Certified Ethical Hacking Course - CEH Certif ...
- 30k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Since hackers are capable of doing substantial security and financial damage, finding ways to shield your network and systems against them is a necessity now. This is where ethical hacking techniques work as a defensive barrier to shield organisations. With escalating reliance on digital technologies, robust cybersecurity measures need to establish an equally strong defence system against cyber attacks. As per Security Magazine, more than 2,200 malicious attacks occur daily- a concerning figure that keeps increasing.
Ethical hackers harness an array of the most common hacking techniques to mimic the behaviour of malicious hackers and use them to repair system vulnerabilities. Wondering what such hacking techniques are? Let us take you through these diverse hacking techniques. But first, let’s start with decoding the basics of ethical hacking!

Ethical hacking is conducted by skilled professionals who are called ‘white hat hackers’.

Let’s explore the types of hacking:
Attackers harness phishing, a deceitful tactic where they impersonate reputable entities in digital communication to deceive victims into revealing sensitive information. This approach often involves sending deceptive emails that appear to be from trustworthy sources, tricking users with security renewal pop-ups, using ‘voice phishing’ to deceive people and steal personal information or creating fake social media posts to steal user information.
Intercepting and analysing packets on networks refers to a practice called sniffing. This practice allows the extraction of sensitive information such as passcodes and financial data. Hackers utilise specialised software and eavesdrop on network traffic to exploit unsecured or incompetently secured networks to fulfil their malicious intent.
In the initial stage of hacking, an attacker actively gathers extensive information about the target system or network. In ethical hacking, this process is known as ‘footprinting.’
Footprinting is used as an investigative attempt to gain the target system’s data, which includes information related to domain names, IP addresses, scanning open ports, and network infrastructure. Using this knowledge, ethical hackers perform pen testing to search for compromised system components and repair them.
Hackers exploit human interaction in social engineering, strategically manipulating individuals psychologically to breach standard security procedures and gain unauthorised access to valuable information.
SQL injection refers to a type of code injection attack where hackers inject malicious SQL code into an SQL query through input data from the application. This leads to backend database manipulation, which can either result in stolen sensitive data, alterations in system data or even the destruction of entire database.
The process of enumeration involves extracting specific details about a target, including user names, network resources, and services. Enumeration comes in the reconnaissance phase of a cyberattack, where the hacker is trying to gain access to as much information as possible from the target system.
This method empowers hackers to pinpoint potential attack vectors by identifying the target system, mapping network topologies, decoding configuration details and much more. Access to such information makes system intrusion easy for hackers.
The Brute-force attack is one of the oldest forms of cyber attack, which involves multiple forceful attempts at gaining the right system credentials to access user systems, networks or accounts. The Brute-force attack process requires systematic guessing of passwords or encryption keys, a process undertaken through exhaustive effort, not exploiting inherent weaknesses.
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks aim to flood systems, networks, or services with an excessive volume of traffic. A DDoS attack leads to the target system or network becoming overwhelmed, which can lead to slow performance, unresponsiveness and eventually a complete downtime– disabling legitimate users to lose access to the space.
If these different types of hacking methods interest you and compel you to delve deeper into this domain, pursuing CEH certification training would be an optimal choice.
