AWS Certification Training
- 181k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
With the advent of cloud computing & containerization, microservices has taken the world by storm. Organizations are hunting for professional with Microservices Training. In the previous blog, you must have learned how to setup and run Spring Boot using Eclipse IDE and CLI. Now in this Spring Boot Microservices blog, let me show how we can create Microservices Application for Top Sports Brands using Spring Boot and Netflix Eureka Server in detail.
Spring Boot enables building production-ready applications quickly and provides non-functional features:
So, let us see what are the challenges with Microservices Architecture
While developing a number of smaller microservices might look easy, but there are number of inherent complexities that are associated with microservices architectures. Let’s look at some of the challenges:
This video will help you to implement Microservices with the help of Spring Boot.
In this spring boot microservices example, we will be creating Top Sports Brands application which will be having 3 services:-
Let us see which of the following tools required to create this spring boot microservices example application.
If you facing any difficulty in installing and running the above tools, please refer to this blog.
To begin with, create a EurekaServer Spring Starter Project in Eclipse IDE. Click on Spring Starter Project and click on Next.
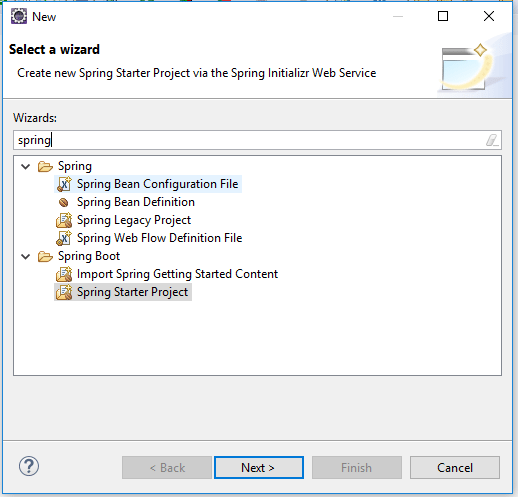
Name your Spring Starter Project as EurekaServer and other Information will be filled automatically.
Note:- Make sure your Internet is connected otherwise it will show an error.

Now, select Eureka Server as a dependency and click on Finish.
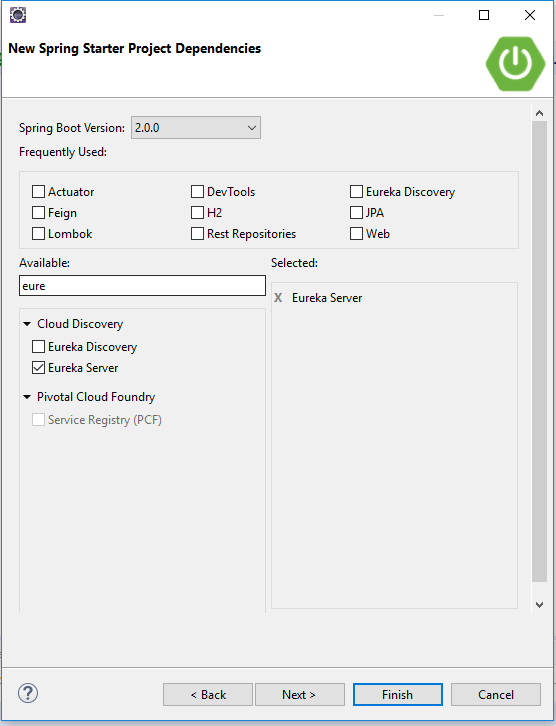
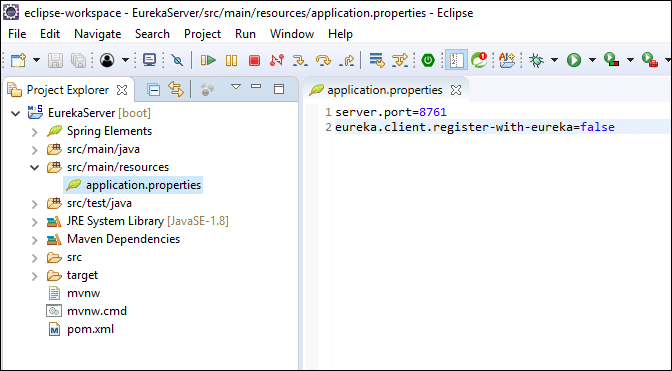
Now, modify EurekaServer/src/main/resources/application.properties file to add a port number and disable registration.
