Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking Internship ...
- 15k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Passwords are the key to our digital world. They serve as secret codes to unlock our email, bank accounts, and business systems. Password management in cybersecurity is essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. It involves securely storing, generating, and updating them using dedicated tools that simplify our daily digital interactions while enhancing security.
This blog features an in-depth look at password management and its role in modern cybersecurity. Let us begin by understanding what it is.
It is the practice of securely storing, accessing, and protecting your passwords to enhance security and privacy across your digital life. As the number of online accounts increases, it becomes challenging to remember a unique secret for each one. Dedicated Password Managers consolidate and safeguard login details in an encrypted vault, generate robust alternatives, and remind you to update them, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
For organizations, this means centralizing the storage of all credentials, which makes it easier for IT teams to oversee access and maintain security standards across multiple systems and users.
In short, it is not only about remembering your logins. It is a complete system that ensures all the passwords you use meet high security standards while remaining easy to access when needed.
They can be divided into two main categories:
Credential protection, also known as password management, is tailored to meet diverse security needs: for individuals or families, it safeguards vital information like email accounts, banking details, and social security numbers, whereas in an organizational setting, it focuses on securing sensitive internal access credentials.
Let’s talk about the different types based on where and how passwords are stored and managed.
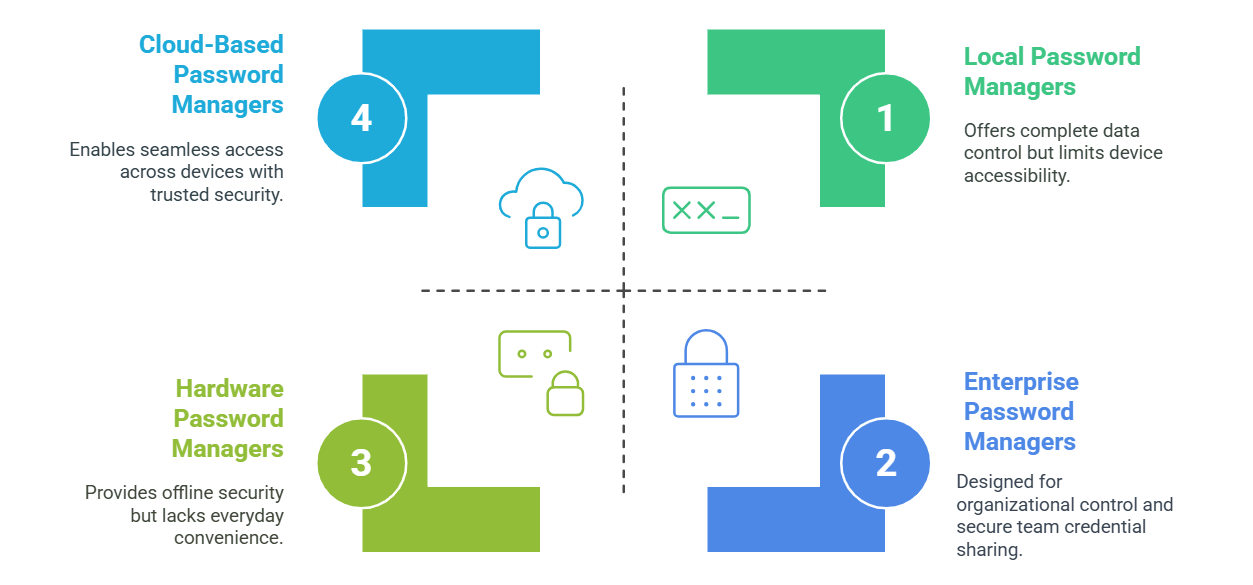
They store credentials directly on your device. This method provides you with full control over your data, as everything is stored locally. Although this method can provide robust security, it may limit accessibility when you need to switch between multiple devices.
They save your encrypted password vault on remote servers. They allow you to sync your credentials across several devices and access them from anywhere. While they offer convenience and ease of use, you must trust the service provider to maintain high security standards for your data.
They are designed specifically for organizations. They offer centralized control and advanced features such as detailed auditing, role-based access control, and secure sharing of credentials among teams. These solutions help IT departments manage thousands of accounts efficiently as the organization grows.
They are physical devices, such as USB tokens or smart cards, that store your passwords offline. They provide an extra layer of protection because they are not connected to the internet, making them less vulnerable to remote attacks. However, they can be less convenient for everyday use compared to software solutions.
Cybersecurity Tutorial
Issues related to managing passwords remain a significant challenge in today’s digital world. Many users tend to reuse the same one for multiple sites, which creates a major vulnerability. Statistics show that over 65 percent of people use the same credentials across different accounts and rarely change them even after a breach occurs. At the same time, about 25 percent of users reset their credentials every month or more simply because they forget them.
Password managers help by storing all credentials in one secure location. This means that users need only remember one master password instead of many different ones. The major risk, however, is that if this master credential is compromised, then all stored passwords become vulnerable.
There are several tools available that enhance cybersecurity by securely storing and organizing your credentials. Below are five top tools designed for both personal and business use.
Keeper Security is a well-known cybersecurity company that offers advanced management and secure file storage solutions. It stores your passwords in an encrypted vault and alerts you if any credentials are compromised or found on the dark web. This tool is safe, easy to use and provides a robust solution for protecting sensitive information.
1Password is designed for individuals and businesses alike. It keeps all your credentials and other sensitive information in an encrypted vault. With its Travel Mode, it removes sensitive data from your devices when crossing borders for added protection. It also supports multi-factor authentication and provides advanced team management capabilities, making it a versatile choice.
Zoho Vault, part of the Zoho suite, offers secure management with features such as encryption, secure sharing, access controls and audit trails. Its user-friendly interface and integration with other Zoho products and third-party applications make it an excellent option for managing digital credentials in a team environment.
Bitwarden is an open-source password manager recognized for its transparency and security. It provides end-to-end encryption, a vault, a generator and cross-platform synchronization. Its compatibility with all devices and the option to self-host give users extra control over their data.
LastPass is a popular and reliable management tool that securely stores and manages your passwords and sensitive information. It offers features such as a vault, a generator, auto-fill capabilities, and secure notes, along with support across multiple platforms. It’s a straightforward and easy-to-use interface, making it a trusted solution for many users.
Having looked at the leading tools in the market, it’s equally important to understand the methods you can use to manage your passwords effectively.
Here are several methods you can use to manage your passwords securely and effectively:
They offer numerous advantages for both individual users and organizations. Here are some of the key benefits:
Challenges of using them include several important considerations:
In conclusion, password management is a vital practice in cybersecurity that secures sensitive data while simplifying our digital lives by centralizing and automating the creation and storage of strong passwords. Various tools, such as Keeper Security, 1Password, Zoho Vault, Bitwarden, and LastPass, offer unique features to address different needs, though it is essential to understand both their benefits and challenges. By adopting best practices such as employing long, unique passcodes, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and maintain a robust defense against cyber threats.
For those eager to deepen their cybersecurity expertise, Edureka’s Cyber Security Training Course offers hands-on experience in key areas such as IAM, network security, and cryptography, preparing you for in-demand roles at top companies.
It is a tool that securely stores, organizes, and manages all your credentials in an encrypted vault. It generates strong keys and autofills login details, so you only need to remember one master key.
Password protection in cybersecurity involves using strong, unique, and complex credentials, often supported by encryption and multi-factor authentication, to secure digital accounts from unauthorized access.
Passwords are vital because they serve as the first line of defense in protecting personal data and sensitive information from cyber threats.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co