Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking Internship ...
- 15k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In the current digital atmosphere, it is very important to understand the difference between network security vs cybersecurity for the proper protection of sensitive data. Though these are often used as identical terms to each other, they stress different aspects of security. Network security is basically concerned with the protection of the network infrastructure, which includes devices and connections, from unauthorized access and other forms of threats. Cybersecurity, on the other hand, is a broader scope that aims to protect all digital assets, including networks, devices, and data, from a wide range of cyber threats.
Network security and cybersecurity are almost similar concepts, with different strategies and practices. However, at a basic level, differences arise from the scope of the approach and the challenges being addressed. Knowing this would help you develop much more effective security strategies that protect all aspects of your digital environment.
A network is a grouping of interconnected devices such as computers, servers, and many wireless networks, which are all possible targets of cyber attacks. Network security protects those devices by establishing methods to prevent unauthorized access, defend against attacks, and keep data safe whenever it’s transmitted or accessed. It allows authorized users access to data and services and keeps malicious users away from the network and its resources.
Let’s use an example to understand it better. Assume you have begun an online transaction. Network security helps with the protection of the online banking system via the methods indicated below:
Now that we understand what network security is, let’s explore the key advantages it offers for safeguarding organizational infrastructure.
Network security is important for every business to protect its data and infrastructure because it offers many important benefits:
1. Protection Against External Threats: Network security is important, given that it guards against outside dangers, including viruses, hackers, and cyberattacks. Firewalls, data encryption technologies, and intrusion detection systems that block attackers from gaining access to sensitive information that hackers could exploit help to prevent illegal access.
2. Enhanced Network Performance and Reliability: Protecting a network can also make it work better and be more reliable. Network security keeps legitimate data moving easily by blocking attacks and bad traffic. This cuts down on downtime and stops bottlenecks. It also makes network processes more stable and effective so businesses can continue operating without having to stop because of security breaches.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data protection and privacy. Network security helps organizations meet these regulatory compliance requirements by ensuring that data is stored and transmitted securely. This is crucial for avoiding legal issues and penalties while maintaining the trust of customers and partners.
4. Data Integrity and Confidentiality: Network security ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access. Encryption and access control mechanisms ensure that data is not altered or tampered with, maintaining its integrity.
5. Prevention of Internal Threats: Apart from guarding against outside attacks, network security helps against internal hazards, including staff members abusing their access rights. Organizations can stop hostile activities from within their network by configuring appropriate access limits and monitoring systems.
While network security provides numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations associated with it.
While network security provides considerable protection, it does pose some challenges that the organizations must consider:

2. Complexity in Configuration and Management: Network security is generally very complex in terms of configuration and management. This often requires certain technical knowledge or expertise because security needs to be installed correctly. Therefore, without the organization having such skills in its system, hiring cybersecurity experts or even outsourcing becomes a high-cost and necessary requirement.
3. Potential Impact on Network Performance: While security measures are necessary to protect the network, they can also slow down network performance. Tools such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion prevention systems sometimes introduce latency that causes data transmission delays. In other cases, security settings may interfere with other applications and networking devices, resulting in compatibility issues that may also affect overall performance.
4. Risk of Overcomplication: An overabundance of security measures may lead to the risk of over-complicating the network environment. If not properly managed, many security layers and tools can result in unnecessary complexity, which might cause misconfigurations and reduce the effectiveness of the security measures.
One growing area of focus in network security is the role of artificial intelligence (AI). Let’s delve into the potential concerns surrounding AI in this field.
Artificial intelligence (AI) adoption into network security presents both major possibilities and difficulties:
1. Advantages of AI in Network Security
2. Challenges Posed by Malicious Use of AI
3. The AI Arms Race
As both cybersecurity defenders and attackers adopt AI, an ongoing arms race emerges. Each side strives to outpace the other, leveraging AI to gain an advantage in the fight for network security.
To address these concerns and strengthen network security, organizations must adopt certain best practices. Here’s what they can do.