Related Post : Reconnaissance in Ethical Hacking
Related Post Mitigate Cross-Site Tracing
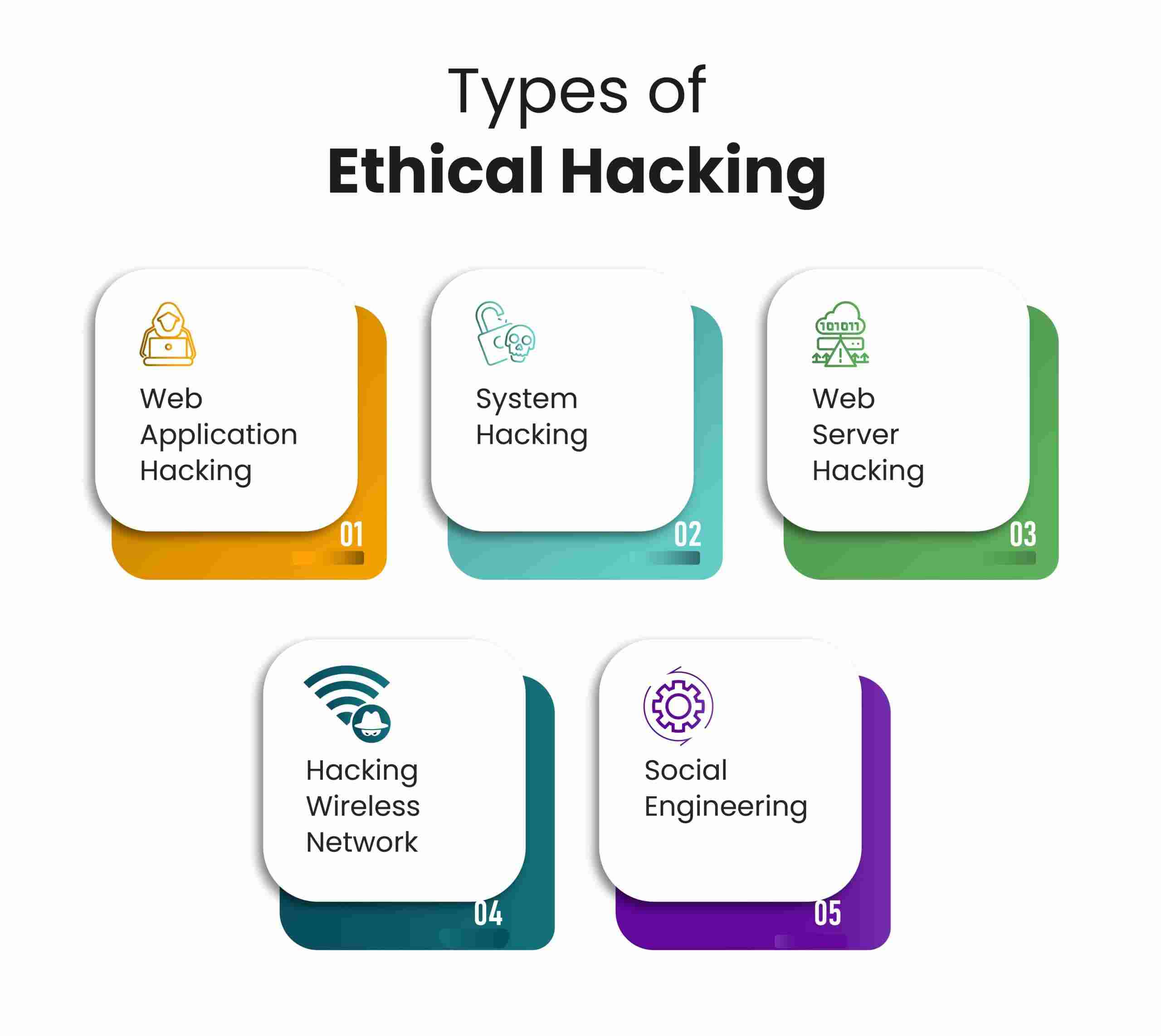
A skilled cyber security professional can become an ethical hacker by mimicking the strategies and techniques of malicious hackers to actively identify and rectify vulnerabilities. The key areas this role focuses on include:
Web application hacking Identifies security weaknesses in web applications. The subsequent step is to propose measures in order to mitigate the risks associated with these identified vulnerabilities.
The focus of system hacking lies in the pursuit of unauthorised access to computer systems. It seizes control by exploiting its vulnerabilities, which enables ethical hackers to strengthen its defence system against all potential intrusions.
Identifying vulnerabilities that might permit unauthorised network access, this method actively tests the security of wireless networks.
