Microsoft SQL Server Certification Training
- 6k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Schema-less databases are the latest buzzword in the IT world. Geek programmers seem to love the flexibility and low cost and these attributes have fired up many a start-up. NoSQL database is schema Agnostic: Information can be stored without doing any upfront schema designing. So with so much demand in the industry for NoSQL, let’s have a look at the Top Cassandra Interview Questions you must know if you are going to apply for a NoSQL Database Developer or a NoSQL Database Administrator. You can even check out the details of relational databases, functions, queries, variables, etc with the SQL Server Training.
As you can see the Salary trend for people having Cassandra Experience, it is quite high. So Let’s begin with the Cassandra Interview Questions
I’ve divided this blog of Cassandra Interview Questions in 3 Parts:
| Feature | Description |
| Schema Agnostic | Information can be stored without doing any upfront schema design |
| Auto-Sharding & Elastic | NoSQL allows the workload to automatically spread across any number of servers |
| Highly Distributable | A cluster of servers can be used to hold a single large database. |
| Easily Scalable | Allows easy scaling to adapt to the data volume and complexity of cloud applications |
| Integrated Caching | Cached data in system memory is transparent to the application developers & operations team. |
There are majorly 4 types of NoSQL Databases,
All of the data within database consists of an indexed key and a value. A key may correspond to one or multiple values (hash table). Provides a great performance and can be very easily scaled as per business needs.

The data record is the JSON/XML representation of key-value pairs. Every record can have a different set of fields.
Document DBs are similar to Key-value pairs, But the difference is that the key is associated with a document

Data is stored in cells are grouped in columns of data rather than as rows of data. Columns are logically grouped into column families.
One row may have one or multiple data records, which is indexed by a partition key.

The type of NoSQL database in which a flexible graphical representation is used. The key purpose is to store relationships between nodes.
Here, Nodes are Id 1, 2 and 3. Properties for Node 1 are Name and Age
Edges are : Id 100, 101, 102, 103, 104 and 105
Apache Cassandra is a free and open-source distributed NoSQL database management system designed to handle large amounts of data across many commodity servers, providing high availability with no single point of failure.

Apache Cassandra has a lot of features, some of them which make it stand out of crowd are:

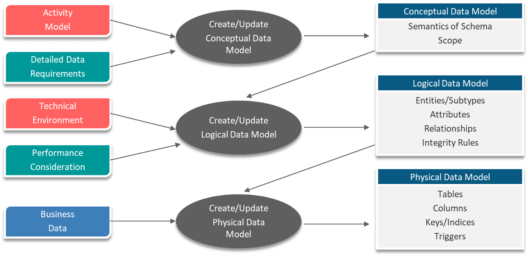
There are majorly 3 types/stages of Data Model

There are 4 main Cassandra Database Elements:

Cassandra-Cqlsh is a query language that enables users to communicate with its database. By using Cassandra cqlsh, you can do following things:
The cassandra.yaml file is the main configuration file for Cassandra. After changing properties in the cassandra.yaml file, you must restart the node for the changes to take effect.

The outermost structure in Cassandra is the cluster. A cluster is a container for Keyspaces
Sometimes called the ring, because Cassandra assigns data to nodes in the cluster by arranging them in a ring
A node holds a replica for a different range of data.
A keyspace is the outermost container for data in Cassandra. Like a relational database, a keyspace has a name and a set of attributes that define keyspace-wide behaviour. The keyspace is used to group Column families together.

CREATE KEYSPACE ABC
WITH replication = { ‘class ’: ‘SimpleStrategy’, ‘replication_factor’: ‘3’}
AND durable_writes = ‘TRUE’;

The parameters used while creating a keyspace are:
![]()
Durable Writes provides a means to instruct Cassandra whether to use commitlog for updates on the current KeySpace or not.
This option is not mandatory. The default value for durable writes is TRUE.
Cassandra stores copies (called replicas) of each row based on the row key. The replication factor refers to the number of nodes that will act as copies (replicas) of each row of data.

The replica placement strategy refers to how the replicas will be placed in the ring
There are different strategies that ship with Cassandra for determining which nodes will get copies of which keys
There are mainly two types of Strategies:

It uses Simple Single Datacenter Clusters. It places the first Replica on a node determined by the Partitioner. Additional Replicas are placed on the next nodes in clockwise (in a Ring) manner without considering Rack or Datacenter location.

This is used when we deploy a cluster across Multiple Datacenters. It is the primary consideration to insert replicas. Can satisfy reads, locally without incurring cross Data-Center Latency and also Handle Failure Scenarios.

