PySpark Certification Training Course
- 12k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Apache Drill is the industry’s first schema-free SQL Engine. Drill isn’t the world’s first query engine, but it’s the first that strikes the fine balance between flexibility and speed. Drill is designed to scale to several thousands of nodes and query petabytes of data at interactive speeds that BI/Analytics environments require.
It can integrate with several data sources like Hive, HBase, MongoDB, file system, RDBMS. Also, input formats like Avro, CSV, TSV, PSV, Parquet, Hadoop Sequence files, and many others can be used in Drill with ease.
The biggest advantage of Apache Drill is that it can discover the schema on the fly as you query any data. Moreover, it can work with your BI tools like Tableau, Qlikview, MicroStrategy etc for better analytics.
Here’s a quote from an industry analyst that summarizes the value of Apache Drill:
“Drill isn’t just about SQL-on-Hadoop. It’s about SQL-on-pretty-much-anything, immediately, and without formality.”
– Andrew Burst, Gigaom Research, January 2015
Drillbit is Apache Drill’s daemon that runs on each node in the cluster. It uses ZooKeeper for all the communication in the cluster and maintaisn cluster membership. It is responsible for accepting requests from the client, processing the queries, and returning results to the client. The drillbit which receives the request from the client is called ‘foreman’. It generates the execution plan, the execution fragments are sent to other drillbits running in the cluster.
One more advantage is that the installation and setup of drill is pretty simple. Let us learn how to install Apache Drill.
The first step is to download the drill package.
Command: wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/drill/drill-1.5.0/apache-drill-1.5.0.tar.gz
Command: tar -xvf apache-drill-1.5.0.tar.gz
Command: ls
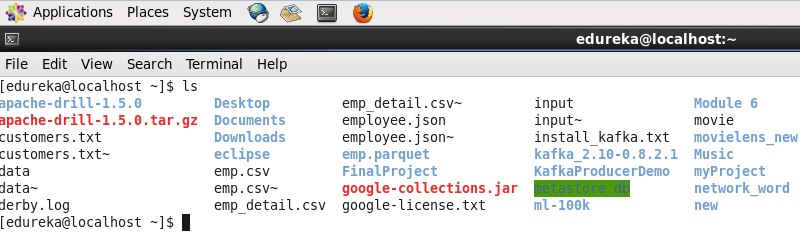
Next, set the environment variables in .bashrc file.
Command: sudo gedit .bashrc
export DRILL_HOME=/home/edureka/apache-drill-1.5.0
export PATH=$PATH:/home/edureka/apache-drill-1.5.0/bin
This command will update the changes:
Command: source .bashrc
Now go to drill conf directory and edit drill-override.conf file with cluster id and zookeeper host & port, we will run it on a local cluster.
Command: cd apache-drill-1.5.0
Command: sudo gedit conf/drill-override.conf

By default, DRILL_MAX_DIRECT_MEMORY will be 8 GB in drill-env.sh, and we need to keep it according to the memory we have.
Command: sudo gedit conf/drill-env.sh

