PMP Certification Training
- 86k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Do you find it increasingly challenging to handle all your service requests? Still stuck with manual processing? What if I told you ServiceNow provides a single system of record on the cloud to solve all your internal bottlenecks. If you are not familiar with ServiceNow please feel free to read my earlier blog. Coming to today’s blog, we would be focusing on ServiceNow ITSM tools by exploring the Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) domain in-depth. We will look into the theoretical concepts in ITSM as well as see how this is implemented on the ServiceNow Platform.
In this ServiceNow ITSM tools blog, we will be looking at each of the ITSM services individually. Let us begin with Incident Management.
First, let us take look at what is an Incident in ServiceNow. When a user faces an issue and wants to get in touch with the support team, the first thing needed is to record the details in a user form. To put it in simple words, an Incident is any issue reported by a user or group of users which is documented with a unique record ID.
To get more clarity on an Incident, let us look at the steps involved in Incident Management:
The issue can be related to either hardware, software, network or any possible combinations of them.
Examples:
The Incident reported is handled according to its priority level. Priority is a combination of an Incident’s impact on the organization as well as its urgency level.
Incidents are classified as P1, P2, P3, P4 according to their respective priority levels:
Example:
An Incident which has a high impact at the organization level with an urgent timeline is considered as a P1 level or Critical level Incident, whereas an Incident with low impact at the user level with a normal timeline is classified as a P5 level or Planning level Incident.
Apart from solving Incidents, it is also important to avoid related incidents and reduce overall incident volume. This can only be done when the underlying problem is identified. This brings us to our next topic Problem Management.
Problem Management deals with identifying the root cause of the Incident. We Analyse how to mitigate or reduce Incidents. Suppose there are many Incidents pertaining to Email. We can perform Root Cause Analysis to identify the root cause.
IT personnel can manually create a record to make a note of the ‘Problem’, Or we can relate to an Incident record.
Updates can be communicated using E-mail. We choose the inbound E-mail configuration to achieve this.
Service Level Agreements (SLA): are used to assign priority to tasks as well as monitor team progress.
Inactivity tracker: We can create events which are triggered when the Problem is not attended within a certain interval of time. This event may be a script or email notification.
Once the Problem is resolved, related Incidents to the Problem will automatically be closed. If we cannot find a solution to the given Problem, we can term it as a Known Error which saves us time in the future.
For those not familiar with CI’s, a Configuration Item (CI) is the fundamental asset in a (Configuration Management Database) CMDB.
Example: Workstation, Server or Business Service
The biggest difference between a static assets list and CMDB is that we map relationships between CIs. This brings us to our next topic Dependency Views. Dependency Views depict the relationships between different Configuration Items. The following diagram is an example of Dependency Views.
Figure: ServiceNow ITSM Tools– Dependency Views
Now we can see the relationships between the Email Exchange Server and various Email Servers. Also, the San Storage Device can be checked.
Next we create Problem Tasks to identify the affected area. We can designate two teams one each for network and server domains. As the Incident is critical, before the particular server is fixed we need a temporary solution such as an alternative server. To permanently solve the issue, it might require a software patch from the server team to fix the Email server.
Once the Problem is identified, we need to fix the issues causing the Problem. This brings us to our next topic which is Change Management.
Change Management is the lifecycle of proposed Changes and the reflected Changes. Once Incidents are reported, we create a Problem and perform Root Cause Analysis. We further create Change Requests based on the given situation. Change tasks are then planned and post-completion their associated incidents and Problems are closed/resolved.
Changes Requests can be classified into Standard or Emergency. Standard Changes need written approval and have a set procedure in place whereas a verbal communication is sufficient for Emergency Changes.
Workflows are used to depict the stages involved in the Change Request lifecycle right from Initiation to Approval. This is depicted in the diagram below.

Figure: ServiceNow ITSM Tools– Change Request Workflow
It is highly beneficial to have a repository of files covering previous support queries and articles relevant to the Platform. This leads up to our next topic Knowledge Management. Moving further with this ServiceNow ITSM Tools blog let take a look at Knowledge Management.
ServiceNow comes with a Knowledge Base which houses articles, Faq’s, troubleshooting. This is a plethora of information spanning several categories. Who can add an article to the knowledge base? The owner or manager is enabled to add Knowledge articles along with contributors who are entitled to add information to the knowledge base. The admin is also allowed to contribute to the Knowledge Base.
In our ServiceNow ITSM tools blog, let us now understand the Knowledge article lifecycle in the ServiceNow Platform.
When an author publishes his article two distinct scenarios are possible:
If the Approval Publish Workflow is configured then the article enters the Draft state which is forwarded to the Reviewer who can either approve or reject the article.
