Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Java is a general-purpose programming language and you need a function to perform desired operations on the applications. These functions are generally referred to as methods. In this article, you will learn how exactly methods in Java work.
Below topics are discussed in this article:
Let’s get started!
A method is basically a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called or invoked at any point in a program, just by utilizing the method’s name. Each method is given its own name. When that name is in a program, the execution branches to the body of that method. Suppose the method is completed, control returns to the area of the code from which it was called, and the program continues on to the next line of code.
Methods are basically referred to time savers, which means that they allow you to have the repetition of sections of code without having to retype the code. In addition to this, methods can also be saved and utilized again and again in a freshly developed program. These methods are used to perform certain actions, and they are also called as functions.
Talking about the different types of methods used, there are two types, which are:
Let’s understand them in detail.
The Standard library methods are built-in methods in Java that are readily available for use. These standard libraries come along with the Java Class Library that is present in a Java archive (*.jar) file with JVM and JRE.
The file stdlib.jar holds together all standard libraries into one single file. To access these libraries, you must add stdlib.jar to your Java classpath. There are several ways to do so. Here are the two ways through which you can do:
% javac-introcs MyProject.java % java-introcs MyProject
Some examples of Standard libraries are:
A method must be declared within a specific class. It is defined with the name of the method, followed by parentheses “()”. Java provides some pre-defined methods, such as System.out.println() and many more.
Syntax:
public static int methodName(int x, int y)
{
// body
}The above code can be broken down into:
And the method definition consists of a method header and a method body.
Now, Let’s understand how to create a user-defined Method in Java?
Syntax:
public static void my()
{
System.out.println(“My Function is created”);
}Here, a method named myMethod() is defined.
You can see three access modifiers – public, static and void before the function name.
To call a method in Java, you have to write the method’s name followed by parentheses () and a semicolon ;
For using a method in a program, it should be called. There are two ways in which a method is called i.e., the method returns a value or it returns nothing.
The process of method calling is simple. When a program invokes a method, the program control automatically gets transferred to the called method. This called method returns control to the caller in these two conditions, they are namely:
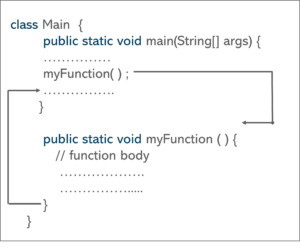
In this case,
Let’s see a Java method in action by defining a Java class.
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("In order to encounter a method");
// method call
myMethod();
System.out.println("the method was executed successfully!");
// method definition
private static void myMethod(){
System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod()!");
}
}When you run the program, the output will be:
In order to encounter a method
Printing from inside myMethod()!
the method was executed successfully!
Now let’s talk about the method parameters.
Method parameters
Parameters are specified after the method name in a class, inside parentheses. You can add as many parameters as you want but just separate them with a comma. Data can be passed to functions as a parameter. Actually, parameters act as variables inside the method.
Let’s take a look at an example to understand this.
public class MyClass
{
static void myMethod(String fname)
{
System.out.println(fname + " Certification course");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myMethod("Java");
myMethod("Kotlin");
myMethod("Selenium");
}
} The output of this will be:
Java Certification course
Kotlin Certification course
Selenium Certification course
You can also use any primitive data type or built-in Java class as a data type for the parameters or you can also use your own classes as parameter types.
So, this is about the method parameters in Java.
Now, let’s understand how to allocate memory for the methods that are called.
Memory allocation for methods calls
This brings us to the end of this article where we have learned the frequently asked questions on the Methods in Java. Hope you are clear with all that has been shared with you in this tutorial.
Make sure you practice as much as possible and revert your experience.
If you found this article on “Methods in Java” relevant, check out the Edureka’s Java Course, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. We are here to help you with every step on your journey, we come up with a curriculum which is designed for students and professionals who want to be a Java Developer. The course is designed to give you a head start into Java programming and train you for both core and advanced Java concepts along with various Java frameworks like Hibernate & Spring.
If you come across any questions, feel free to ask all your questions in the comments section of “Methods n Java” and our team will be glad to answer.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co