DevOps Certification Training Course with Gen ...
- 193k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend
- Live Class
In this blog, we will be discussing various Docker commands that you will frequently use while working with Docker. Specifically, we will cover Docker Image Commands, Docker Container Commands, using the Docker command line, environment variables, and customizing the default output format for Docker commands. The trend of Docker container has been growing uncontainably with organizations actively looking for professionals possessing Docker Certification Training and a sound knowledge of these Docker commands will give you the needed expertise.
In my previous blogs, I have covered What is Docker, and how you can use it. Today, in this blog, I will talk about the Top 15 Docker Commands that you will be using frequently while you are working with Docker. The trend of Docker container has been growing uncontainably with organizations actively looking for professionals possessing Docker Certification Training and a sound knowledge of these Docker commands will give you the needed expertise.
Following are the commands which are being covered:
1. docker –version
This command is used to get the currently installed version of docker
2. docker pull
Usage: docker pull <image name>
This command is used to pull images from the docker repository(hub.docker.com)
Usage: docker run -it -d <image name>
This command is used to create a container from an image
This command is used to list the running containers
This command is used to show all the running and exited containers
Usage: docker exec -it <container id> bash
This command is used to access the running container
7. docker stop
Usage: docker stop <container id>
This command stops a running container
Usage: docker kill <container id>
This command kills the container by stopping its execution immediately. The difference between ‘docker kill’ and ‘docker stop’ is that ‘docker stop’ gives the container time to shutdown gracefully, in situations when it is taking too much time for getting the container to stop, one can opt to kill it
Usage: docker commit <conatainer id> <username/imagename>
This command creates a new image of an edited container on the local system
This command is used to login to the docker hub repository
Usage: docker push <username/image name>
This command is used to push an image to the docker hub repository
This command lists all the locally stored docker images
Usage: docker rm <container id>
This command is used to delete a stopped container
Usage: docker rmi <image-id>
This command is used to delete an image from local storage
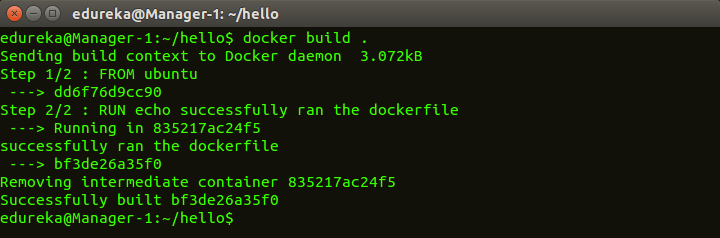
Usage: docker build <path to docker file>
This command is used to build an image from a specified docker file
Docker copy
Usage: COPY <source_file> <destination_directory>
This command copies files or directories from the host machine’s file system to the container’s file system during Docker image construction.
Usage: docker history <image_name>
Using this command, you may examine the evolution of a Docker image or its constituent parts.
Usage: docker logout [REGISTRY_URL]
This command is used to log out or remove the credentials used to authenticate with a Docker registry.
Usage: docker logout [REGISTRY_URL]
This command is used to log out of a Docker registry or to delete the credentials used to login with it.
Usage: docker network create <network_name>
This command manages Docker networks. Docker networks enable containers to connect securely and isolatedly with one another and with external network resources.
Usage: docker restart [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER…]
This command is used to restart one or more Docker containers that are currently operating. Restarting a container entails gently pausing it and then restarting it with the same configuration and parameters.
Usage: docker search [OPTIONS] TERM
This command searches for Docker images on Docker Hub, a public registry for Docker images.
Usage: docker volume create my_volume
This command creates a new Docker volume named “my_volume” in the Docker container. Volumes in Docker are generated independently of containers.
Want to learn more about docker commands? Here is a Docker Tutorial to get you started. Alternatively, you can take a top down approach and start with this Devops Tutorial.
Now that you have understood what is DevOps, check out our DevOps Certification Training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. The Edureka DevOps Certification Training course helps learners gain expertise in various DevOps processes and tools such as Puppet, Jenkins, Nagios, Ansible, Chef, Saltstack and GIT for automating multiple steps in SDLC.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co
I’m a docker newbie. This article was very useful. Thanks!