If the Instant Publish Workflow is configured then the article is immediately published and appears in the Knowledge Base.
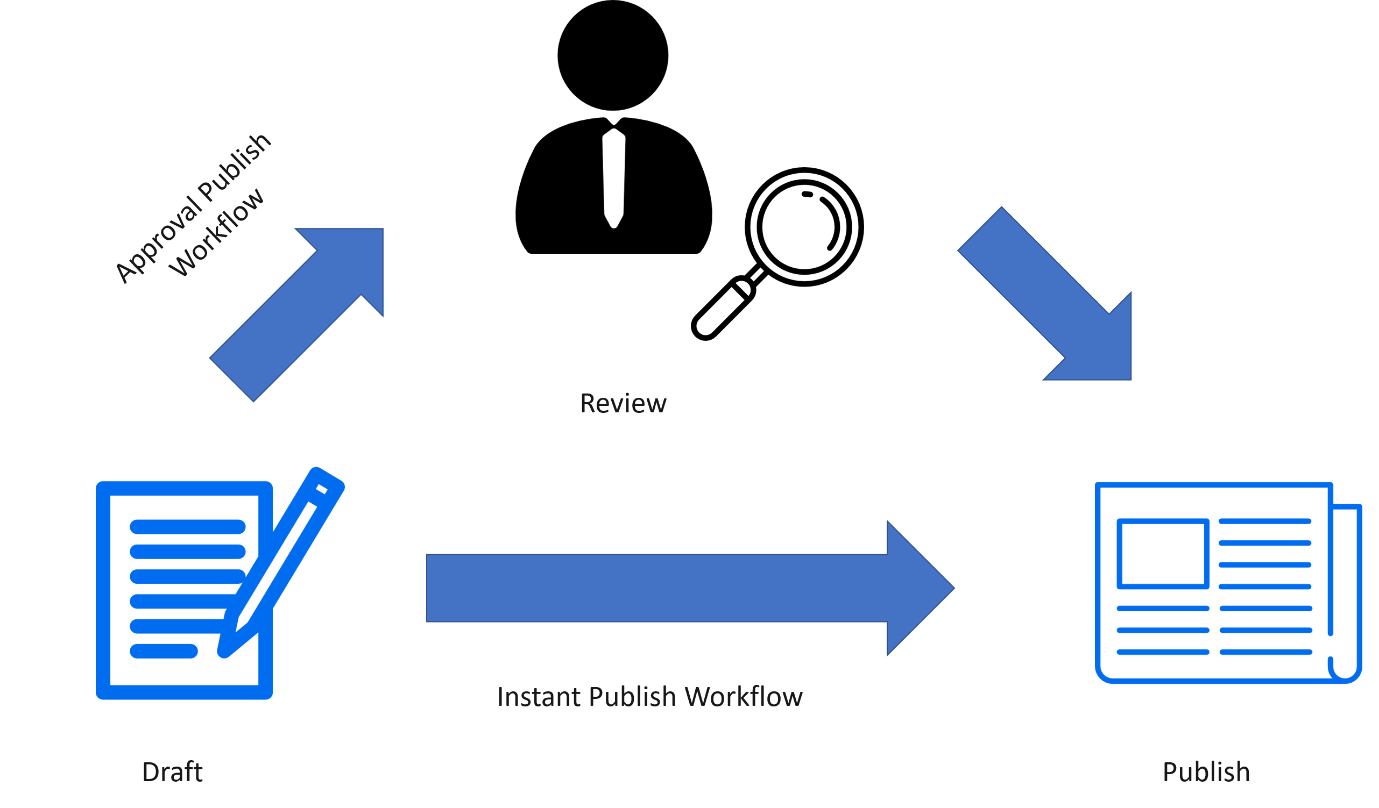
Figure: ServiceNow ITSM Tools– Publishing Articles
The article can be removed from the Knowledge Base if it is no longer useful. This process is known as retirement.
If the Approval Retire Workflow is implemented then the article moves to the pending retirement state and the owner of the Knowledge Base needs to approve its retirement.
If the Instant Retire Workflow is implemented then the article skips the review and directly moves to retired phase. Once the article has retired it does not appear in the Knowledge Base. However, the article still resides within the system and can be restored to the Draft state when needed.
