Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
At an entry-level, one of the most frequently asked interview questions is about Java HashMap vs Hashtable. So you must be fully prepared to answer anything related to HashMap or Hashtable. Java makes use of HashMap and Hashtable to store data in the form of key and values. So, this article will help you know the major differences between these two.
I’ll be discussing the topics in the following order:
Let’s begin!
HashMap is a Map-based collection class in Java which is used to store data in Key and Value pairs. It helps in implementing the Map interface in Java. It is basically a part of Java’s collection since Java version 1.2 and provides the basic implementation of the Map interface in Java. To access a value within the HashMap, one must know its Key.
It is termed as HashMap because it uses a technique called Hashing. Hashing is a process of converting a large String to a smaller one by keeping the value of the String as constant. The resulting compressed value helps in indexing and faster searches.
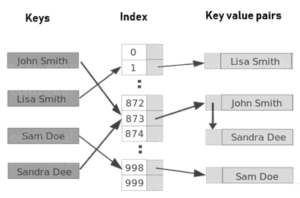
A Hashtable is a data structure that is used to store keys/ value pairs. In a Hashtable, data is stored in an array format, where each data value has its own unique index value. You can access data really fast if you know the index of the desired data.
Java Hashtable class implements a hashtable, that maps keys to values. It inherits the Dictionary class and implements the Map interface.
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
K: It is the type of keys that by the map.
V: This is the type of mapped values.
Now that you guys have understood how HashMap and Hashtable in Java works, let’s take a look at the parameters to understand the differences between HashMap and Hashtable.
Now let’s point out the major differences between HashMap and Hashtable.
| Parameters | HashMap | Hashtable |
Synchronization | Non-synchronized meaning that it is not thread-safe and cannot be shared between many threads without a proper synchronization code. | Synchronized and can be shared with many threads |
Null keys | Allows only one null key and multiple null values | Does not allow null key or its value |
Legacy System | This is a part of Java Collections | Hashtable is a legacy class was not part of the initial Java Collections |
Iterator | Iterator is fail-fast and it throws a concurrentModificationException if any other thread tries to modify the map | The enumerator is not fail-fast |
Inheriting class | Inherits AbstractMap class | Inherits Dictionary class |
Now, when can you use Java HashMap and Hashtable?
This brings us to the end of this article where we have learned the differences between Java HashMap and Hashtable. Hope you guys are clear with this topic.
If you found this article on “Java HashMap vs Hashtable” relevant, check out the Edureka Java Certification Training, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe.
The course is designed to give you a head start into Java programming and train you for both core and advanced Java concepts along with various Java frameworks like Hibernate & Spring.
If you come across any questions, feel free to ask all your questions in the comments section of “Java HashMap vs Hashtable” and our team will be glad to answer.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co