A column family is a container for an ordered collection of rows, each of which is itself an ordered collection of columns. We can freely add any column to any column family at any time, depending on your needs. The comparator value indicates how columns will be sorted when they are returned to you in a query.

A row is a collection of sorted columns. It is the smallest unit that stores related data in Cassandra. Any component of a Row can store data or metadata
The different elements/parts of a row are the

The Primary Key is a column that is used to uniquely identify a row

There are 3 types of Primary Keys:
These were some Beginner Level Cassandra Interview Questions, you must know about.
So, let’s move ahead with some Advance Cassandra Interview Questions
The column is also called partitioning key. Data is partitioned on the basis of that column. Data is spread on different nodes on the basis of the partition key.


race_name is the partitioning key and race_position is the Clustering key. Data will be partitioned on the basis of race_name and data will be clustered on the basis of race_position. Clustering is the process that sorts data in the partition. Retrieval of rows is very efficient when rows for a partition key are stored in order, based on the clustering column.

race_year and race_name are the composite partition key and data will be partitioned on the basis of both columns. Data will be clustered on the basis of the rank. It is used when too much data is present on the single partition.
Gossip Protocol in Cassandra is a peer-to-peer communication protocol in which nodes can choose among themselves with whom they want to exchange their state information. The nodes exchange information about themselves and about the other nodes that they have gossiped about, so all nodes quickly learn about all other nodes in the cluster.

The process of Acknowledging messages helps in failure detection. When a node is down/failing it is unable to send or receive messages and hence the Acknowledgements are not received.



64-bit hash value partition key with Range: 263 to 263-1
It uses MD5 hash values with Range: 0 to 2127-1
A snitch determines which datacenters and racks, nodes belong to. They inform Cassandra about the network topology and allows Cassandra to distribute replicas specifically, the Replication strategy places the replicas based on the information provided by the new snitch.
There are many types of snitches, to name a few:
When write request comes to the node:

All writes are automatically partitioned and replicated throughout the cluster Cassandra periodically consolidates the SSTables, discarding unnecessary data.
Read Operation is easy because clients can connect to any node in the cluster to perform reads. If a client connects to a node that doesn’t have the data it’s trying to read, the node it’s connected to will act as the coordinator node.



It is the process of freeing up space by merging largely accumulated datafiles. It improves performance by reducing the number of required seeks.
Anti-entropy is the replica synchronization mechanism, ensuring that data on different nodes is updated to the newest version
Cassandra uses Merkle tree for anti-entropy repair. A Merkel Tree is a hash tree where leaves are hashes of the values of individual keys.
Anti-entropy repair is very useful and is often recommended to run periodically to keep data in sync.
Hinted Handoff is a mechanism to ensure availability, fault-tolerance and graceful degradation in Cassandra. The node that receives the hint will know when the unavailable node comes back online again, because of Gossip.
Logs are written to the system.log and debug.log file in the Cassandra logging directory
We can configure logging programmatically or manually. The simplest way to get a picture of what’s happening in your database is to just change the logging level to make the output more verbose, by default it is set at INFO.
JMX (Java Management Extension) is a Java technology that supplies tools for managing and monitoring Java applications and services. Cassandra makes use of JMX to enable remote management of the servers.

Snapshot represents the state of the data files at a particular point in time. Snapshot command is used while taking a backup and creates hard links for SSTables in the snapshots folder which can later be used to restore the node,

JConsole is used to Monitor and perform analysis on the Server activities. Once you’ve connected to a server, the default view includes four major categories about your server’s state, which are updated constantly:

The Nodetool Utility is a command-line utility that comes out of the box with Cassandra and is a great tool for administration and monitoring. It communicates with JMX to perform operational and monitoring tasks exposed by MBeans.
Roles enable authorization management on a larger scale than security per user can provide. A role is created and may be granted to other roles. Hierarchical sets of permissions can be created with the help of it.
Cassandra comes with a popular utility called py_stress that can be used to run a stress test on Cassandra cluster. The Cassandra-stress tool is a Java-based stress testing utility for basic benchmarking and load testing a Cassandra cluster. This is an effective tool for populating a cluster and stress testing CQL tables and queries.
So, I hope these Cassandra Interview Questions helped you to brush up your knowledge of Apache Cassandra.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you at the earliest.
If you wish to build a career in the domain of Cassandra and gain expertise in NoSQL Databases, get enrolled in live-online Edureka Apache Cassandra Certification Training here, that comes with 24*7 support to guide you throughout your learning period.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co