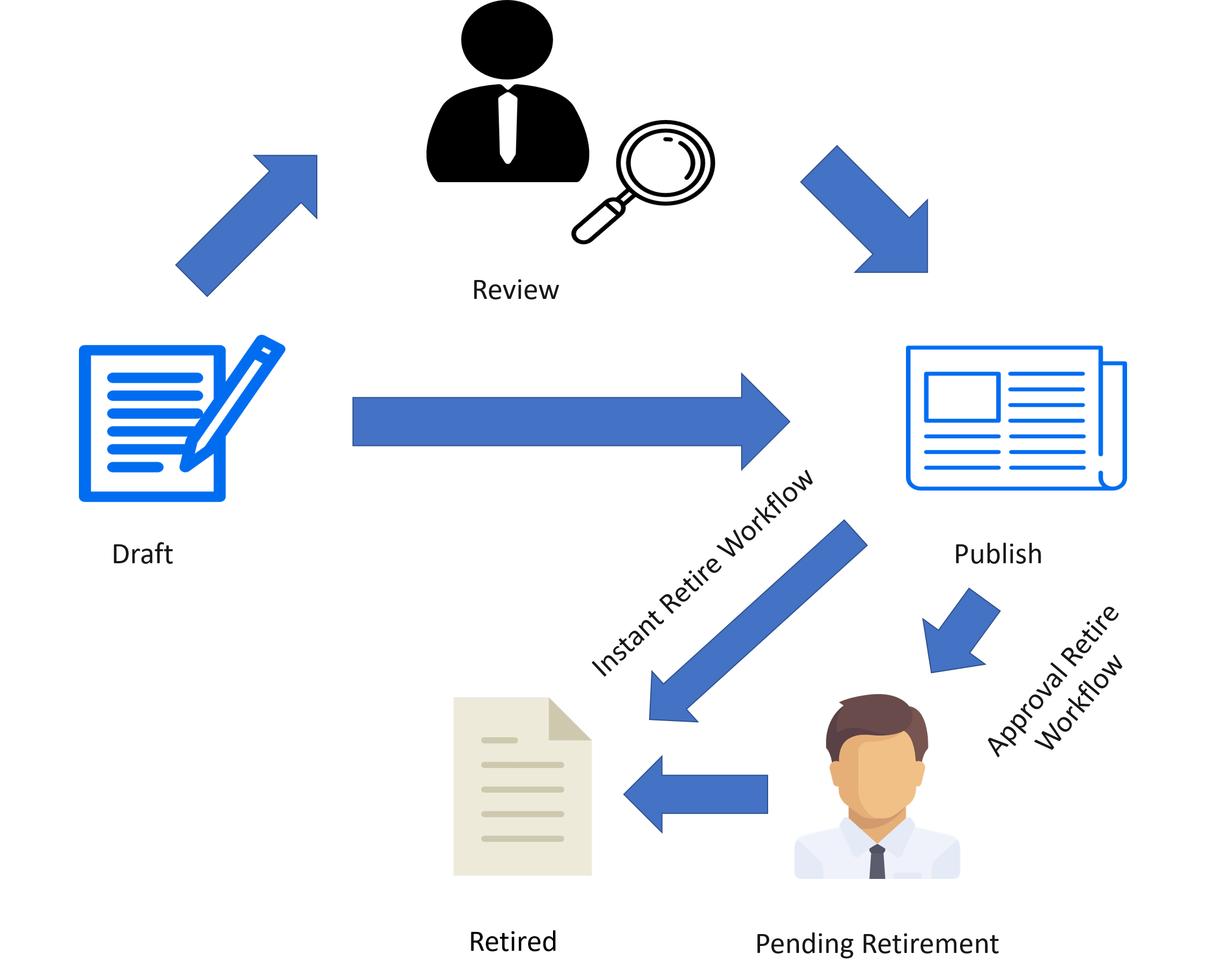 Figure: ServiceNow ITSM Tools – Retirement of Articles
Figure: ServiceNow ITSM Tools – Retirement of Articles
Now that you are familiar with the ITSM concepts, let us move ahead and explore the different ITSM tools provided by ServiceNow.
You can even check out the details of ITIL with the ITIL Certification.
We will now have an in-depth view of ServiceNow ITSM tools. I will be walking you through the entire lifecycle starting from creating an Incident, then performing Root Cause Analysis to avoid such Incidents in the future. We will also look at the process of Change Requests, needed to solve the Problem and Resolve the Incident. I will also show you how to export the problem as an article to the Knowledge Base.
