Electric Vehicle (EV) Foundation Training Cou ...
- 1k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
The knowledge of Networking is the most crucial requirement for every interview. Often, these questions seem really easy, but turn up to be confusing when you go on to answer them. In this article, you will be learning some of the most important Networking Interview Questions along with the answers.
To begin with, here are the ten most important Networking Interview Questions:
Q1. Differentiate between a router, a hub, and a switch.
Q2. What is a link?
Q3. What do you mean by a Node?
Q4. What does a backbone network mean?
Q5. What is Network Topology?
Q6. Explain what is LAN?
Q7. What are Routers?
Q8. What is a Point-to-Point Network?
Q9. What is OSI Model?
Q10. Give a brief about each layer in the OSI Model.
| HUB | SWITCH | ROUTER |
| Connects two or more Ethernet devices | Connects two or more LAN devices | Can connect devices or a LAN and WAN |
| Does not perform filtering | Filters packets before forwarding them | Highly configured to filter and send packets |
| Least intelligent, least expensive and least complex | Similar to a hub, but more effective | Extremely smart and complex |
A link basically is the connection between two or more computers or devices. It can be anything depending on whether it is a physical connection or a wireless one. Physical links include cables, hubs, switches, etc and wireless links wireless access points, routers, etc.
The point of intersection in a network is called a Node. Nodes can send or receive data/ information within a network. For example, if two computers are connected to form a network, there are 2 nodes in that network. Similarly, in case there are computers, there will be three nodes and so on. It is not necessary for a node to be a computer, it can be any communicating device such as a printer, servers, modems, etc.
In any system, backbone is the most principle component that supports all other components. Similarly, in networking, a Backbone Network is a Network that interconnects various parts of the network to which it belongs and has a high capacity connectivity infrastructure.
The physical layout of the computer network is called as Network Topology. It gives the design of how all the devices are connected in a network.
| Type | Description |
| Bus Topology | All the devices share a common communication line |
| Star Topology | All nodes are connected to a central hub device |
| Ring Topology | Each node connects to exactly two other nodes |
| Mesh Topology | Each node is connected to one or more nodes |
| Tree Topology (Hierarchical Topology) | Similar to star topology and inherits the bus topology |
| Daisy Chain Topology | All nodes are connected linearly |
| Hybrid Topology | Nodes are connected in more than one topology styles |
| Point-to-Point Topology | Connects two hosts such as computers, servers, etc |
A LAN or Local Area Network the network between devices that are located within a small physical location. It can be either wireless or wired. One LAN differs from another based on the following factors:
A router is some device that transfers the data packets within a network. It basically performs the traffic directing functions within a network. A data packet can be anything such as an email, a web page, etc. Routers are located at the place where two or more networks meet or the gateways.
Routers can either be stand-alone devices or virtual. Stand-alone routers are traditional devices where as virtual routers are actually softwares that act like physical ones.
A Point-to-Point network refers to a physical connection between two nodes. It can be between any device of a network such as a computer, printer, etc.

For example, as you can see in the above diagram, all the nodes are connected to each other i.e Device 1 is connected to Device 2 and Device 3 , Device 2 is connected to Device 3 and Device 1 and Device 3 is connected to Device 2 and Device 1 using physical links.
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It is a conceptual model that standardizes communication functions of telecommunication. It has 7 layers which are:
 Q10. Give a brief about each layer in the OSI Model.
Q10. Give a brief about each layer in the OSI Model.| Layer Name | Protocol | Description |
| Physical Layer | Symbol | Transfers raw bits of data over a physical link |
| Data Link Layer | Frame | Reliable transmission of data frames between nodes connected by the physical layer |
| Network Layer | Packet | Structures and manages a network with multiple nodes including addressing, routing and traffic control |
| Transport Layer | Segment, Datagram | Reliable Transmission of data packets between the different points of a network |
| Session Layer | Data | Manages the communication sessions |
| Presentation Layer | Data | Transmission of data between the service device and the application |
| Application Layer | Data | Specifies the shared communication protocols and the interface methods |
To learn about Network Programming in Java and Python in detail refer to the following blogs:
An anonymous FTP is a way of allowing a user to access data that is public. The user does not need to identify himself to the server and has to log in as anonymous.
So in case you are asked to use anonymous ftp, make sure you add “anonymous” in place of your user id. Anonymous FTPs are very effective while distributing large files to a lot of people, without having to give huge numbers of usernames and password combinations.
A network is a connection between different devices. These devices communicate with each other using physical or wireless connections. Physical connections include twisted pair cables, optic fibers, and coaxial cables..wireless networks can be established with the help of waves such as radio waves infrared waves and microwaves
Networks basically serve many purposes such as:
A Subnet Mask is the number describing the range of IP addresses that can be used within a network. They are used to assign subnetworks or subnets. These subnetworks are various LAN’s connected to the internet.