To install drill only in a single node, you can use embedded mode, where it will run locally. It will automatically start the drillbit service when you run this command.
Command: ./bin/drill-embedded
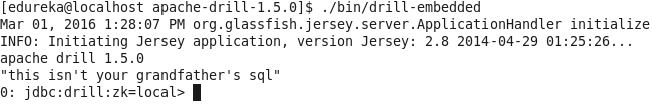
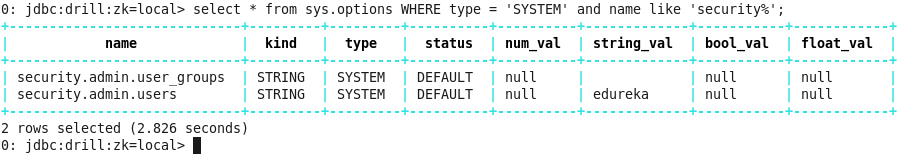
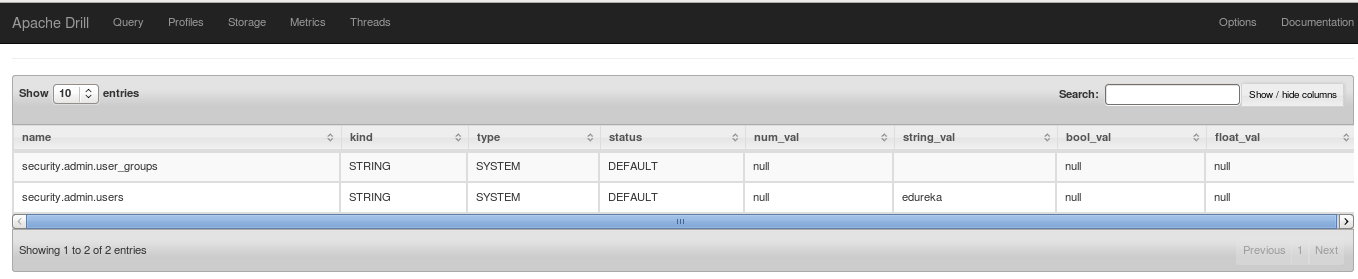
You can run a simple query to check the installation.
Command: select * from sys.options WHERE type = ‘SYSTEM’ and name like ‘security%’;
To check the web console of Apache Drill, we need to go to localhost:8047 in the web browser.
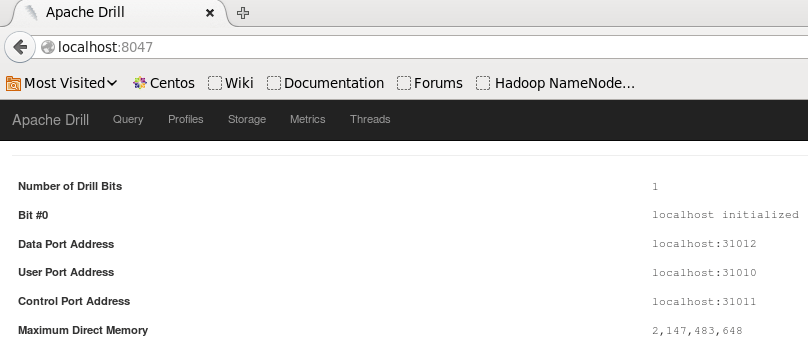
You can run your query from the Query tab as well.
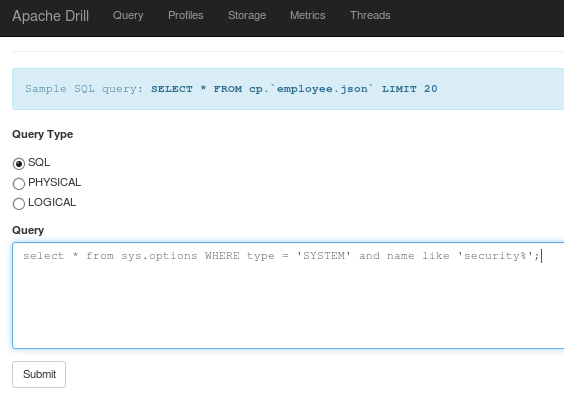
To run drill in distributed mode, you need to edit cluster ID and add ZooKeeper information in drill-override.conf as below.
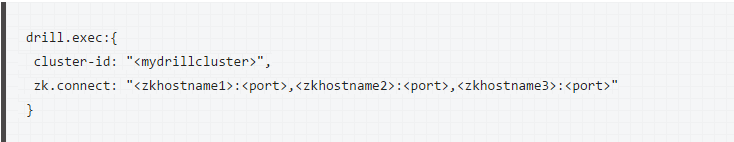
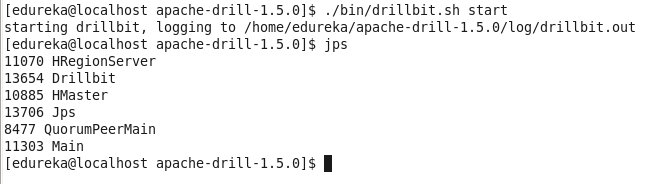
Then we need to start ZooKeeper service on each node. After that you have to start the drillbit service on each node with this command.
Command: ./bin/drillbit.sh start
Command: jps
Now, we use below command to start the drill shell.

Now, we can execute our queries on the cluster in the distributed mode.
This is the first blog post in a two-part Apache Drill blog series. The second blog in the series is coming soon.
Got a question for us? Mention them in the comment section and we will get back to you.
Related Posts:
Get Started with Apache Spark and Scala
Get Started with Big Data and Hadoop
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co