Follow the instructions below in order to create an Incident in the ServiceNow Platform
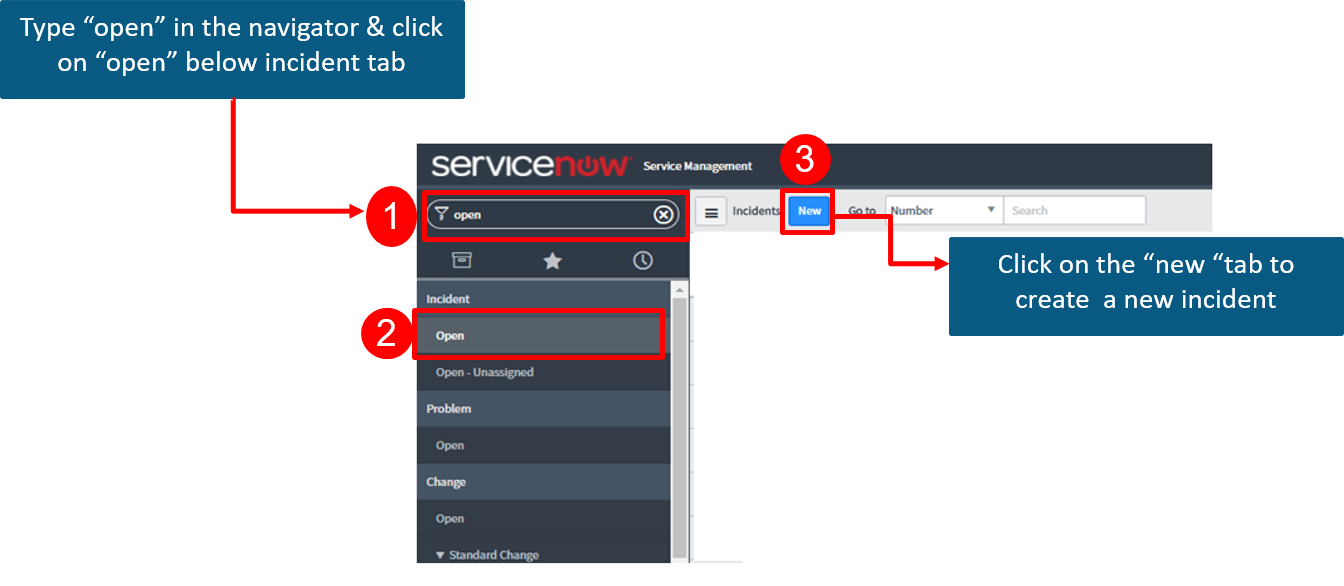
We create an Incident record to report the issue Email service is not working. The record contains the Task Assignee, Impact on the organization, affected Business services and Configuration items, Urgency as well as a Description of the issue. The below diagram depicts the same.