To protect their networks effectively, businesses need to take preventative steps. Here are some important best practices that will make your network safer and help you stay ahead of new cyber threats:
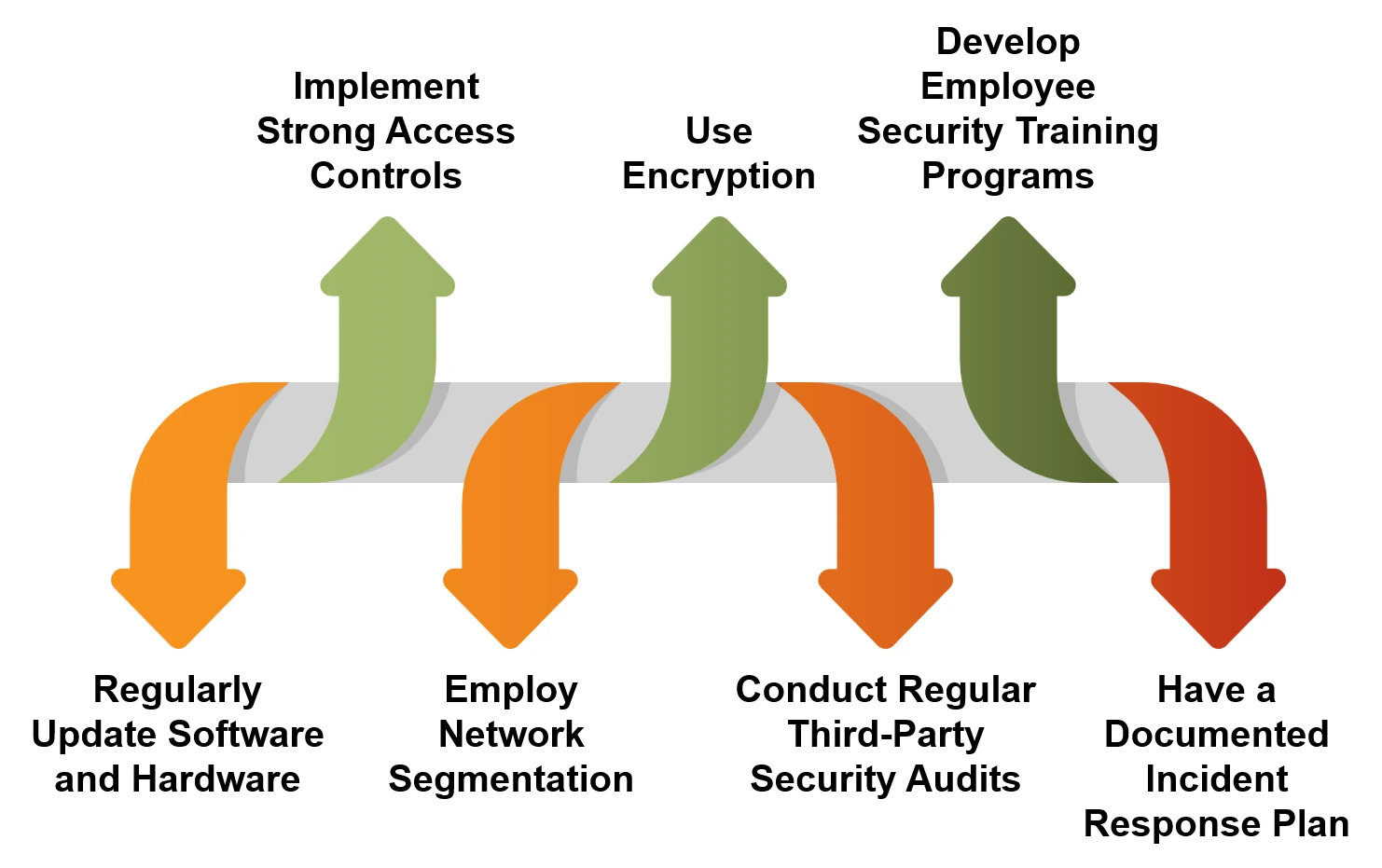
2. Implement Strong Access Controls: Limit access to critical data with multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC).
3. Employ Network Segmentation: Design zones within the network that contain vulnerabilities and stop malware from spreading.
4. Use Encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest to prevent it from being intercepted and accessed by unauthorized people.
5. Conduct Regular Third-Party Security Audits: Examine your network’s security posture to spot and fix weaknesses. Stress-test your systems and replicate actual threats using a reputable outside third party.
6. Develop Employee Security Training Programs: Educate staff members about data security best practices, phishing schemes, and security policies.
7. Have a Documented Incident Response Plan: Develop and consistently update an incident response strategy to handle security breaches rapidly and successfully. Make sure the plan is easily available to all key managers and employees.
If you want to explore network security in detail, check out the following video:
Network Security Tutorial
While network security is critical, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Let’s shift our focus to cybersecurity and understand its broader scope.
Cybersecurity is the approach to protecting digital systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and malicious attacks. Its foremost objective is to assure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets.
