Microsoft SQL Server Certification Training
- 6k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In the era of 2.5 Quintillion bytes of data being generated every day, data plays a crucial role in decision making for business operations. This quite quintessentially makes us handle data in databases and gives us the need to use database management systems. With various kinds of Database Management System(DBMS) present in the market today, the Relational Database Management System(RDBMS) is one of the most popular systems available. This type of DBMS, uses a structure that allows the users to identify and access data in relation to another piece of data in the database, and MySQL is one such popular RDBMS. Well, knowing MYSQL opens the doors for you to become a Database Administrator. I believe that you are already aware of these facts and this has made you land on this MySQL Interview Questions article.
In this article on MySQL Interview Questions, I will be discussing the top questions related to MySQL asked in your interviews. These questions are collected after consulting with people having excellent skills in this field. For your better understanding, I have divided the article into the following sections:

So, let’s get started guys.
| Mysql_connect | Used to open a new connection to a database. |
| You can open and close the database connection based on the request. | |
| Opens a page everytime the page is loaded. | |
| Mysql_connect vs Mysql_pconnect | |
| Mysql_pconnect | Used to open a persistent connection in a database. |
| You cannot close the database connection. | |
| There is no need to open and close a connection everytime a page is loaded. | |
MySQL Server’s default port is 3306. Apart from this, another standard default port for the SQL Server in TCP/IP is 1433.
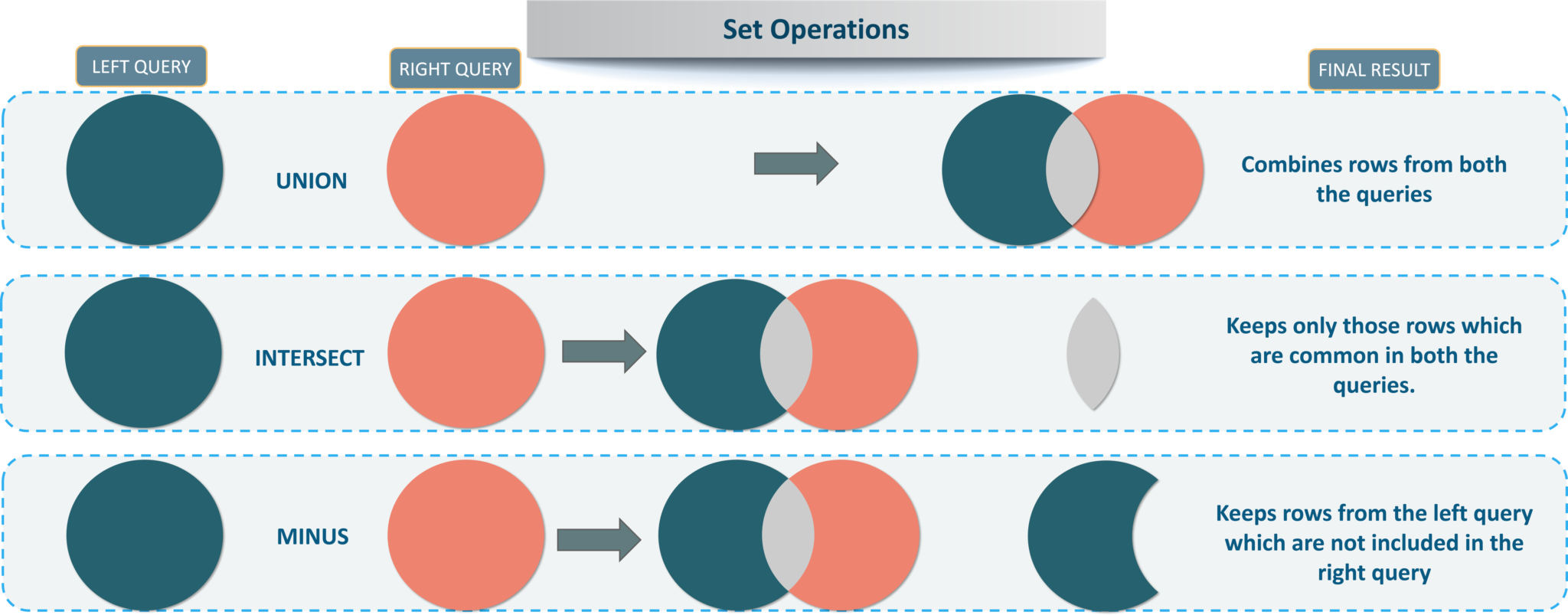
The various set operations available in MySQL are as follows:
Refer to the below image:
 Q4. Can you tell the order of SQL SELECT statement?