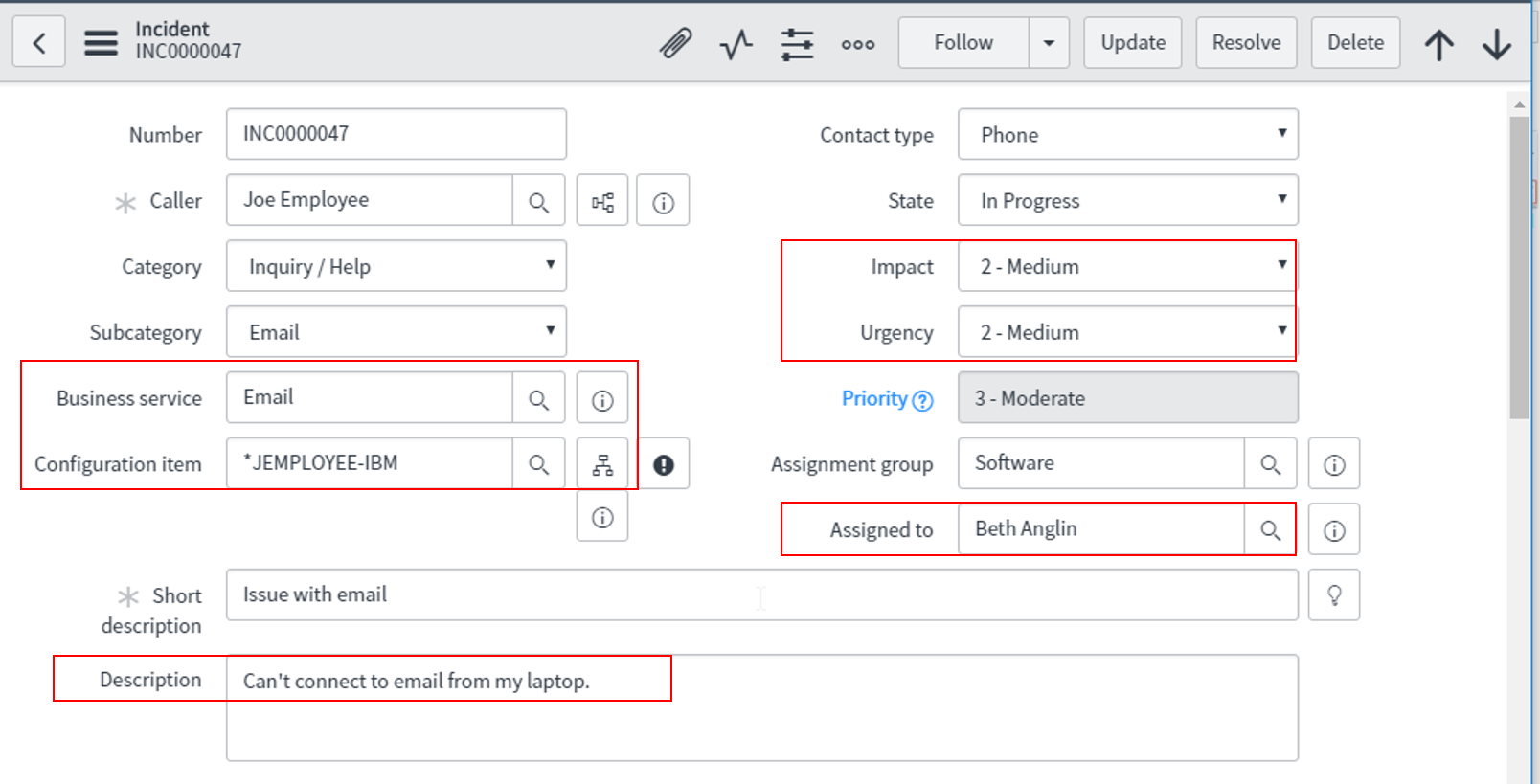 Step 2: Create a Problem
Step 2: Create a Problem To perform Root Cause Analysis, we create a Problem by clicking on the Incident properties tab as shown below.
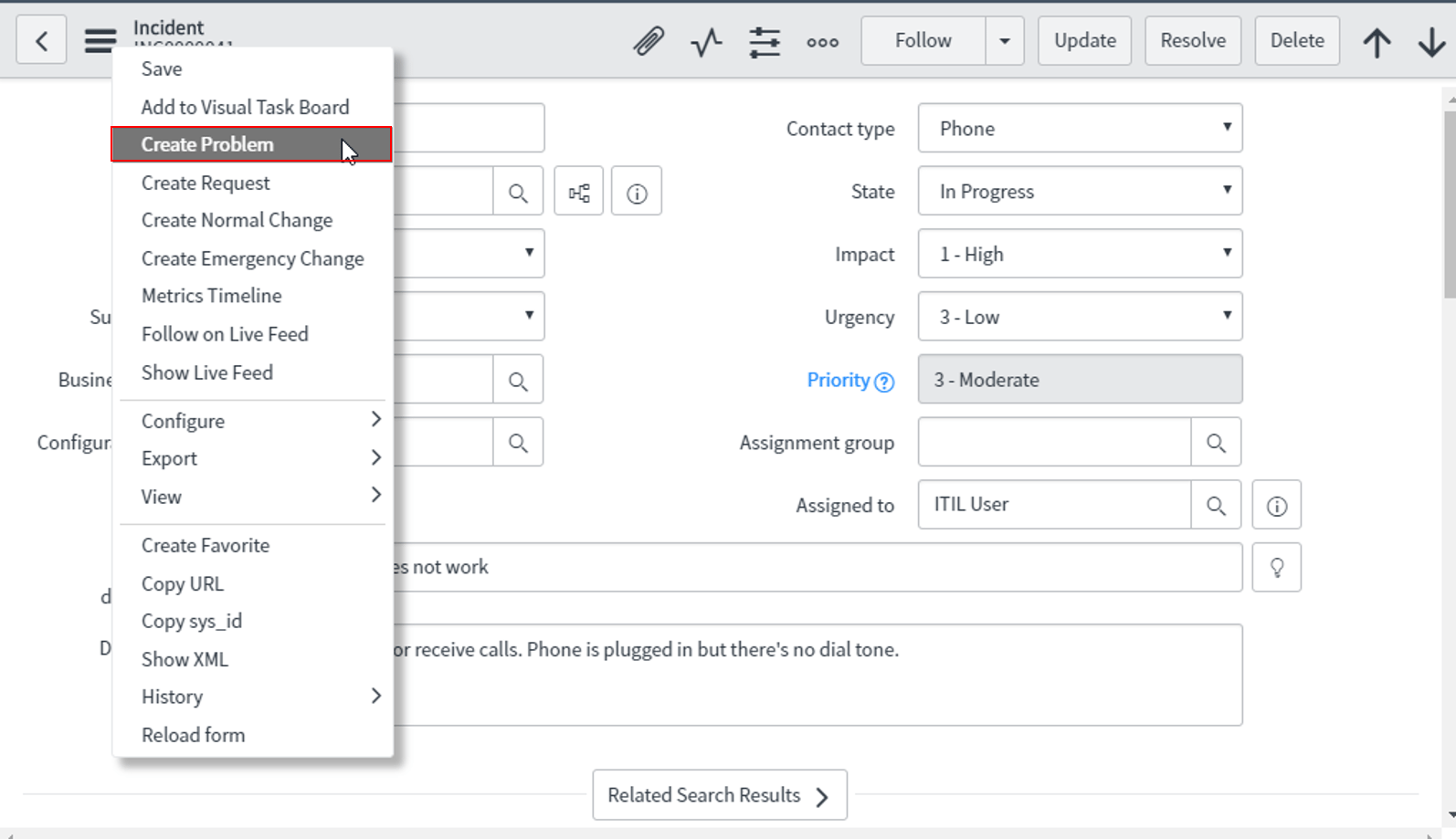
After having a look at the dependency view, we can go ahead and create Problem tasks and assign it to a specific group or user.
