The above video is the recorded session of the webinar on the topic “Introduction to Hadoop Administration”, which was conducted on 14th August
Big data is the term for a collection of data sets so large and complex that it becomes difficult to process using on-hand database management tools or traditional data processing applications. The challenges include capture, curation, storage, search, sharing, transfer, analysis, and visualization of the huge amount of data. Begin from the basics and get an in-depth understanding of the concepts from the Hadoop Administration Course.
Here is a presentation on the topic ‘ Introduction to Hadoop Administration’:
Limitations of existing Data Analytics Architecture:
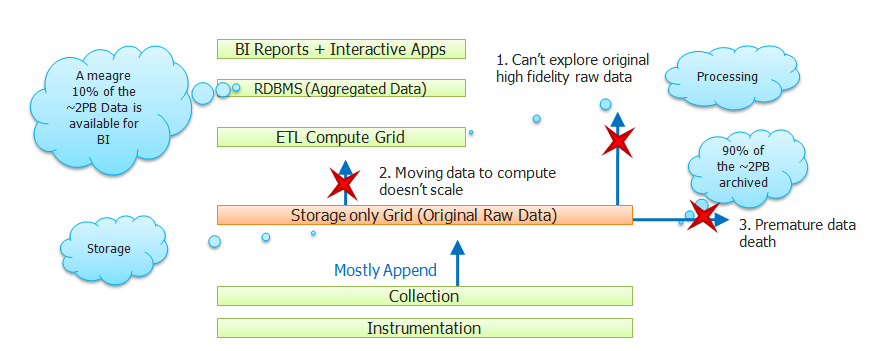
In the earlier data analytics architecture, there were certain limitations like not being able to explore original high fidelity raw data, computable data not being scalable and premature data death. The above diagram clearly explains where the failures occur during data analytics process.
How Hadoop overcomes the setbacks:
With Hadoop, several of the above mentioned setbacks are overcome.
Hadoop – Key Characteristics that Makes it Popular:
- Reliable
- Flexible
- Economical
- Scalable
Top Companies Using Hadoop:
- Yahoo!
- IBM
- Rackspace
- Amazon
- eBay
- Morgan
Skills Required to Become a Hadoop Administrator:
- General operational expertise such as good troubleshooting skills, understanding of Capacity Planning.
- Hadoop skills like HBase, Hive, Pig, Mahout, etc.
- Should be able to deploy Hadoop cluster, monitor and scale critical parts of the cluster.
- Good knowledge of Linux.
- Familiarity with open source configuration management and deployment tools such as Puppet or Chef and Linux scripting.
- Knowledge of Troubleshooting Core Java Applications is a plus.
Hadoop Administrator Responsibilities:
- Responsible for implementation and administration of Hadoop infrastructure.
- Testing HDFS, Hive, Pig and MapReduce access for Applications.
- Cluster maintenance tasks like Backup, Recovery, Upgrade, Patching.
- Performance tuning and Capacity planning for Clusters.
- Monitor Hadoop cluster and deploy security.
Read more here.
Hadoop 1.X Vs Hadoop 2.X:
Hadoop 2.X has the added feature – YARN. YARN takes out all the granular details managed by the administrator and thereby eases the job of a Hadoop Administrator.
Hadoop 1.X Core Components:
HDFS and MapReduce are the core component of Hadoop 1.X. While the HDFS is responsible for distribution for files across the nodes, tracks NameNode locations and is natively redundant, the MapReduce is responsible for splitting the tasks across the processor, assembiling the distributed data and managing the JobTracker.
Hadoop 2.X Core Components:
Hadoop 2.X is the advanced version of Hadoop 1.X. Here, the core components are predominantly the same, along with added features like High Availability, resource management and job scheduling/monitoring, shared resource for cluster and maintain API compatibility with previous established releases of Hadoop.
Get a better understanding of the core Hadoop concepts from the Hadoop Admin Classes in Pune.
Main Components of HDFS:
There are two main components in HDFS. They are:
NameNode:
- Master of the system
- Maintains and manages the blocks which are present on the DataNodes
DataNodes:
- Slaves which are deployed on each machine and provide the actual storage
- Responsible for serving read and write requests for the clients
Got a question for us? Mention them in the comments section and we will get back to you.
Related Posts:
Hadoop Administration Training
Job Responsibilities of a Hadoop Administrator
Skills Required to Become a Hadoop Administrator