This Subnet mask is basically a 32-bit number and it masks the IP address and then divides the IP address into two parts i.e the network address and the host address. Subnet Masks are created by setting all the network bits to “1” and all the host bits to “0”s. There are two network addresses that cannot be assigned to any host on the network i.e The “0” and “255” which are assigned to network and to the broadcast address, and this is why they cannot be assigned to any host.
The TCP/ IP Model is a compressed version of the OSI Model. This Model contains 4 layers unlike the OSI Model which are:
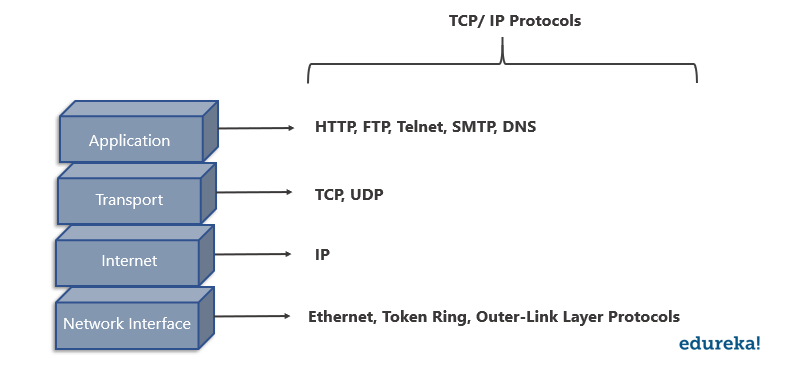 Q15. What is the difference between the OSI Model and TCP/ IP Model?
Q15. What is the difference between the OSI Model and TCP/ IP Model?
| TCP/ IP Model | OSI Model |
Has four layers | Has seven layers |
More reliable | Less reliable |
No strict boundaries | Has strict boundaries |
Horizontal Approach | Vertical Approach |
Q16. What is a UTP cable?
A UTP cable is a 100 ohms cable made up of copper. It consists of 2-1800 unshielded twisted pairs that are surrounded by a non-metallic case. These twists provide immunity to electrical noise and EMI.
Q17. What is the maximum length allowed for a UTP cable?
The maximum length allowed for a UTP cable is 100m. This includes 90 m of solid cabling and 10m of standard patch cable.
Q18. Explain what is HTTP and which port does it use?
HTTP or HyperText Transfer Protocol allows communication over the Internet. This protocol basically defines how messages are to be transmitted and formatted over the world wide web. HTTP is a TCP/ IP protocol and it uses the port number 80.
Features of HTTP Protocol:
Q19. What is NAT?
NAT stands for Network Address Translation. It deals with remapping one IP Address space with another by changing the IP headers of the packets that are being transmitted across a traffic routing device.
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol is a connection-oriented protocol that establishes and maintains a connection between communicating devices until both of them are done exchanging messages. This protocol determines how application data can be broken down into packets that can be delivered over a network. It also sends and receives packets to and from the network layer and is in charge of flow control, etc.
UDP or the User Datagram Protocol is used to create a low-latency and loss-tolerating communications between applications connected over the internet. UDP enables process-to-process communication and communicates via datagrams or messages.
| Factor of comparison | TCP | UDP |
Connection | Connection made before application messages are exchanged | Connection not made before application messages are exchanged |
Use | For applications needing more reliability and less speed | For applications needing more speedy and less reliability |
Use by Protocols of the Application Layer | File transfer, e-mail, etc | Multimedia, DNS |
Reliability | Messages will be delivered in order and without errors | No guarantee that the messages will be delivered in order and without errors |
Data Segments | Data segments rearranged in required order | All segments are independent, therefore has no inherent order specification |
Acknowledgment | ACK is received | ACK is not received |
Flow Control | Has the congestion control mechanism | No flow control option |
Check for Errors | Resends erroneous segments | Discards Erroneous segments |
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a dynamic routing protocol. It makes use of hop count as its primary metric to find the best path between the source and the destination. It works in the application layer and has an AD (Administrative Distance) value of 120.
A firewall is a network security system which is used to monitor and control the network traffic based on some predefined rules. Firewalls are the first line of defense and establish barriers between the internal and external networks in order to avoid attack from untrusted external networks. Firewalls can be either hardware, software or sometimes both.
 Q25. Explain what is NOS?
Q25. Explain what is NOS?A Network Operating System (NOS) is an Operating System that is designed to support workstations, databases, personal computers, etc over a network. Some examples of NOS are MAC OS X, Linux, Windows Server 2008, etc. These Operating Systems provide various functionalities such as processor support, multiprocessing support, authentication, Web services, etc.
Denial of Service (DoS) is a kind of attack that prevents a legitimate user from accessing data over a network by a hacker or an attacker. The attacker floods the server with unnecessary requests in order to overload the server thereby preventing the legitimate users from accessing its services.