While network security centers its focus specifically on guarding computer networks, cybersecurity, however, takes a whole view of all digital information, applications, and other systems. It protects sensitive data from unauthorized access, including the prevention of cyber crimes like data breaches or cyber extortion attempts, and ensures proper and secure functioning of these digital environments.
Let’s take an example to understand it better. Suppose you have started an online funds transfer. Here, cybersecurity plays a role in protecting this transaction in the following manners:
 Your financial details are Encrypted during the transaction. The details become unreadable for unauthorized entities.
Your financial details are Encrypted during the transaction. The details become unreadable for unauthorized entities.With a clear idea of what cybersecurity entails, let’s discuss the advantages it brings to protecting the digital landscape.
Cybersecurity is important for keeping digital systems and data safe and trustworthy in a world that is becoming more and more linked.
1. Comprehensive Protection Against Threats: Cybersecurity provides robust protection against a wide range of other cyber threats, such as phishing, ransomware attacks, malware, and unauthorized access. By proactively attending to these risks, it ensures the safety of systems.
2. Safeguards Sensitive Information: It prevents the theft or misuse of sensitive data, like personal information, financial records, or intellectual property. This protection is important for maintaining trust among customers, employees, and stakeholders.
3. Minimizes Financial Losses: It reduces the risk of financial losses through cybercrime, downtime of operations, or penalties in relation to regulatory breaches. This is achieved by preventing data breaches and other security incidents.
4. Boosts Organizational Reputation: Strong cybersecurity makes an organization safer by earning the trust of clients and business partners as a promise to keep data secure.
5. Ensures Business Continuity: When an event occurs, cybersecurity helps businesses quickly return to normal so they can continue operating even if there are possible attacks.
Although cybersecurity is essential, it’s not without its drawbacks. Let’s look at the challenges that come with implementing it.
Cost, complexity, and performance issues can make it hard to set up and manage cybersecurity measures.
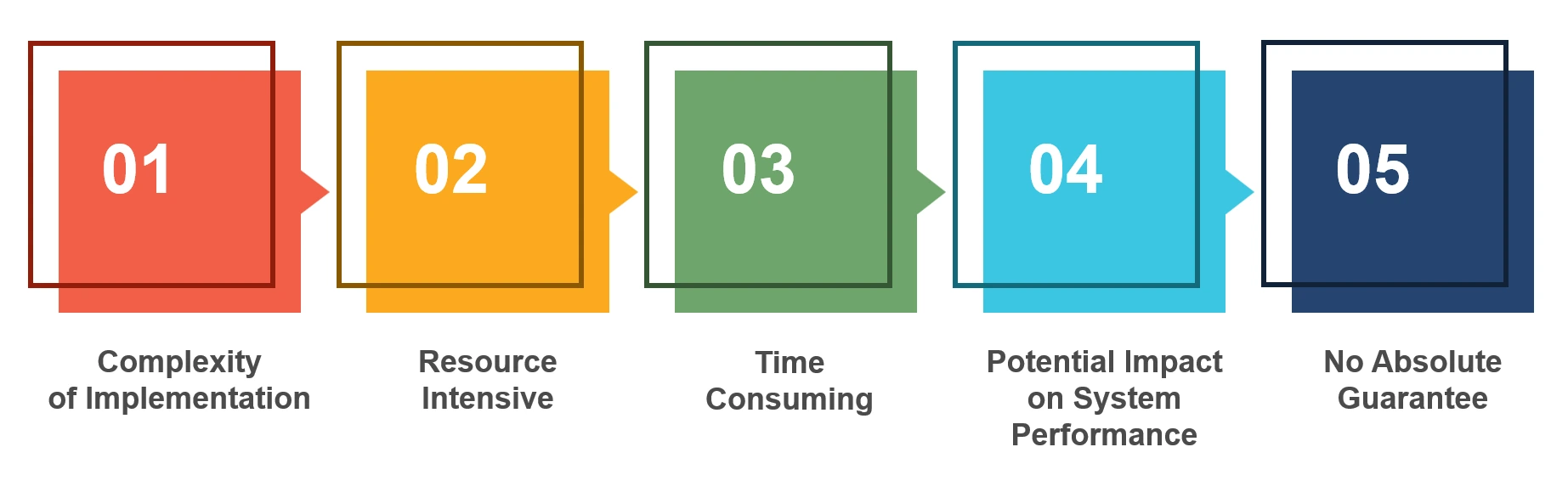
2. Resource-Intensive: The maintenance of robust cybersecurity measures involves a lot of financial investment, skilled personnel, and regular training to keep up with the evolving threats.
