Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In PHP, special functions can be defined in such a way that they can be called automatically and does not require any function call to execute the code inside these functions. This feature is available in a special method known as magic methods. In this article, we will discuss the top Magic Methods in PHP.
Methods that begin with 2 underscores(__) are generally called Magic methods in PHP. These methods names are limited to some list of PHP supported keywords that are reserved. So any function should not be defined with the name of PHP magic methods.
Usually, these functions should be defined by the user and there is no need to call them explicitly.
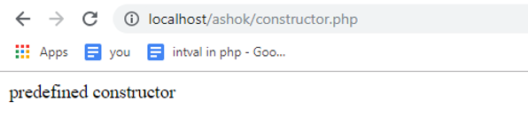
class sample
{
function user_def()
{
echo "user defined constructor";
}
function __construct()
{
echo "predefined constructor";
}
}
$obj= new sample();
?>
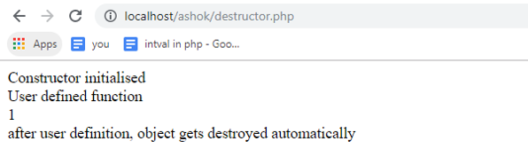
<?php class sample { function __construct() { echo "Constructor initialised"." "; } function user_def() { echo "User defined function "." "; } function __destruct() { echo "after user definition, object gets destroyed automatically"." "; } } $obj= new sample(); $obj->user_def();
//check object is destroyed or not
echo is_object($obj)."
";
?>
<?php class Sample { function user_define() { echo "This is user defined function "; } function __call($fun, $arg) { echo "function that not exists:" . $fun." "; echo "parameter list of method that does not exist:"; print_r($arg); } } $obj = new Sample(); $obj->run("teacher"); // If the method which is not existed is called within the object, then the __call() method will be called automatically.
$obj->eat("ashok", "orange");
$obj->user_define();
?>
<?php class Sample { function user_define() { echo "This is user defined function "; } public static function __callStatic($fun, $arg) { echo "Method that does not exist:" . $fun . " "; echo "parameter list of method that does not exist:"; print_r($arg); } } $obj = new Sample(); $obj::run("Student"); // If the method does not exist is called within the object, then the __callStatic() method will be called automatically. $obj::eat("ashok", "orange"); $obj->user_define();
?>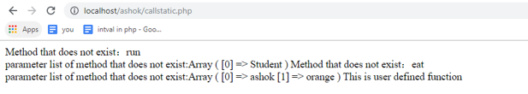
<?php class Student { private $name; private $reg; function __construct($name="", $reg=1) { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
}
public function __get($propertyName)
{
if ($propertyName == "reg")
{
if ($this->reg>30)
{
return $this->reg - 10;
} else
{
return $this->$propertyName;
}
}
else
{
return $this->$propertyName;
}
}
}
$obj = new Student("Ashok", 60); // Instantiate the object with the Student class and assign initial values to the properties with the constructor.
echo "Name:" . $obj->name . "
"; // When the private property is accessed, the __get() method will be called automatically,so we can get the property value indirectly.
echo "reg:" . $obj->reg . "
"; // The __get() method is called automatically,and it returns different values according to the object itself.
?>
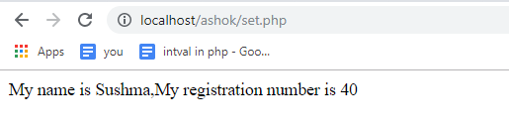
<?php class Student { private $name; private $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30) { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
}
public function __set($property, $value)
{
if ($property=="reg")
{
if ($value > 150 || $value < 0) { return; } } $this->$property = $value;
}
public function fun()
{
echo "My name is ".$this->name.",My registration number is ".$this->reg;
}
}
$obj=new Student("Ashok", 40); //Note that the initial value will be changed by the code below.
$obj->name = "Sushma"; //The "name" property will be assigned successfully. If there is no __set() method, then the program will throw an exception.
$obj->age = 16; //The "reg" property will be assigned successfully.
$obj->reg = 160; //160 is an invalid value, so it fails to be assigned.
$obj->fun();
?>
<?php class Student { public $gender; private $name; private $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
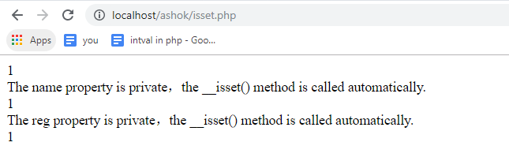
public function __isset($content)
{
echo "The {$content} property is private,the __isset() method is called automatically.