Q4. Can you tell the order of SQL SELECT statement?The order of SQL SELECT statement is as follows:
SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER BY.
The Database Whitebox Testing deals with the tables, data model, schema and referential integrity rules. It also deals with the triggers, logical views with database consistency and ACID properties.
Database Black Box Testing deals with data mapping, data storing and retrieving. The Database Black Box Testing is used for techniques such as Equivalence Partitioning and Boundary Value Analysis.
An expression which consists of a temporary set of results defined in a SQL statement is said to be a Common Table Expression(CTE).
There are mainly five types of tables present in MySQL. Out of all these database engines, the default database engine used in MySQL is MyISAM. Refer below to know the five types of tables:
Considered as a pointer to point to one row in a set of rows, a Cursor is nothing but a control which enables traversal over the records in the table. So, the cursor is used for performing traversing actions such as addition, retrieval, and removal of records in a database.
A NULL value is a field with no value present in that particular field. Since the NULL value cannot be compared to any other NULL values, you cannot use the comparison operators such as =, <, or <>. To compare the fields with NULL values, you have to use the IS NULL and IS NOT NULL operator.
Refer below for Syntax of IS NULL and IS NOT NULL.
SELECT column_names FROM table_name WHERE column_name IS NULL; SELECT column_names FROM table_name WHERE column_name IS NOT NULL;
BLOB(Binary Large Object) is used to hold a variable amount of data and holds up to 65,535 bytes of data. The following are the four types of BLOB.
TEXT is used to store string values and holds up to a maximum length of 65,535 characters. The following are the four types of TEXT
To display the maximum salary in SQL, you can use the inbuilt function called MAX().
The NVL function, IFNULL function, and the ISNULL function all of them are used to replace the NULL value with another value. The ORACLE users use the NVL function, MySQL users use the IFNULL function and the SQL servers use the ISNULL function
For example, let us say we have a column(column_3) which has NULL values.
So, if you run the below statement, the output you would get is a NULL value.
SELECT column_1 * (column_2 + column_3) FROM Example_Table
Now, to overcome this, you can use the above three functions as follows:
SELECT column_1 * (column_2 + NVL(column_3,0)) FROM Example_Table SELECT column_1 * (column_2 + IFNULL(column_3,0)) FROM Example_Table SELECT column_1 * (column_2 + ISNULL(column_3,0)) FROM Example_Table
| GUI Testing | Database Testing |
| Also known as User Interface Testing of Front-end Testing. | Also known as Back-End Testing or Data Testing. |
| Deals with items that interact with users. | Deals with items that are hidden from users. |
| Testers need not know SQL. | Testers need to know SQL. |
| GUI Testing focuses on the outlook of the application | Database Testing focuses on the integrity of data in the front end with the data present in the back end |
Consider the table named “Employee”.
Now, to find the Nth salary consider the below statement.
SELECT DISTINCT(salary) FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT n-1,1
So, if you want to find out the 7th largest salary, consider the below query.
SELECT DISTINCT(salary) FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 6,1
Now, let’s move on to the next set of questions, which is the PHP MySQL Interview Questions.
The command used to create a database using both PHP and MySQL is mysql_create_db(“Database Name”).
Both of them are similar but vary with a single difference. Mysql_fetch_object return as object and Mysql_fetch_array returns an array. This means that you cannot access the data by their offsets but can only access through its fields names.
The different ways in which you can retrieve data in the result set of MySQL using PHP are as follows:
MySQL’s Set function can take a maximum of 64 values, but can also consider 0 values.
The reason behind selecting Lamp stack is very simple. Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP are open source software. The security of the Linux operating system is much more than Windows. The Apache server is a better server than others in the perspective of functionalities and security. MySQL is one of the most popular open source databases is used with PHP to perform various functionalities.
You can simply declare the two dates, and then use the strtotime function to subtract both the dates and find the differences between the days in seconds.
Consider the below example.
date1 =’2018-09-15′;
date2 = ‘2018-10-15’;
days = (strtotime($date1) – strtotime($date2)) / (60 * 60 * 24);
You can use the mysql_num_rows function to find the number of rows in a resultset.
Consider the below example.
output = mysql_query(sql, database_name); number_of_rows = mysql_num_rows(output); echo "The number of forws found are equal to: $number_of_rows";
The function used to encrypt the data is AES_ENCRYPT() and the function used to decrypt the data is AES_DECRYPT().