3. Time-Consuming: Monitoring networks, conducting vulnerability assessments, and responding to incidents demand significant time and effort, potentially diverting resources from other critical operations.
4. Potential Impact on System Performance: Some of the security solutions, like firewalls and encryption, are not only sometimes performance-sensitive and may produce compatibility problems with other applications available in the system; they need proper management.th existing applications, requiring careful management.
5. No Absolute Guarantee: Advanced mechanisms cannot give 100% protection against all types of cyber attacks. Sophisticated threats, which also evolve continuously, may attack unknown vulnerabilities.
If you want to explore cybersecurity in detail, check out the following video:
What is Cyber Security?
Despite their differences, network security and cybersecurity share common ground. Let’s explore these similarities.
Network security and cybersecurity are both ways to keep data, systems, and networks safe from risks and people who shouldn’t be able to access them. Although they work on different things, they use the same digital security tactics and tools.
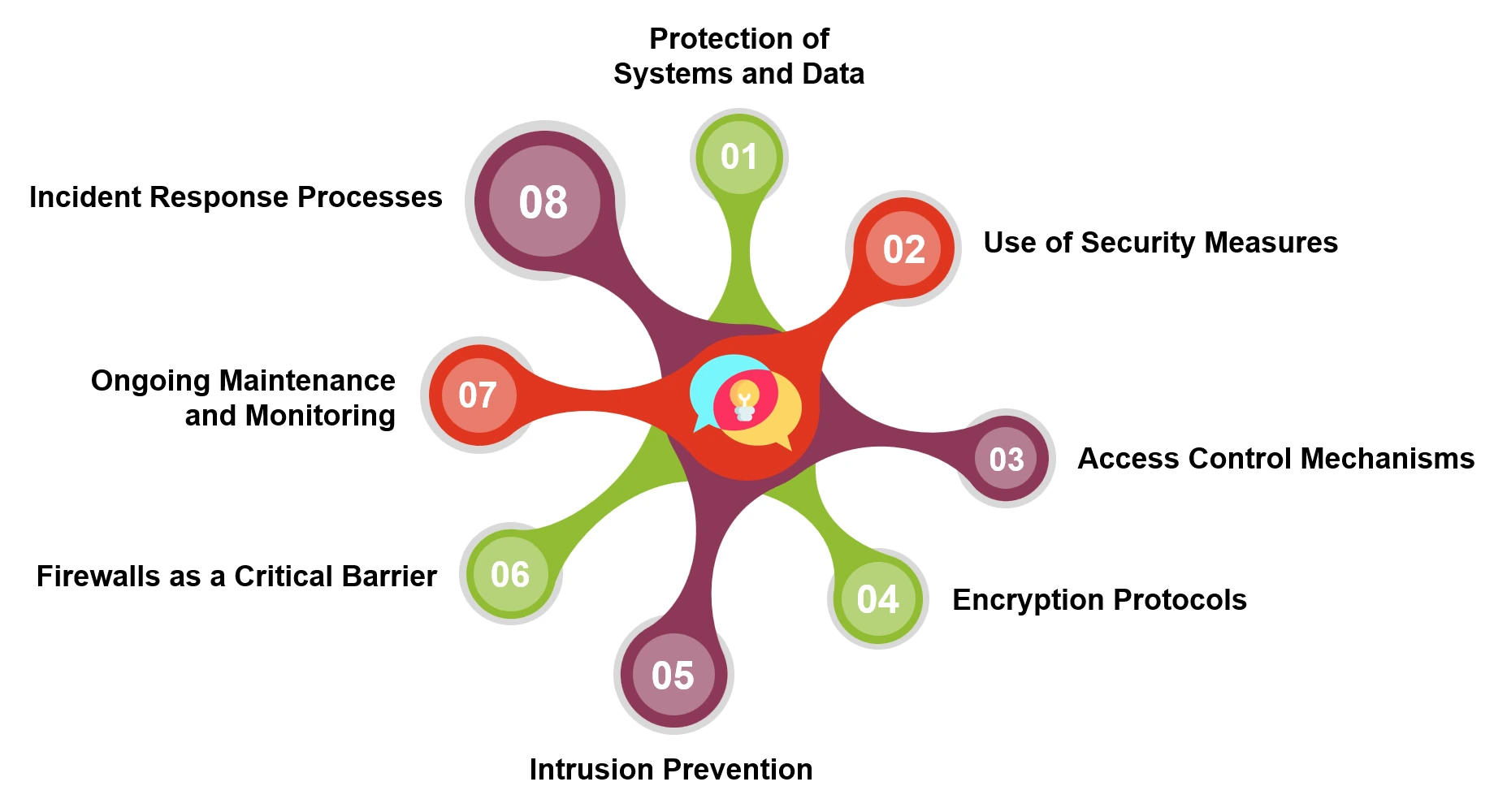
2. Use of Security Measures: Both utilize tools such as firewalling, encryption, an intrusion detection system, and security measures to effectively detect and mitigate risks against harmful threats.