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. It is a character encoding standard used in the electronic communication field. The ASCII codes basically represent text.
IEEE stands for Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineer. It is the world’s largest technical professional society and is devoted to advancing innovation and technological excellence.
MAC or Media Access Control address is a computer’s unique number assigned to a Network Interface Controller (NIC). It is a 48-bit number that identifies each device on a network and is also referred to as the physical address. MAC addresses are used as a network address for communications within a network such as an Ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc.
During transmission of data packets in two-way communication, the receiver sends an acknowledgment (control frame or ACK) to the receiver after receiving the data packets. However, the receiver does not send the acknowledgment immediately, but, waits until its network layer passes in the next data packet. Then, the ACK is attached to the outgoing data frame. This process of delaying the ACK and attaching it to the next outgoing data frame is known as piggybacking.
DNS or Domain Name System is a naming system for devices connected over the internet. It is a hierarchical and decentralized system that translates domain names to the numerical IP Addresses which is required to identify and locate devices based on the underlying protocols.
All devices connected to the internet have unique IP addresses which are used to locate them on the network. The process involves conversion on hostnames into IP addresses. For example, in case the user wants to load some web page (xyz.com), this hostname is converted into an IP address that can be understood by the computer in order to load that web page.
| Domain | Workgroup |
Has one or more computer acting as a server | All computers are peers |
Has a centralized database | Each computer has its own database |
Computers can be on different LANs | All computers are on the same LAN |
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First. It is basically a routing protocol that is used to find the best path for packets that are being transmitted over interconnected networks.
Round Trip Time or Round Trip Delay Time refers to the time taken for a signal to be sent and the ACK of that signal to be received.
DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network management protocol. It is used on the UDP/IP networks and it automatically assigns IP addresses to the devices on the network. This, in turn, reduces the need of a network admin to manually assign IP addresses thereby reducing errors.
ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol and is a part of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is basically a supporting protocol to the Internet protocol and is used to send error messages and information regarding the success or failure of communication with another IP address. For example, if a service is not available an error is reported.
A ping is a computer program that is used to test the reachability of a host and check if can accept requests on an IP network. It works by sending an ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Echo to some computer on the network and waits for a reply from it. It can also be used for troubleshooting.
Optic fibers have a number of advantages such as:
A client/ server network is a network where one computer behaves as a server to the other computers. The server is usually more powerful than the clients and serves the clients.
 Q40. In a network that contains two servers and twenty workstations, where is the best place to install an Anti-virus program?
Q40. In a network that contains two servers and twenty workstations, where is the best place to install an Anti-virus program?The best solution is to install anti-virus on all the computers in the network. This will protect each device from the other in case some malicious user tries to insert a virus into the servers or legitimate users.
Ethernet is a network technology used in LAN, MAN and WAN that connects devices using cables for the transmission of data. It provides services on the Physical and Data Link layers of the OSI Model.
SLIP stands for Serial Line Internet Protocol which allows a user to access the internet using the modem.
| CSMA/ CD | CSMA/ CA |
The effect is after a collision | The effect is before a collision |
Minimizes the recovery time | Reduces the possibility of a collision |
Usually used in wired networks | Usually used in wireless networks |
Tunnel mode is used to encrypt the whole IP packet including the headers and the payload. It is basically used in a Site-to-Site VPN to secure communications between security gateways, firewalls, etc.
IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version 6 and is the latest version of the Intenet Protocol. The IP address length is 128 bits which resolves the issue of approaching shortage of network addresses.
RSA is a cryptosystem used to secure data transmission named after Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Len Adleman. This algorithm has a public key for encryption while the decryption key is kept secure or private. The encryption key is created using two large prime numbers and is published along with an auxiliary value. Anybody can make use of this public key for encryption but only someone with the knowledge of the prime numbers can decrypt it. However, this algorithm is considered to be slow and for the same reason, it is not used very often to encrypt data.
An encoder is a program, circuit or a device that converts data from one format to another. Encoders convert analog signals into digital ones.
A decoder is a program, circuit or a device that converts the encoded data into its actual format. Decoders convert digital signals to analog ones.
Sneakernet is the unofficial term for the transfer of electronic information by physically moving media which can be anything such as a Floppy disk, USB flash, optical disks, etc.
Protocols are a set of rules that govern communication. The key elements of a Protocol are as follows:
| Name | Description |
Syntax | Refers to the structure and format of data |
Semantics | Refers to the meaning of each portion of bits |
Timing | Refers to when data should be sent and received |
This brings us to the end of this article on Networking Interview Questions. I hope you are clear with all that has been shared with you. Make sure you practice as much as possible and revert your experience.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “Networking Interview Questions” blog and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
To get in-depth knowledge on any trending technologies along with its various applications, you can enroll for live Edureka Online training with 24/7 support and lifetime access.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
Very informative interview questions for network engineer.