server.port=8761
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
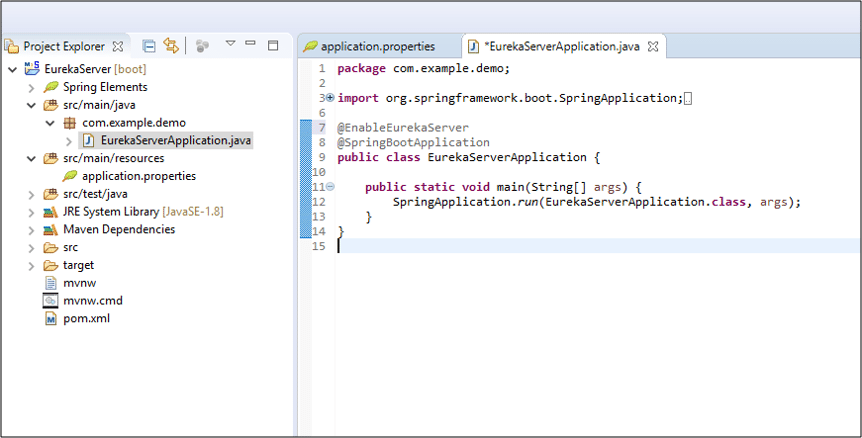
Open EurekaServer/src/main/java/com/example/EurekaServiceApplication.java and add @EnableEurekaServer above @SpringBootApplication.
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
This annotation will configure a registry that will allow other applications to communicate.
 To start the Application: Right Click on the Project –> Run As –> Click on “Spring Boot App“
To start the Application: Right Click on the Project –> Run As –> Click on “Spring Boot App“
 After it starts, you should be able to open
After it starts, you should be able to open http://localhost:8761 and see there are no services available.Now open http://localhost:8761. Here Spring Eureka Server will open and will show no service will be running.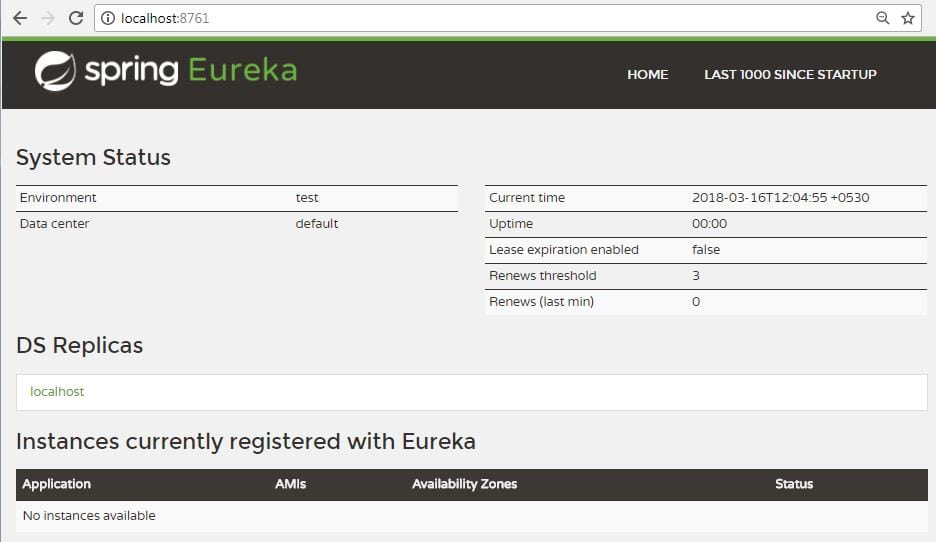
Again create a new project. Use Item-catalog-service for the artifact name and click on Next.

Add the following dependencies:
Click on Finish.

Now, create an Item entity, toItemCatalogServiceApplication.java . The code below assumes you’re putting all classes in the same file.
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Entity
class Item {
public Item(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
}
@RepositoryRestResource
interface ItemRepository extends JpaRepository<Item, Long> {}
@Component
class ItemInitializer implements CommandLineRunner {
private final ItemRepository ItemRepository;
ItemInitializer(ItemRepository itemRepository) {
this.itemRepository = itemRepository;
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
Stream.of(""Lining", "PUMA", "Bad Boy", "Air Jordan", "Nike", "Adidas", "Reebok")
.forEach(item -> itemRepository.save(new Item(item)));
itemRepository.findAll().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
If you’re using an editor that doesn’t auto-import classes, here’s the list of imports needed at the top of ItemCatalogServiceApplication.java.