";
echo isset($this->$content);
}
}
$obj = new Student("Ashok", 30); // Initially assigned.
echo isset($obj->gender),"
";
echo isset($obj->name),"
";
echo isset($obj->reg),"
";
?>
<?php class Student { public $gender; private $name; private $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
public function __unset($content)
{
echo "It is called automatically when we use the unset() method outside the class.
";
echo isset($this->$content);
}
}
$obj = new Student("Ashok", 30); // Initially assigned.
unset($obj->gender);
unset($obj->name);
unset($obj->reg);
?>
<?php class Student { public $gender; public $name; public $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=25, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg= $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
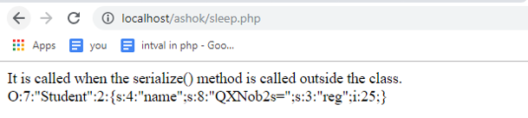
public function __sleep()
{
echo "It is called when the serialize() method is called outside the class.
";
$this->name = base64_encode($this->name);
return array('name', 'reg'); // It must return a value of which the elements are the name of the properties returned.
}
}
$obj = new Student('Ashok'); // Initially assigned.
echo serialize($obj);
echo '
';
?>
<?php class Student { public $gender; public $name; public $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg =$reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
public function __sleep()
{
echo "It is called when the serialize() method is called outside the class.
";
$this->name = base64_encode($this->name);
return array('name', 'reg'); // It must return a value of which the elements are the name of the properties returned.
}
public function __wakeup()
{
echo "It is called when the unserialize() method is called outside the class.
";
$this->name = 2;
$this->gender = 'Male';
}
}
$obj= new Student('Ashok'); // Initially assigned.
var_dump(serialize($obj));
var_dump(unserialize(serialize($obj)));
?>
<?php class Student { public $gender; public $name; public $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
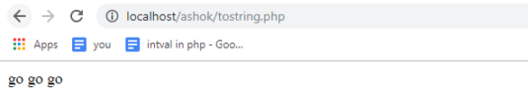
public function __toString()
{
return 'go go go';
}
}
$obj = new Student('Ashok'); // Initially assigned.
echo $obj;
?>
<?php class Student { public $gender; public $name; public $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
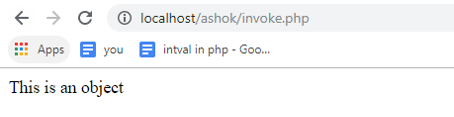
public function __invoke()
{
echo 'This is an object';
}
}
$obj = new Student('Ashok'); // Initially assigned.
$obj();
?>
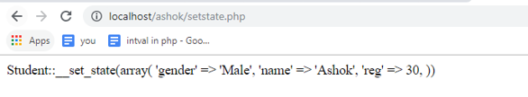
<?php class Student { public $gender; public $name; public $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
}
$obj = new Student('Ashok'); // Initially assigned.
var_export($obj);
?>
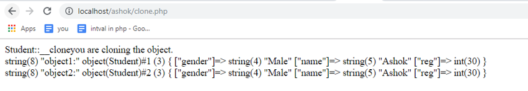
<?php class Student { public $gender; public $name; public $reg; public function __construct($name="", $reg=30, $gender='Male') { $this->name = $name;
$this->reg = $reg;
$this->gender = $gender;
}
public function __clone()
{
echo __METHOD__."you are cloning the object.
";
}
}
$obj = new Student('Ashok'); // Initially assigned.
$obj2 = clone $obj;
var_dump('object1:');
var_dump($obj);
echo '
';
var_dump('object2:');
var_dump($obj2);
?>
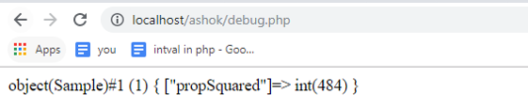
<?php class Sample { private $prop; public function __construct($val) { $this->prop = $val;
}
public function __debugInfo()
{
return [
'propSquared' => $this->prop ** 2,
];
}
}
var_dump(new Sample(22));
?>
With this, we come to ann end of this magic method in PHP article. I hope you got an idea of the various magic methods in PHP.
Check out the PHP Certification Training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of ”Magic Methods in PHP” and I will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co