Blockchain Developer Certification Course
- 25k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend
- Self Paced
In the fourth blog of the series (Ethereum – Smart Contract Interaction using Web3), we looked into how web3 can be used to interact with a smart contract deployed the local Ethereum blockchain (Ganache). We were introduced to the key elements that are required to get started with programming. We looked at how all the interactions can be divided into two categories.
Today, we are going to talk about how can we deploy a smart contract using web3js. We are going to build on top of the knowledge, from the previous blogs. So let us get started.
At the end fo this blog, we will be able to clearly define the following.
We are going to need the following prerequisites installed, you must have already available on your system as they were required for hands-on in previous blogs. In case you do not have the prerequisite installed. Please install the following.
We have installed the prerequisites. Now we are going to set up the project in Visual Studio Code.
npm init
npm install web3 --save npm install ethereumjs-tx --save
Now, we are going to add the relevant code. Let us get started.
const Web3 = require('web3');
const EthereumTx = require('ethereumjs-tx').Transaction;
const rpcURL = 'http://127.0.0.1:7545'; const web3 = new Web3(rpcURL);

let abi = '[{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"value","type":"uint256"}],"name":"update_quantity","outputs":[],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"get_quantity","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"inputs":[],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"constructor"}]'
let bytecode = '608060405234801561001057600080fd5b50606460008190555060ca806100276000396000f3fe6080604052348015600f57600080fd5b506004361060325760003560e01c806380219655146037578063ed0109a5146062575b600080fd5b606060048036036020811015604b57600080fd5b8101908080359060200190929190505050607e565b005b6068608c565b6040518082815260200191505060405180910390f35b806000540160008190555050565b6000805490509056fea265627a7a7230582002f975dfd70c1b1f649671805826a83fc9b92457fe7dd245527f56b7776d043464736f6c634300050a0032';
// Contact ABI let deploy_contract = new web3.eth.Contract(JSON.parse(abi));
// address from Ganache let account = '0xd935580Ce80986aD46D31e2dA55564Eb93A09318';
let payload = {
data: bytecode
}
let parameter = {
from: account,
gas: web3.utils.toHex(800000),
gasPrice: web3.utils.toHex(web3.utils.toWei('30', 'gwei'))
}deploy_contract.deploy(payload).send(parameter, (err, transactionHash) => {
console.log('Transaction Hash :', transactionHash);
}).on('confirmation', () => {}).then((newContractInstance) => {
console.log('Deployed Contract Address : ', newContractInstance.options.address);
})
Find out our Blockchain Training in Top Cities/Countries
| India | Other Cities/Countries |
| Bangalore | New York |
| Hyderabad | UK |
| Kerala | USA |
| Chennai | Canada |
| Mumbai | Australia |
| Pune | Singapore |
// Library Imports
const Web3 = require('web3');
const EthereumTx = require('ethereumjs-tx').Transaction;
// Connection Initialization
const rpcURL = "http://127.0.0.1:7545";
const web3 = new Web3(rpcURL);
// Data set up
let abi = '[{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"value","type":"uint256"}],"name":"update_quantity","outputs":[],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"get_quantity","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"inputs":[],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"constructor"}]'
let bytecode = '608060405234801561001057600080fd5b50606460008190555060ca806100276000396000f3fe6080604052348015600f57600080fd5b506004361060325760003560e01c806380219655146037578063ed0109a5146062575b600080fd5b606060048036036020811015604b57600080fd5b8101908080359060200190929190505050607e565b005b6068608c565b6040518082815260200191505060405180910390f35b806000540160008190555050565b6000805490509056fea265627a7a7230582002f975dfd70c1b1f649671805826a83fc9b92457fe7dd245527f56b7776d043464736f6c634300050a0032';
//Contract object and account info
let deploy_contract = new web3.eth.Contract(JSON.parse(abi));
let account = '0xd935580Ce80986aD46D31e2dA55564Eb93A09318';
// Function Parameter
let payload = {
data: bytecode
}
let parameter = {
from: account,
gas: web3.utils.toHex(800000),
gasPrice: web3.utils.toHex(web3.utils.toWei('30', 'gwei'))
}
// Function Call
deploy_contract.deploy(payload).send(parameter, (err, transactionHash) => {
console.log('Transaction Hash :', transactionHash);
}).on('confirmation', () => {}).then((newContractInstance) => {
console.log('Deployed Contract Address : ', newContractInstance.options.address);
})node server.js
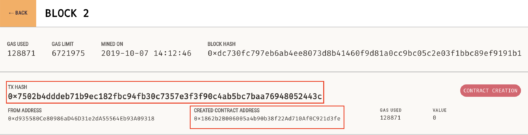
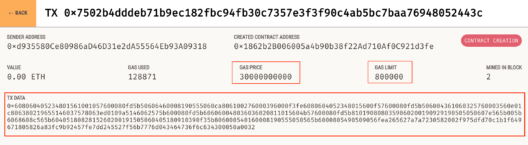
As has been mentioned, the key take away of this blog has been the complete hand-on for deploying a smart contract. Subsequently looking at what are the building block of information to achieve the deployment. To conclude we have just scratched the surface with Web3 in this blog series. Next, we are going to look at few more components of the Ethereum ecosystem in the next blog. In case, you are looking to explore web3 further do check out the documentation of web3.js. Stay tuned for more.
If you wish to learn Ethereum and build a career in Blockchain Technologies, then check out our Blockchain online course which comes with instructor-led live training and real-life project experience. This training will help you understand What is Ethereum Blockchain in depth and help you achieve mastery over the subject.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “Smart Contract Deployment using Web3” blog and we will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co