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.rest.core.annotation.RepositoryRestResource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
Add an application name in item-catalog-service/src/main/resources/application.properties file to display in the Eureka service, and set the port to 8088.
server.port=8088
spring.application.name=item-catalog-service
Now, Create the Cloud Properties file
Click on File –> New –> Other –> File and add the below code in this file and save it.
eureka.instance.hostname=${vcap.application.uris[0]:localhost}
eureka.instance.nonSecurePort=80
eureka.instance.metadataMap.instanceId=${vcap.application.instance_id:${spring.application.name}:${spring.application.instance_id:${server.port}}}
eureka.instance.leaseRenewalIntervalInSeconds = 5
eureka.client.region = default
eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds = 5
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=${vcap.services.pwa-eureka-service.credentials.uri}/eureka/Now, to start the Application:
Right Click on Project –> Run As –> Click on “Spring Boot App“
Note: In case of error try this step: Right Click on the Project –> Run As –> Click on “Maven Build“
Now open http://localhost:8761. Here you will see Item Catalog service will be running.
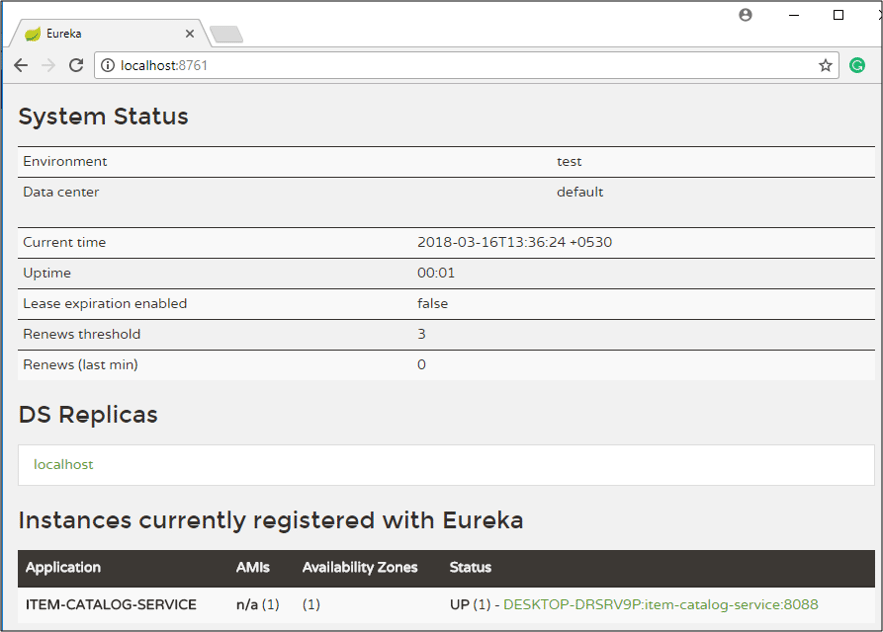
You will see the list of items from the catalog service.
Open http://localhost:8088/items
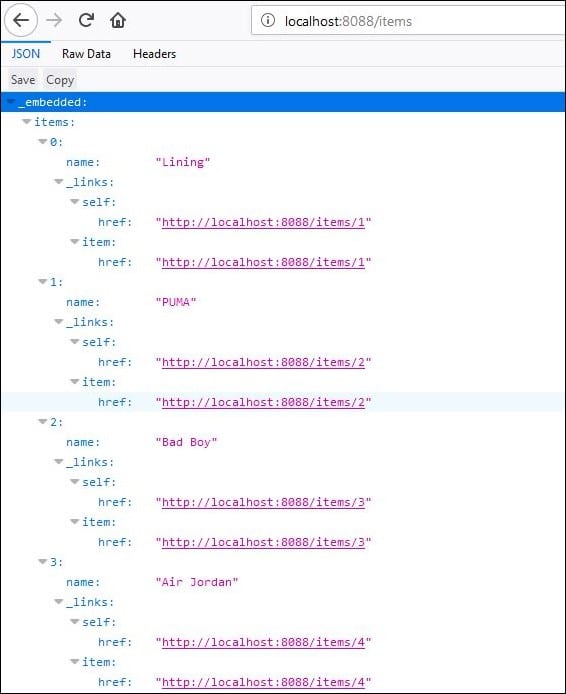
Now let us move forward and create the Edge Service.