The aim of server hacking is to identify vulnerabilities within server configurations and software. This identification serves as a preventive measure against unauthorised access or data breaches.
Related Post : Man in the Middle Attack
Related Post : Getting started with exploit development and reverse engineering
Top 10 HACKING Techniques (2025)

Well, this is where protection and prevention strategies come in.
The following strategies lay out how we can safeguard systems and data against these vulnerabilities, integrate ethical hacking techniques and gain insights into the types of hacking techniques that cybercriminals frequently use.
Implementing robust access control measures is crucial for countering brute force attacks and unauthorised access attempts. This necessitates the use of complex passwords by employing multi-factor authentication (a system that ensures stringent control over permissions) and continuous monitoring. Organisations can mitigate the risk of information theft by hackers through a strategic approach: they restrict access to sensitive data.
Actively utilising ethical hacking techniques for regular security audits and penetration testing is a proactive strategy aimed at identifying and subsequently addressing vulnerabilities. Ethical hackers employ identical methods to those of malicious counterparts. However, they operate within strict controls and authorisation–an approach that bolsters overall system security. These assessments serve as preventive measures, potentially revealing the system’s defence weaknesses before any potential exploit occurs.
Significantly, human error often orchestrates successful cyber attacks. Educating and training staff on current hacking techniques in cyber security by equipping them to identify phishing attempts, malicious links, or suspicious attachments can mitigate the risk of information breaches. Thus, it is essential that we empower individuals through awareness programs.
Known vulnerabilities in software and operating systems become targets of many techniques of hacking. We can fortify our defence against these exploits by regularly updating and patching the software to close security gaps. To streamline this process, we should employ automated patch management tools since they guarantee that our systems always stand protected from the latest threats.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are essential parts of a strong cybersecurity plan. They keep an eye on network activity for anything fishy or known attack methods, stopping hacks as they happen. With IDS and IPS in place, organisations can block different hacking methods that aim to mess with services or swipe important data.
Encryption is a crucial tool in cybersecurity that makes data unreadable to unauthorised users. Organisations use it to protect against hacking attempts that aim to intercept or steal sensitive information– whether it’s stored or transmitted. This is especially important for financial transactions and the protection of personal data. Therefore, it’s not just a choice but a necessary action they must take.
Ultimately, an organisation that fosters a security culture establishes serious engagement with cybersecurity. Regular discussions about the significance of security, updates on emerging hacking methods, and encouragement to report any suspicious activities form integral parts of this approach.
If all these discussions pique your interest, you could look at embarking on a career in ethical hacking and be at the forefront of cybersecurity efforts, protecting organisations from data breaches and cyber threats. You could be playing a vital role in securing information systems and ensuring the privacy and integrity of sensitive data.
Related Post : Ethical Issues in Information Technology
To safeguard digital assets in the contemporary world, one must possess a deep understanding of both ethical and malicious hacking techniques. By employing ethical hacking practices, organisations can maintain their systems’ security and data integrity and ensure they always stay ahead of potential cyber threats.
Newcomers to the field can establish a robust foundation in cybersecurity and ethical hacking techniques by embarking on an Ethical Hacking Tutorial offered by Edureka. This tutorial spans various subjects, including comprehension of the ethical hacking process, along with practical applications using cutting-edge hacking tools and methodologies.
Related Post Reverse lookups for footprinting
Related Post Prevent brute force Node.js
Commonly, ethical hacking involves assessing the target, probing for flaws, gaining access, maintaining access for a thorough analysis, and even hiding the traces.
Ethical hackers use various tools, such as Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark, to study and gain access to systems and prevent future attacks.
When it comes to ethical hacking, hackers like to implement methods such as penetration testing, social engineering tests and vulnerability assessments in order to find system vulnerabilities.
Examples of coding languages that are regularly used by ethical hackers include Python, JavaScript, and SQL to write out scripts and automate hacking processes.
Related Post SQL LIMIT clause and injection attack risks
Related Post Role and automation of WHOIS data in footprinting
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co