Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking Internship ...
- 15k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Did you know recent surveys state that over 8,00,000 people fall prey to cyberattacks, which occur every 39 seconds? This creates a pressing situation where organisations should consider and work on developing comprehensive cybersecurity risk management strategies such as ethical hacking. Ethical hacking is a proactive approach that acts as a protective shield for organisations against multi-dimensional cyber threats. This approach is primarily processed using 5 phases of hacking. This article explains the step-by-step phases of ethical hacking implemented by cyber experts.
Ethical hacking comprises a process that involves bypassing computer security systems, networks or applications to discover their vulnerabilities and protect them against unauthorised access. Contrary to black hat hackers who maliciously hack, white hat hackers or ethical hackers distinguish themselves with legal authorisation and licences. This form of hacking is sanctioned because it serves to fortify cyber defences rather than compromise them.
Here’s a comprehensive table to understand the differences and contrasts between Ethical (white hat) and unethical (black hat) hacking processes:
| Features | Ethical Hacking | Black Hat Hacking |
| Intent | To improve system security by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities. | To exploit vulnerabilities for personal gain or to inflict harm. |
| Authorisation | Has explicit permission from the owner of the system. | No permission from the owner, acts are illegal. |
| Outcome | Enhances the security and protects against attacks. | Leads to data breaches, theft, and damage. |
| Techniques | Uses similar techniques, just as malicious hackers, for a constructive purpose. | Uses hacking techniques for malicious purposes. |
| Ethics | Follows a strict code of ethics and legal guidelines. | Operates without ethical considerations, often breaking laws. |
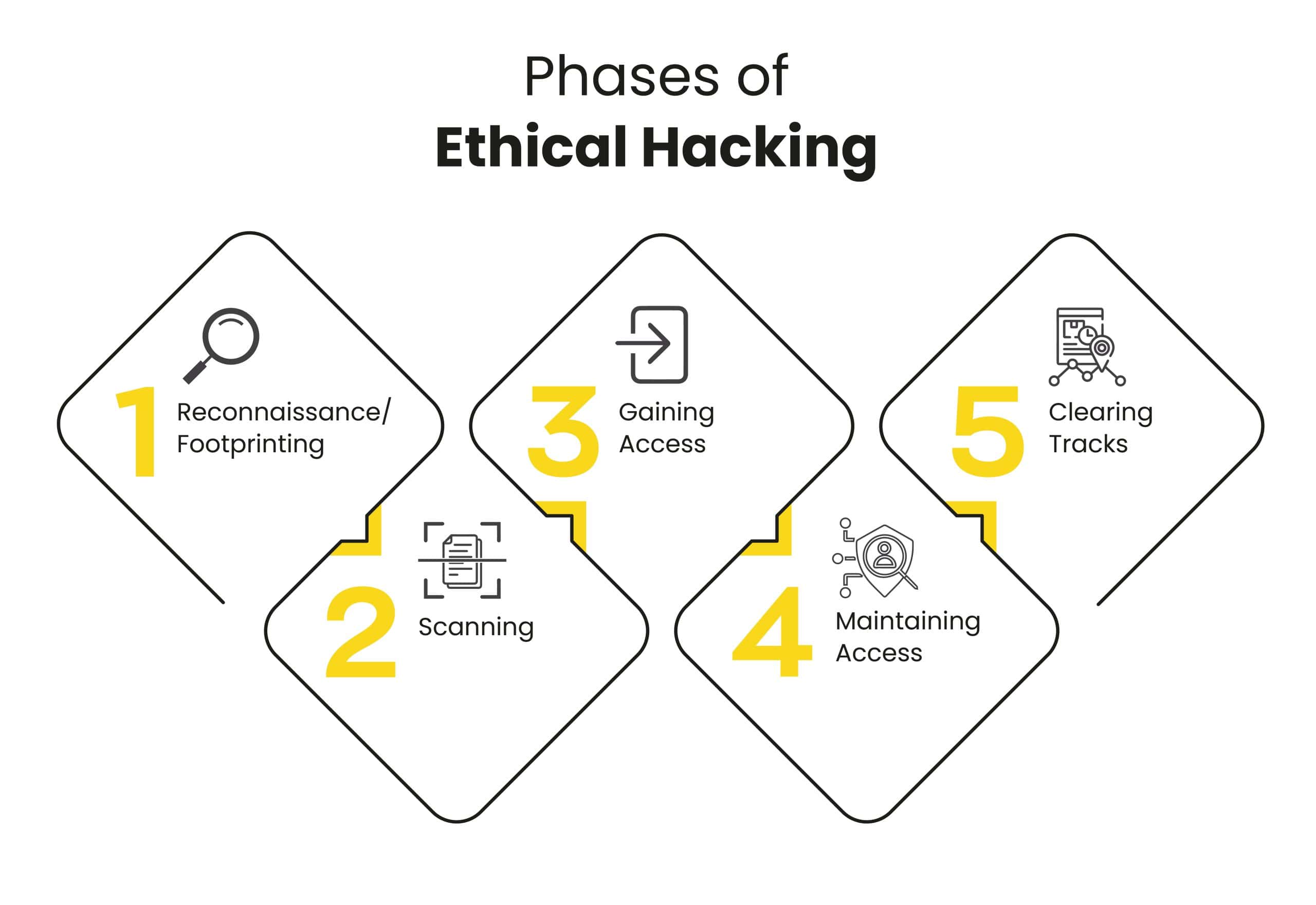
Ethical hacking, in its essence, operates via five distinct and indispensable hacking steps. Understanding these 5 phases of hacking is pivotal to mastering the overall ethical hacking tutorial:
This is the first phase of ethical hacking, where hackers actively accumulate a bunch of important information about the target system. This includes identifying IP addresses, domain particulars, network services and potential entry points. Reconnaissance works in two forms:
In the scanning phase, ethical hackers actively employ an array of tools to scrutinise the target’s networks and systems for vulnerabilities. They utilise automated instruments specifically to identify open ports, live systems, as well as services operational on servers. This evaluation enables ethical hackers to gain insights into the overall security stance of the target infrastructure.
Ethical hacking methodology states that the scanning phase contains different types of networking scanning practices, which you can find in our quick guide to network scanning!
Engaging in this critical phase of ethical hacking requires the exploitation of identified vulnerabilities for unauthorised systems or network access. Simply put, in this phase of hacking, ethical hackers attempt to trespass on target infrastructures and attempt to exploit the system, using methods usually followed by black hat hackers.
Methods may range from SQL injection to cross-site scripting and other techniques. An ethical hacker’s objective is to understand the potential damage a malicious hacker could inflict by exploiting such a vulnerability.
After gaining access, the ethical hacker crucially secures a backdoor into the system to maintain this entrance. Understanding how attackers persist within a compromised system hinges on this step. This phase also aids penetration testers in assessing vulnerabilities and developing strategies for mitigating such risks across organisations.
In the final phase, the ethical hacker meticulously covers their tracks to evade security system detection without leaving any evidence of the hacking process. Understanding potential methods that attackers may employ to avoid detection is crucial during this stage. This process aids in enhancing a target system’s capabilities for identifying intrusions.
Phases of Ethical Hacking
Also Read Types of WiFi Hacks and How to Prevent It
Related Post :Ethical Hacking vs Cyber Security – Key Differences Explained
IBM reported that the annual average cost of a data breach globally was USD 4.45 million in 2023, experiencing a 15% increase in the last three years. This underscores not only the acute financial impact these incidents can inflict upon businesses but also their potential to cripple them.
In preempting these breaches, ethical hackers play a pivotal role in identifying vulnerabilities across myriad domains within organisational IT infrastructures. Let’s explore some of the ethical hacking methods to shed light on how hackers launch cyberattacks across different domains.
