Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking Internship ...
- 15k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Mobile devices have become an essential part of our daily lives, and with approximately 5 billion users worldwide, the prevalence of mobile security threats is a major concern. Millions of applications are downloaded every day, transforming these devices into powerful tools for communication, work, and entertainment. However, this widespread adoption also makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
For example, in December 2024, the FBI issued a warning after uncovering a critical vulnerability in the way text messages are exchanged between Android and iPhone devices. The issue arises because messages sent via Rich Communication Services (RCS) are not end-to-end encrypted, unlike iMessages exchanged between iPhone users or messages sent between Android devices via Google Messages. This gap in security means that when an Android device communicates with an iPhone, the message is only encrypted between the device and the server, leaving it vulnerable to interception in transit. Cybercriminals exploited this weakness by capturing unencrypted data over major telecom networks such as AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon. Their methods enabled them to intercept sensitive information like personal messages, banking details, and other confidential data. This recent exploit underscores the urgent need for robust encryption protocols and secure communication practices to protect our mobile devices.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the top 7 mobile security threats that are putting both personal and organizational data at risk and explore effective strategies to defend against these dangers.
Cybercriminals target mobile devices on multiple fronts by exploiting vulnerabilities in mobile operating systems, malicious applications, and network infrastructures. These attacks can lead to data loss, credential theft, and account compromise, posing serious risks to both personal privacy and organizational security. As employees increasingly use personal devices for work purposes, a single compromised mobile device can expose a wealth of sensitive information.
With an overall understanding of mobile security threats in mind, it’s time to delve into the seven specific risks you need to guard against.
Mobile devices are highly versatile tools that, unfortunately, also offer multiple entry points for cyberattacks. Threat actors can compromise these devices using various methods such as phishing, malware, social engineering, exploitation of operating system flaws, and even through physical theft. Below are the seven primary mobile security threats you should guard against.
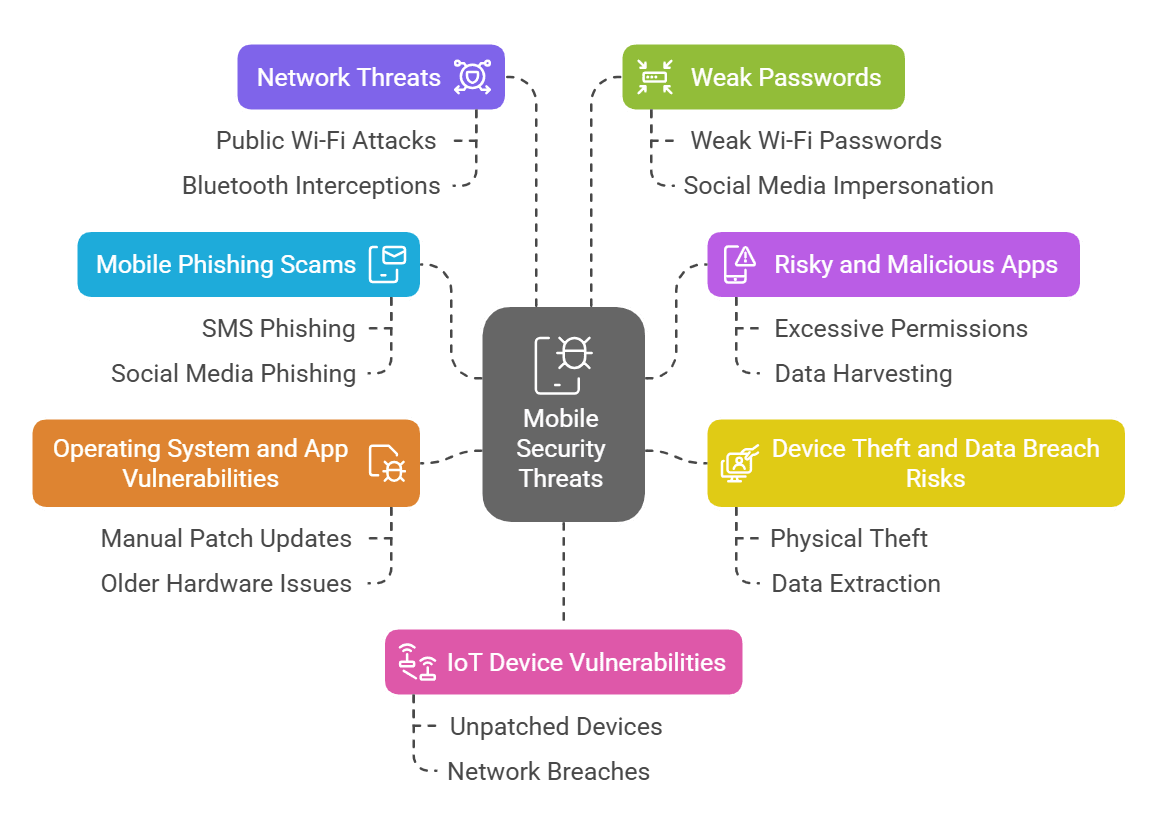
Phishing is a well-known tactic in which attackers impersonate trusted entities to extract sensitive information. On mobile devices, phishing scams are even more challenging to detect due to smaller screen sizes and simplified interfaces. Cybercriminals may use SMS messages, chat services, social media platforms, dating apps, or even QR codes to deliver their deceptive messages. These scams often target passwords, banking details, or sensitive organizational data by posing as a boss or coworker requesting confidential information.