In our example, the Problem identified after Root Cause Analysis found a compromised network adapter so we assign Problem Tasks to the network group and assign Fred Luddy as the associated user.

Once the Problem is identified the task assignees take a call whether a Change Request is needed to Resolve the Problem. The Problem state is Changed to Pending once a Change Request is initiated.
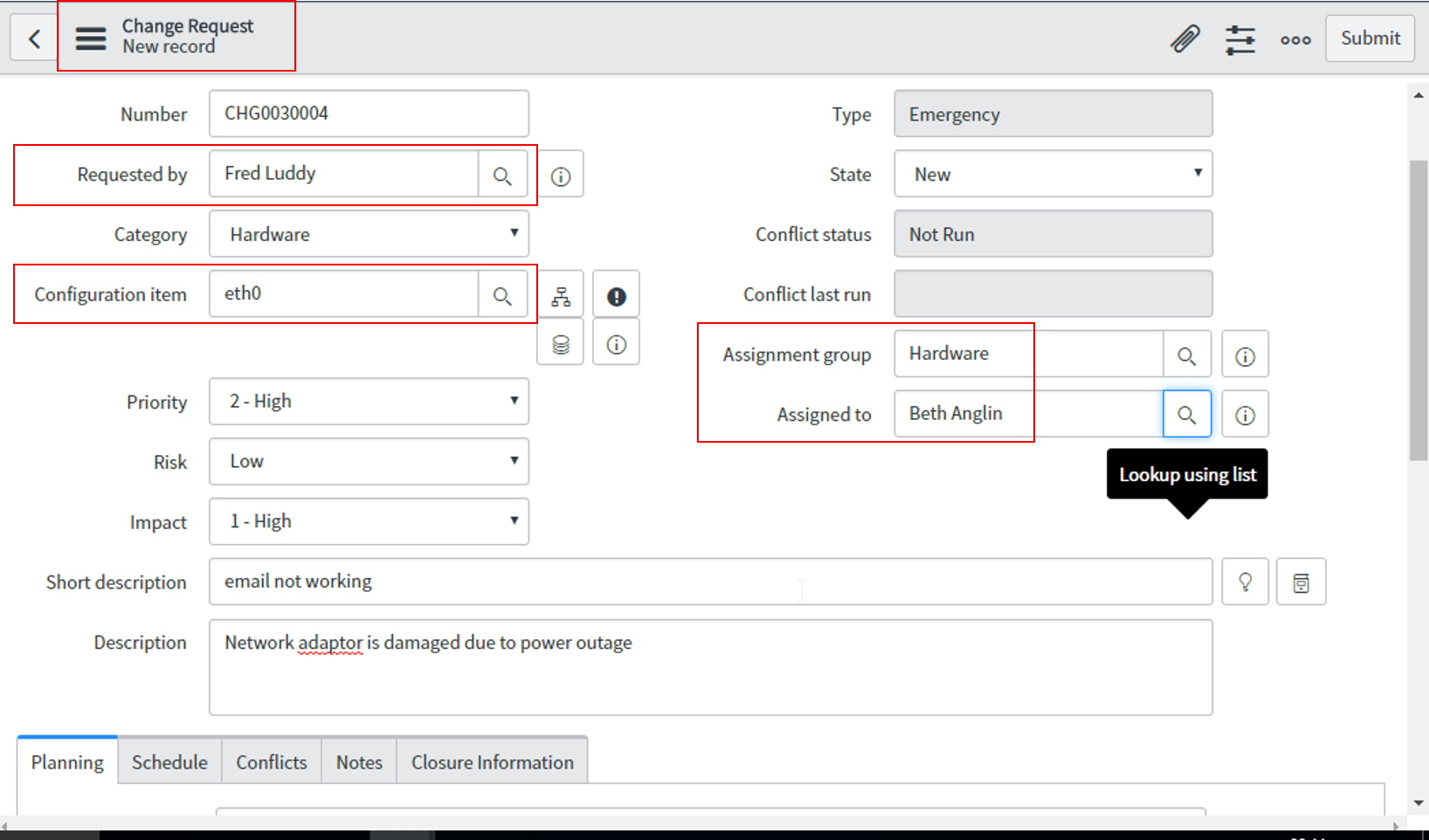
In our example, the assignee Fred Luddy takes care of the Change Request to replace the identified network adapter.
