and tested. So, instead of checking the entire source code developers only need to focus on a particular commit. This leads to frequent new software releases. |
| Developers have to wait for test results | Developers know the test result of every commit made in the source code on the run. |
| The whole process is manual | You only need to commit changes to the source code and Jenkins will automate the rest of the process for you. |
After “What is Jenkins” my next blog i.e. Jenkins Tutorial focuses on the distributed architecture of Jenkins and also explains how to create a build in Jenkins.
If you found this blog on “What is Jenkins” relevant, check out the DevOps Certification Course by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. The Edureka DevOps Certification Training course helps learners gain expertise in various DevOps processes and tools such as Puppet, Jenkins, Nagios and GIT for automating multiple steps in SDLC.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
Hi Guys, I will share my thoughts how Jenkins is used.
1.Jenkins is a powerful CI application that allows continues integration and continues delivery of projects.
2.It is an most popular and open source tool.
3.It’s interesting with different number of testing and development technologies.
Hi,
I am looking an answer of a query and hope you can help me on that.
I want to Integrate Jenkins with some tools but want to know whether this integration is possible or not ?
1.) Jenkins Integration with WinAMS ?
2.) Jenkins Integration with GHS ?
I would like to know whether direct plug in available for these integrations are available or not ? If not then is there any alternative way to acheaive the following ?
Looking forward to your quick response.
Regards,
Kapil Jain
(Kapil.Jain@lnttechservices.com)
Could you please share Jenkins day to day issues faced by DevOps engineer.
Good article, It helps a lot who is new with jenkins.
Hey Dileep, we are glad to have helped. Subscribe to our channel and stay connected with us. Cheers :)
Hi, thanks for the wonderful explanation about CI with Jenkins.
i have a question here,how Jenkins is useful when application testing is completely manual in a project.
Jenkins is really useful tool for automating just about anything, but it’s most commonly used for continuous integration and delivery to build, test, and deploy software projects. With regards to testing, Jenkins is a powerful way to define when, where, and how to run your automated tests.
Hope this helps :)
It is an awesome lecture.. Thank You… I have a question: at this time of the video https://youtu.be/p7-U1_E_j3w?t=778, I understood that we use maven for building the code (the compiling) and we use something like Selenium for testing, and something like Ansible for deployment and Nagios for monitoring… while at the end of the video you used maven to do all of them using maven different phases… when we is it applicable to use maven only to do all of them, and when we should use the other tools?
Hi There, Maven is the tool which is used only to build the source code and compile, jenkins is the tool which integrates all the other tools, i hope this answers your question, anything else, please reply
When we configure jenkins url (deployed in server) in github webhook for triggering a build when every push/commit happens to github, is there not a security breach on the server as we are exposing the server url where the jenkins is installed? The server is exposed to outside world. Is there any other way instead of exposing the server?
Hi, I read the complete tutorial series and got full details of DevOps . It has been presented such a way that anyone from development/delivery backround can understand easily . Thank you the wonderful articles.
Hey Kalyan, thanks for the wonderful feedback! We’re glad we could be of help.
Do check out more Jenkins tutorials here: https://www.youtube.com/edurekaIN.
Do subscribe to our blog to stay posted on upcoming blog posts. Cheers!
Such a nice explanation which clearly explains the need for Jenkins. Thanks a lot for the explanation.
Hey Sai Kumar, thanks for the wonderful feedback! We’re glad we could help.
Do subscribe to our blog to stay posted on upcoming blog posts. Cheers!