Some applications request permissions that far exceed what is necessary for their functionality. These apps may silently harvest personal data or metadata and, in some cases, install malware onto the device. Even experienced users can be misled when apps mimic well-known and trusted programs. When employees download unvetted applications on either corporate or personal devices, they can inadvertently introduce cybersecurity risks into an organization. This issue is commonly associated with shadow IT, where unauthorized apps are used for work purposes.
Mobile devices are small and portable, making them an attractive target for thieves. While stealing a desktop computer in an office might be difficult, a smartphone can be easily snatched from a crowded restaurant or public transport. Once in possession of the device, an attacker can either wipe it clean for resale or extract valuable information such as passwords, confidential documents, or access credentials stored locally or in cloud applications.
No operating system is immune to flaws. Both Android and iOS, along with the apps running on these platforms, are regularly found to have vulnerabilities. Although vendors like Google and Apple work hard to patch these weaknesses, the process is not always instantaneous. Users are often required to download these patches manually, and in bring-your-own-device environments, administrators have limited control over timely updates. Additionally, older hardware might not support the latest security updates, leaving devices exposed to exploitation.
Even with secure settings and up-to-date patches, mobile devices can be compromised through network-based attacks. One common threat is a man-in-the-middle attack, where an attacker intercepts data while it is in transit. Public Wi-Fi networks and unsolicited Bluetooth connections are typical vectors for such attacks. In some cases, even encrypted files may be vulnerable if the decryption key is available on the same device that sent them.
Weak passwords are a significant vulnerability on any platform, and mobile devices are no exception. If a thief gains physical access to a device with an easily guessable PIN or password, they can quickly obtain full control of the device. Furthermore, weak passwords used in Wi-Fi networks or online accounts can allow attackers to infiltrate a device remotely, install unauthorized apps, or impersonate users on social media platforms. Regularly updating and strengthening passwords is crucial to reduce these risks.
IoT gadgets, while often not holding sensitive data themselves, can serve as gateways into otherwise secure networks. The diversity in manufacturers and connection protocols makes it difficult to assess which devices are trustworthy and how frequently they receive security patches. Vulnerable IoT devices connected to a network can provide cybercriminals with an entry point to launch further attacks on more critical systems and data.
Having reviewed the key threats, it is essential to discuss how to protect your mobile device. The following section outlines six effective ways to bolster your mobile security.
Most Common Cybersecurity Threats
Mobile device protection relies on a combination of security measures that safeguard both data at rest and data in transit. Below are six key strategies to enhance the security of your mobile device.