One of the most prominently used hacking techniques is social engineering, which refers to an act of manipulation to retrieve crucial personal details from the recipient. This genre of manipulative cyberattack enables perpetrators to manipulate people mentally and get them to share their confidential details, such as bank account details, PIN numbers, passwords and more.
As a preventive measure, ethical hackers run social engineering awareness and simulated phishing campaigns to make more people learn about this manipulative tactic and idea of which organisation is more susceptible to such attacks, respectively.
Web applications often face inherent security flaws and vulnerabilities. This enables organisations to become an easy target for web application hacking where hackers sieve through such system vulnerabilities to either steal data or to manipulate it. By running a vulnerability scan analysis, ethical hackers pinpoint the target area and work on strengthening it.
At the system level, ethical hackers actively search for potential exploits that attackers may use to install malware or gain unauthorised access to individual computers or devices within a network. They rigorously test techniques like password cracking and privilege escalation to fortify these endpoints against possible attacks.
An organisation’s IT infrastructure relies heavily on servers and databases, which ethical hackers also scrutinise for vulnerabilities. Weak points can result in data breaches or service disruptions from attacks like DoS (denial-of-service), SQL injection, server misconfiguration and more. In an effort to tackle this form of intrusion, ethical hackers run extensive penetration tests and vulnerability assessments, further developing robust security measures to mitigate the risk of DoS attacks.
Related post Building a simple vulnerability scanner
Here’s how you can navigate the challenging realm of ethical hacking – learning how to become an ethical hacker in just a few steps:
Step 1: Educational background
Aspirants who aim to establish a career in ethical hacking should consider structuring a robust foundation with a relevant background. Start by pursuing a bachelor’s and a master’s degree in IT, Cyber Security, CS or any relevant field.
Step 2: Cultivate technical skills
Being one of the most challenging fields, ethical hacking requires you to cultivate a special set of skills that is in demand and is relevant. These sets include skills including programming languages, Linux, database management, computer networking skill, penetration testing skill and much more.
Step 3: Additional certifications
Pursue specialized training in cybersecurity and ethics-driven hacking. Certified Ethical Hacker certification and Cyber security training can strengthen your skillset as well as to add credibility to your resume.
Step 4: Opt for Security certification
Specialised certifications relevant to ethical hacking and cybersecurity, are imperative to enter this competitive domain. Some of them include CEH, OSCP, Certified Information Systems Security Professional(CISSP), GPEN and more.
Step 5: Create a portfolio and seek opportunities
You also have to step up and present your best self before prospects by building an impactful portfolio. An portfolio can help you showcase your skills, expertise to potential employers or organizations looking to outsource ethical hacking services or hire ethical hackers. Your portfolio can include your prior internship experience, open-source projects, training modules, etc., highlighting your drive to pursue this role. Apply to your choice of company and stay motivated till you find your dream job!
Check out Edureka’s CEH certification training, which presents a comprehensive curriculum for those with an interest in understanding the nuances of cybersecurity and ethical hacking. This certification course will help you prepare and pass the CEH v12 examination to become an ethical hacker.
Enrol now and set yourself up to redeem a rewarding career!
Related post Building a simple vulnerability scanner
The 5 phases of ethical hacking include Reconnaissance, Scanning, Gaining Access, Maintaining Access and Covering Tracks.
While all ethical hacking steps are crucial, ‘Reconnaissance’ is often considered to be the most critical one. This pre-processing phase requires vital information about a target system to create strategies aiming towards their points of concern and to provide optimised solutions.
To protect yourself against hacking, perform routine vulnerability tests, adopt robust security measures, provide staff security education, and remain abreast of trending cyber security issues and potential threats.
Some of the benefits of ethical hacking include:
In order to emerge as a competent ethical hacker, one must have a strong tech background. Courses like BCA, BE, BTech or BSc can work as a firm base for establishing a career in cyber security as an ethical hacker. Along with this, fluency in multiple programming languages, cyber security certifications like CISSP or CEH, and work experience are also required.
Related Post Information gathering with Python scraping
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co