Spring Boot Microservices: Creating an Edge Service
It is similar to the standalone Item service created in Bootiful Development with Spring Boot and Angular. However, it will have fallback capabilities which prevent the client from receiving an HTTP error when the service is not available.
Again create a new project. Use edge-service for the artifact name
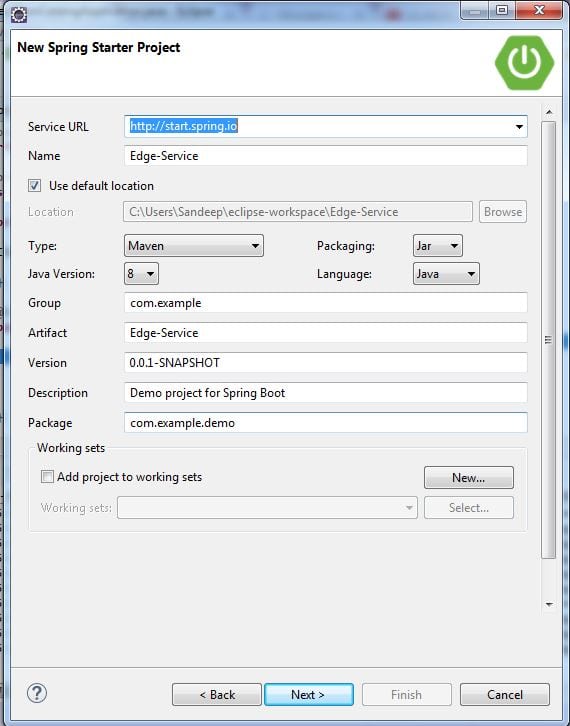
Click on Finish.
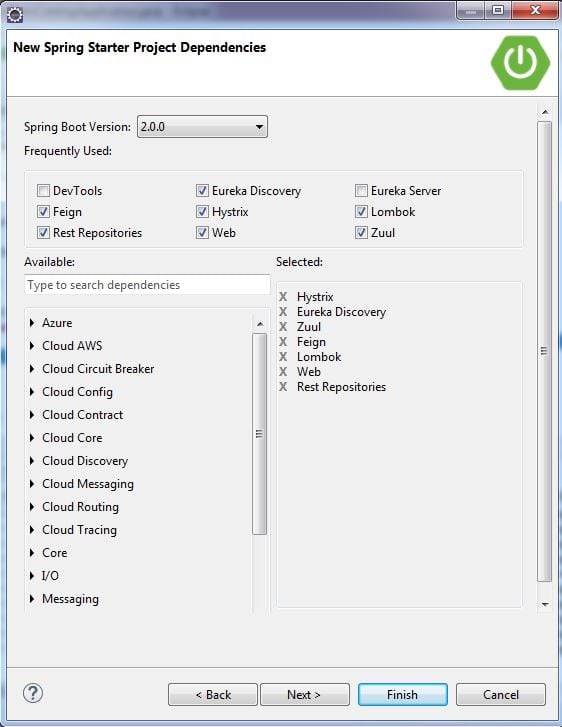
Since the item-catalog-service is running on port 8088, you’ll need to configure this application to run on a different port. Modify edge-service/src/main/resources/application.properties to set the port to 8089 and set an application name.
server.port=8089
spring.application.name=edge-service
Now, Create the Cloud Properties file
Click on File –> New –> Other –> File and add below code in this file and save it.
eureka.instance.hostname=${vcap.application.uris[0]:localhost}
eureka.instance.nonSecurePort=80
eureka.instance.metadataMap.instanceId=${vcap.application.instance_id:${spring.application.name}:${spring.application.instance_id:${server.port}}}
eureka.instance.leaseRenewalIntervalInSeconds = 5
eureka.client.region = default
eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds = 5
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=${vcap.services.pwa-eureka-service.credentials.uri}/eureka/
To enable Feign, Hystrix, and registration with the Eureka server, add the appropriate annotations toEdgeServiceApplication.java:package com.example.edgeservice;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
import org.springframework.hateoas.Resources;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableCircuitBreaker
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableZuulProxy
@SpringBootApplication
public class EdgeServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EdgeServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
Create a Item DTO (Data Transfer Object) in this same file. Lombok’s @Data will generate a toString() methods, getters, setters, and appropriate constructors.