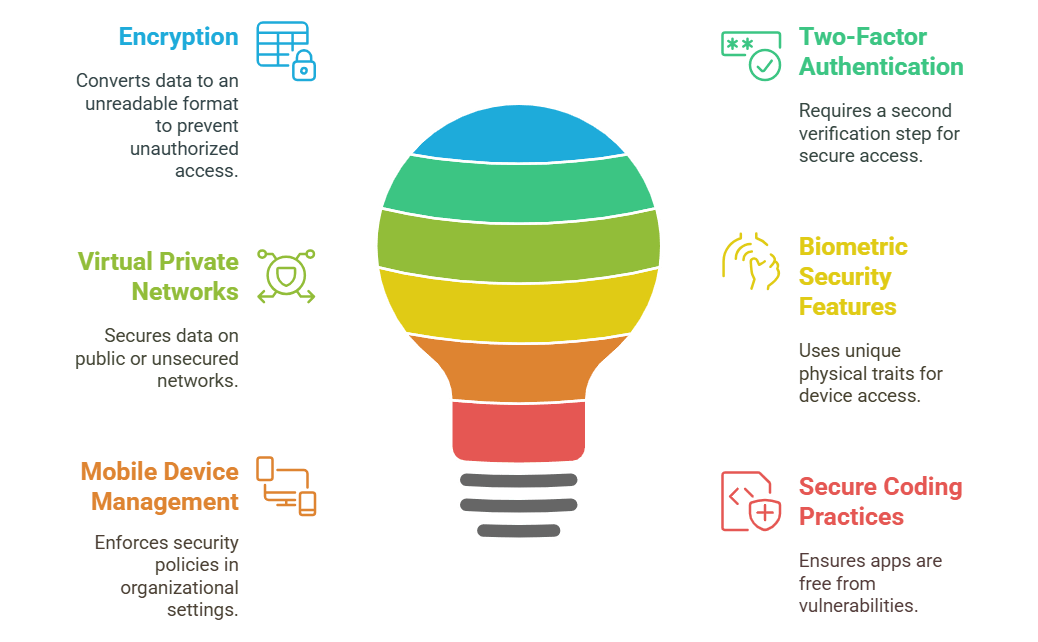
Encryption is a critical measure for protecting the data stored on your device. By converting your data into an unreadable format, only those with the correct decryption key can access the information. Modern mobile operating systems offer built-in encryption features that can be enabled in the device settings. This ensures that if your device is lost or stolen, sensitive information remains inaccessible to unauthorized users.
It adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password. This may involve receiving a code via SMS or using an authenticator app. With 2FA enabled, even if your password is compromised, the additional verification step helps prevent unauthorized access to your accounts and personal data.
It protects your data when you connect to public or unsecured networks. A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic, making it difficult for hackers to intercept your information. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi in places such as cafes, airports, or hotels.
It features such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, or iris scanning provide a convenient and secure way to unlock your device. These methods verify your identity using unique physical characteristics, which makes it harder for unauthorized users to access your mobile device and sensitive data.
For organizations, Mobile Device Management solutions are essential for enforcing security policies across all mobile devices. MDM software allows IT administrators to manage app installations, enforce encryption and password policies, and remotely wipe data if a device is lost or compromised. This centralized control helps maintain a consistent and robust security posture within an organization.
For developers, secure coding practices are vital to ensure that mobile applications are free from vulnerabilities. This involves implementing thorough input validation, secure data storage, proper error handling, and regular security testing throughout the development process. By integrating security measures into the coding lifecycle, developers can reduce the risk of apps that expose sensitive data or are susceptible to attacks.
By implementing these protective measures, you can significantly reduce your exposure to mobile security threats.
As mobile devices continue to integrate into every aspect of our lives, the importance of defending against mobile security threats cannot be overstated. From phishing scams to weak passwords, the range of risks is extensive, and so are the defenses. By implementing robust security measures like encryption, 2FA, VPNs, biometric security, MDM, and secure coding practices, you can significantly reduce your exposure to cyber risks and protect your personal and business data.
For those eager to deepen their cybersecurity expertise, Edureka’s Cyber Security Training Course offers hands-on experience in key areas such as IAM, network security, and cryptography, preparing you for in-demand roles at top companies.
Preventing security threats on mobile devices often involves:
While mobile threatening isn’t a standard term, it is often used to describe the various mobile security threats that target smartphones and tablets. These threats include phishing scams, malware, device theft, and more.
It refers to the set of measures and technologies used to defend mobile devices against cyber attacks. This includes practices like encryption, secure coding, two-factor authentication, VPNs, and the use of Mobile Device Management systems.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co