Once the Change Request is Completed/Closed all associated Problems are automatically Resolved.

All the related Incidents are Closed automatically after one day. We may also close them manually by setting the State parameter to Closed/Resolved.
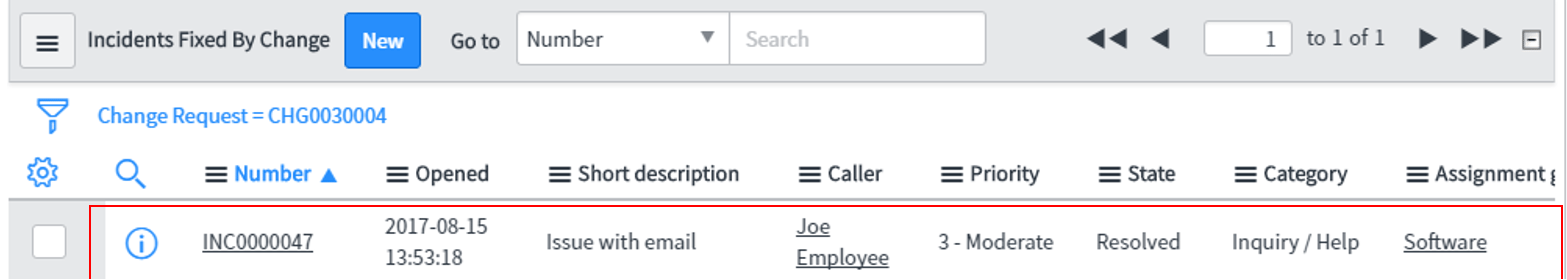
We can directly extract information from the filled form of the Problem record. This can be added as an article to the Knowledge Base to provide support to users who might encounter the same issue in the future.
To implement this, we open the associated Problem record and hover to the Post Knowledge option.
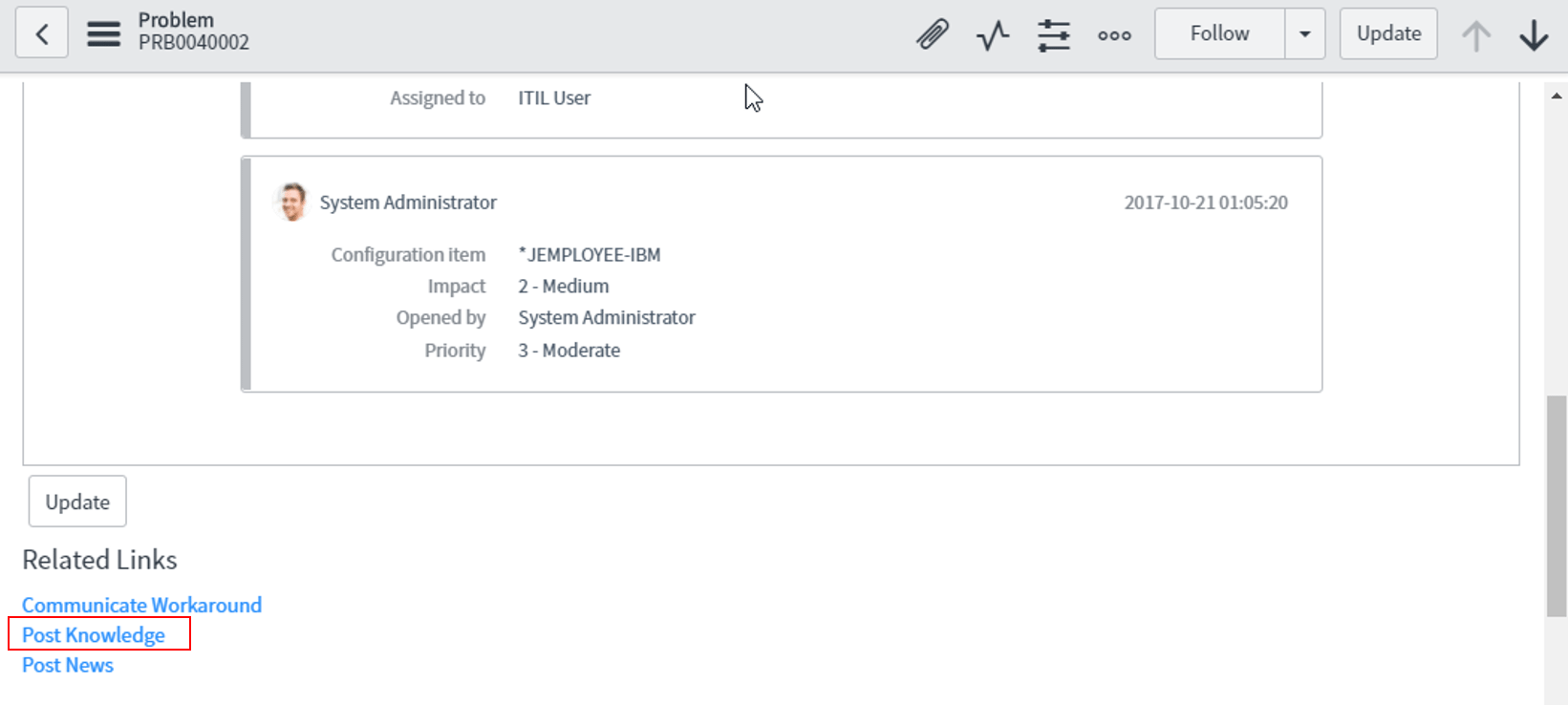
In the below diagram, we can see that the Knowledge article has been added and the associated Problem is also listed.
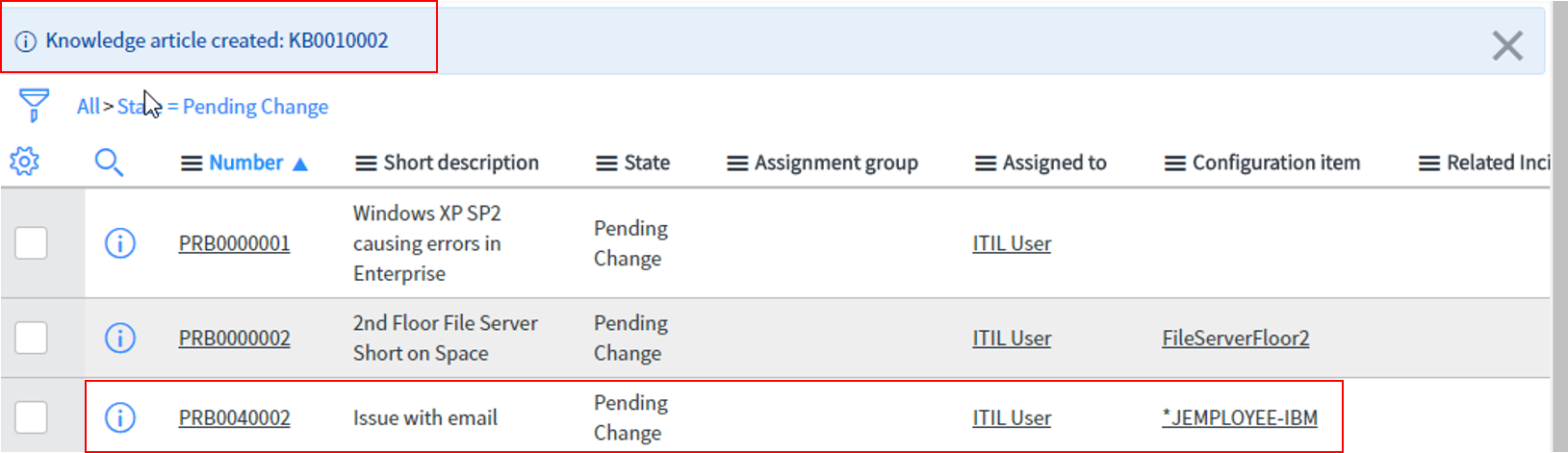
It is currently in the Draft State and will be published to the knowledge Base post-approval.

This brings us to the end of today’s blog. I am confident you get the idea how ServiceNow ITSM tools come with a sense of consumerism touch. This is often found prevalent in social media applications, however was due for a long time in the ITSM sector. ServiceNow aims to replicate that ease of use we experience in our day-day tasks to internal support tasks within the organization.
If you found this blog on “ServiceNow ITSM Tools” useful, check out the ServiceNow Admin Certification course by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. This course will give you a strong hold on the ServiceNow platform with a full depth coverage right from administrative functions as well automated workflows.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co