You can encrypt the username and password using the following functions respectively:
SET USERNAME=USERNAME("Username");
SET PASSWORD=PASSWORD(”Password”);
The SELECT statement is used to select data from a database and the data returned is stored in a result table, called the result-set. The SELECT statement can be either individually used or can be used with other statements such as ORDER BY, GROUP BY, and HAVING clause.
To increase the performance of a MySQL SELECT query, you can use the LIMIT clause to limit MySQL from further search in a table, after collecting the required number of records. Apart from this, we can also use the LEFT JOIN or the RIGHT JOIN to retrieve data from two or more tables.
$message and $$message are both PHP variables. $message is used to store the variable data and $$message is used to store the variable of a variable. So basically, data is stored in $message and $$message is used to store the data that can be changed dynamically.
You can write a program to select the students details from the student table and use the loop to just print the name of students.
example_query = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM 'students' WHERE 'student_id' = '1';");
while(output = mysql_fetch_array(example_query))
{
echo output['Students_Name'];
}
MySQL comes with a utility mysqldump to provide the database backup and restore. The command you can use for backup and restore are as follows respectively.
//To take the backup of database mysqldump database > backup -file.sql; //To restore the database mysqldump database < backup -file.sql;
You can also use the phpMyAdmin user interface to backup your database. If you wish to backup, the database you just have to click on the “export” link on the phpMyAdmin main page.
ereg_replace and eregi_repalce() are regular expressions used to replace the matching characters. The only difference between these functions are eregi_replace() function ignores the case distinction when it matches alphabetic characters.
You can use the following three options:
Option 1: You can use the PHP Copy to move files from server to server. Refer to the syntax below:
/* Copy the file from source url to server */ $copy = copy( $remote_file_url, $local_file );
Option 2: You can use the PHP FTP to move files from server to server. Refer to the syntax below.
/* Download $remote_file and save to $local_file */ ftp_get($connect_it,$local_file,$remote_file,FTP_BINARY)
Option 3: You can use the ZIP and UNZIP Files option in PHP.
Now, let’s move on to the next set of questions, which is the Complex MySQL Interview Questions.
The best practices to be followed for SQL optimizations depend on the individual to individual, but the following list consists of the most popular practices that are advised to follow. Refer below.
The various options to create an index are as follows:
| Heap Table | Temporary Table |
| Heap Table exists in the memory | A temporary table is valid only during the session. |
| Heap Tables are shared among a various number of clients. | Temporary tables are not shared among the clients. |
| Temporary tables need a special privilege to create tables. | Heap Tables are storage engines which do not need special privileges. |
GUID columns affect the clustered index sorting performance as the nature of the random GUID value generated is larger than the integer data types.
CHARACTER columns affect the sorting performance of the character data types, larger-size values, non-increasing values, and non-static values which often tend to change. These values cannot be compared as binary values, as the characters comparison mechanism depends on the used collection.
–secure-file-priv option limits the MySQL Server from loading the directories using the LOAD DATA INFILE.
If you wish to see the directory that has been configured then you may use the SHOW VARIABLES LIKE “secure_file_priv”;
You have mainly two options to tackle:
| B-Tree | Hash Indexes |
| A B-Tree index can be used for column comparisons like =, >, <, >=, <= or BETWEEN operators. | A Hash-Index can be only used for equality comparisons that use =, >=, <=. |
| B-Tree can be used to search the next entry in the order. | Hash Index cannot be used to search for the next entry in the order. |
| Any leftmost prefix of the key can be used to find the rows. | Only whole keys are used to find a row. |
Each and every MyISAM Table is stored on disk in the following three files:
| MongoDB | MYSQL |
| An open source database that stores JSON like documents which vary in structure. | An open source relational database management system which stores relational data. |
| Each and every individual record are stored as documents. | Each and every individual record are stored as rows in a table. |
| Documents from a particular class or a group are stored in a collection. | A similar type of records are stored in a table. |
The answer is quite simple. You cannot use the WHERE clause to restrict the groups. Instead of this, you have to use the HAVING clause.
Your query should be as follows:
SELECT EmployeeID, AVG(Salary) FROM EmployeeDetails HAVING AVG(Salary) > 75 GROUP BY EmployeeID
Normalization is the process of organizing data to avoid duplication and redundancy. There are many successive levels of normalization. These are called normal forms. Each consecutive normal form depends on the previous one. The first three normal forms are usually adequate.
Now, let us move on to the next set of questions which is the Tricky MySQL Interview Questions.