@Data
class Item {
private String name;
}
Create a ItemClient interface that uses Feign to communicate to the Item-catalog-service.
public class EdgeServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EdgeServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Data
class Item {
private String name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@FeignClient("item-catalog-service")
interface ItemClient {
@GetMapping("/items")
Resources<Item> readItems();
}
Create a RestController below the ItemClient that will filter out less-than-top brands and shows a /top-brandsendpoint.
@RestController
class GoodItemApiAdapterRestController {
private final ItemClient itemClient;
public GoodItemApiAdapterRestController(ItemClient ItemClient) {
this.itemClient = itemClient;
}
@GetMapping("/top-brands")
public Collection<Item> goodItems() {
return itemClient.readItems()
.getContent()
.stream()
.filter(this::isGreat)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private boolean isGreat(Item item) {
return !item.getName().equals("Nike") &&
!item.getName().equals("Adidas") &&
!item.getName().equals("Reebok");
}
}
Start the edge-service application with Maven or your IDE and verify it registers successfully with the Eureka server.

Now invoke localhost:8089/top-brands, you will see the list of top brands from the catalog service.
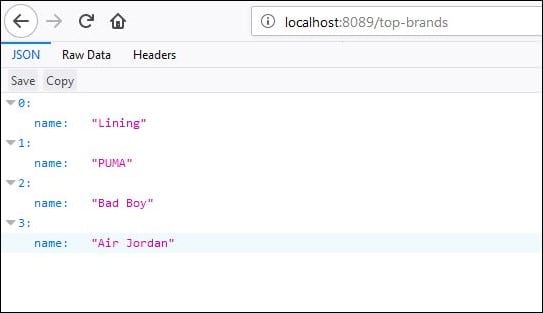
Note: If you shut down the item-catalog-service application, you’ll get a 500 internal server error.
$ http localhost:8089/top-brands
HTTP/1.1 500
Connection: close
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Date: Fri, 16 Mar 2018 12:51:22 GMT
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
X-Application-Context: edge-service:8089
{
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"exception": "feign.RetryableException",
"message": "connect timed out executing GET http://item-catalog-service/items",
"path": "/top-brands",
"status": 500,
"timestamp": 1328088897672
}
To fix this, you can use Hystrix to create a fallback method and tell the goodItems() method to use it.
public Collection<Item> fallback() {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "fallback")
@GetMapping("/top-brands")
public Collection<Item> goodItems() {
return …
}
Restart the edge-service and you should see an empty list returned.
$ http localhost:8089/top-brands
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Date: Fri, 16 Mar 2018 12:59:02 GMT
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
X-Application-Context: edge-service:8089
[]
Start the item-catalog-service again and this list should eventually return the full list of top brands names.
If you want the Source Code for this Application, please leave your comment in comment section.
So, this was all about the Spring Boot Microservices blog. If yoy are preparing for your Spring Boot interview? Check out these 50 essential Spring Boot interview questions to ace your upcoming interview!
If you wish to learn spring framework and build your own applications, then check out this Spring Certification course online to learn more about Spring Frameworks.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of ” Spring Microservices” and I will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
Very nice article on microservices with spring-boot. Thanks for the blog. Could you please share the source code to sandeeproniyaar@gmail.com?
Hey Sandeep, we have sent the files. Please do check and see if you have received it. Cheers!
Could you please share the source code to raja.aecit@gmail.com
Hey Raja, we have sent the files. Please do check and let us know if you need anything else. Cheers!
please send me the source code at -tnzngdw@gmail.com
Hey Tenzin, we have shared the files to you over mail. Kindly do check your mail and let us know if you need any help. Cheers!
please share the code to puneeth.mypadi@gmail.com
Hey Puneeth, we have shared the files to you over mail. Kindly do check your mail and let us know if you need any help. Cheers!
my item-catalog-servie status is showing down. I don’t know what to do??
how can i change status to Up?
please share the source code yessine.abid@live.fr
Nice article. Please send the source to tech.java.jey@gmail.com
can u please provide code to me at noorulhaque447@gmail.com…please…its very urgent…
Hey Noorul, sorry for the delay in getting back. We have just sent the source code to you over mail. Cheers!
Very nice video and blog to start with Spring micro-services. Kindly send me source code of all applications – vrajeshjayswal@gmail.com
Hey Vrajesh, glad to hear you loved the video and the blog. Do check out our YouTube channel for other tutorials. Cheers!
Please send me source code to my email sk_bigdata@outlook.com
Hi Sri, you can find the source code in your mail. Cheers!