3. Access Control Mechanisms: Role-based Access Control (RBAC) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) both ensure that only people who are allowed can access certain resources.
4. Encryption Protocols: Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) are common in both domains. They encrypt data to prevent tampering during transmission.
5. Intrusion Prevention: Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) in both cyber and network security detect and mitigate threats using signature-based and anomaly-based detection.
6. Firewalls as a Critical Barrier: Firewalls and Unified Threat Management (UTM) solutions are critical to monitoring and filtering network traffic, providing robust defense mechanisms.
7. Ongoing Maintenance and Monitoring: Both require continuous monitoring, regular vulnerability assessments, and timely patching to remain effective against emerging threats.
8. Incident Response Processes: Structured incident response frameworks are critical to addressing security incidents promptly and minimizing their impact.
Network Security and Cybersecurity might sound similar, but they focus on different areas. Let’s break it down with a simple comparison table.
| Aspect | Network Security | Cybersecurity |
| Scope of Protection | Focuses on securing data transmitted across a network and protecting the infrastructure, including routers, switches, and communication protocols. | Encompasses the entire IT ecosystem, safeguarding endpoints, applications, servers, user behavior, and the overall digital landscape. |
| Objective | Ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data during transmission through network-specific measures. | Protects against cyber threats across all vectors, including malware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). |
| Focus Area | Targets network components like firewalls, VPNs, and IDS/IPS to prevent unauthorized access and maintain secure communication. | Addresses the overall security posture, integrating technologies, policies, and processes to protect all digital assets. |
| Data Protection | Protects data in transit across networks using protocols like TLS/SSL. | Safeguards sensitive data at rest, in transit, and during processing using encryption and secure storage mechanisms. |
| Threats Addressed | Focuses on network-specific threats like DDoS attacks, Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks, and trojans. | Includes threats like social engineering, phishing, data breaches, and cyber fraud. |
| Applications | Applies primarily within organizational or cloud networks to secure data flow and prevent intrusions. | Extends to broader environments, including endpoint devices, user accounts, and cloud services. |
| Hierarchy | A subset of cybersecurity, focusing specifically on network-related defenses. | A broader domain that also encompasses network security. |
| Examples of Measures | Firewalls, IDS/IPS, VPNs, and multi-factor authentication for network access. | Endpoint protection, secure authentication, and cybersecurity awareness training. |
| Job Roles | Roles include Network Security Engineer and Architect, focusing on IT infrastructure. | Positions like Cybersecurity Analyst and Architect handle broader threat detection and recovery. |
| Physical and Cloud Security | Secures network hardware and cloud-hosted services within the network. | Covers physical devices, cloud environments, and services using advanced tools like CASB. |
Network Security and Cybersecurity are interconnected but distinct domains. Each one is crucial for safeguarding digital environments. Where one focuses on protecting data during transmission, and the other ensures comprehensive protection across all digital assets and threats.
To conclude, Network security is more about keeping the system safe, whereas Cybersecurity protects all digital assets. By combining both, businesses can make sure they have a powerful defense against constantly changing risks in creating a safe and secure digital space.
If you’re looking to build a strong foundation in cybersecurity and master essential skills, check out Cybersecurity Certification Course This course is designed to equip you with in-depth knowledge and practical experience to excel in the domain. Start your journey today!
Network security is concerned with safeguarding the integrity and functionality of a network and its data, while cyber security is concerned with protecting all components of a digital environment, such as data, devices, and networks.
It is crucial because it ensures that the transit and storage of information in any network are not intercepted, misused, or threatened, thereby maintaining the security of sensitive information.
Yes, it is a subset of cybersecurity. Cybersecurity encompasses a wider range of security measures that safeguard data and systems, whereas network security is specifically concerned with protecting the network infrastructure.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co