Usage of index completely depends on if you consider the primary index or not. Consider you have a student table. Now, suppose if an Index is present on StudentID, StudentFirstName, and StudentLastName then you can consider a query as follows:
SELECT * FROM StudentDetails WHERE StudentID=3 and StudentFirstName='Jatin'
Now, if you consider that the above two columns in the query are the secondary index columns, then the index will not be invoked. Else, if the above two columns contain the first column while creating an index(i.e. the primary index), then the index will definitely be invoked.
In the above scenario, I have considered that StudentID and the StudentFirstName as primary columns, so an Index will be used in this case.
| StudentID | FirstName | MiddleName | LastName |
| 1 | Rohit | Kumar | NULL |
| 2 | Sakshi | Chowdhary | NULL |
| 3 | NULL | Yash | Singhania |
| 4 | Akash | NULL | Kumar |
| 5 | Avinash | NULL | Daksh |
You can use the COALESCE function to return the first non-null value from the table. Consider the below query.
SELECT StudentID, COALESCE(FirstName, MiddleName, LastName) as Name FROM StudentDetails;
The answer to this question is quite logical. If you have three tables with thousands of tuples in each of them, then you are first supposed to filter the rows in those tables and then transform the table. This would be beneficiary as if you transform the table, then the number of columns may increase reducing the performance. Due to such performance issues, a lot of memory will be used and the output will appear on your screen after quite a long wait of time.
To validate emails you can use the regular expressions function (REGEXP_LIKE). Consider the below query.
SELECT
Email
FROM
Employee
where NOT REGEXP_LIKE(Email, ‘[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+.[A-Z]{2,4}’, ‘i’);
To send an email from the database, you can use the stored procedures. Follow the below procedure to send the emails:
USE [YourDB] EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients = 'abc@example.com; def@example.com;xyz@example.com’ @body = ' Sample Body Text', @subject = 'Example Email' ; GO
To solve this problem statement you can use the JOINS concept. You simply have to perform a JOIN on the Department.Ssn and the DepartmentID in the other tables.
Now, if you are sure that the Ssn exists in all the three considered tables, then you can use the INNER JOIN. Also, if you are not sure that you have matching rows, then you can use the LEFT JOIN. Consider the below query.
SELECT d.Ssn, d.EmployeeName, c.desc ContactDetailsDesc, a.desc AddressDetailsDesc from Department d inner join EmployeeContactDetails c on d.id = c.DepartmentID inner join address a on d.id = a.DepartmentID where d.EmployeeName = 'abc' and c.ord = 1 and a.ord = 1
To check the procedures, you can consider the following query.
SELECT * FROM SampleSource WHERE Type=’PROCEDURE’ AND NAME IN (‘SP_CONNECTED_AGG’,’SP_UNCONNECTED_AGG’);
To find the procedures columns information, you can consider the following query.
SELECT OWNER, OBJECT_NAME, ARGUMENT_NAME, DATA_TYPE, IN_OUT from ALL_ARGUMENTS order by OWNER, OBJECT_NAME, SEQUENCE;
WHERE col * 4 < 16
WHERE col < 16 / 4
If we compare both the statements, then the second WHERE clause would be comparatively faster than the first one. That is because, for the first statement, MYSQL would retrieve the value of ‘col’ for each and every row, multiplied by four. After that, it would compare the result to 16. Also, in the first case no Index can be used, and hence it makes it further slow.
BETWEEN operator is used to display rows based on a range of values in a row whereas the IN condition operator is used to check for values contained in a specific set of values.
SELECT * FROM Students where ROLL_NO BETWEEN 10 AND 50;
SELECT * FROM students where ROLL_NO IN (8,15,25);
Q10. What are the different types of Collation Sensitivity?
Following are the different types of collation sensitivity:
So this brings us to the end of the MySQL Interview Questions blog. I hope this set of MySQL Interview Questions will help you ace your job interview. All the best for your interview!
Apart from this MySQL Interview Questions Blog, if you want to get trained from professionals on this technology, you can opt for a structured training from edureka! Click below to know more.
Check out this MySQL DBA Certification Training or SQL Training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. This course trains you on the core concepts & advanced tools and techniques to manage data and administer the MySQL Database. It includes hands-on learning on concepts like MySQL Workbench, MySQL Server, Data Modeling, MySQL Connector, Database Design, MySQL Command line, MySQL Functions etc. End of the training you will be able to create and administer your own MySQL Database and manage data.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “MySQL Interview Questions” and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co