Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Java multithreading programs witness the use of extensive Java Callable and Future. Under the prerequisite knowledge of threads and multi-threading, readers will be better able to grasp the discussion in this article. As I will be explaining Callable Interface in Java in this article.
However, let me just give a brief introduction to the concept of threads. A thread is a separate path of execution, in case you need to carry out a repetitive task, the work can be broken into multiple tasks and assign them to threads. Multi-threading is nothing but assigning multiple threads to execute different tasks in parallel to get the result quickly.
For Java 5, the class “java.util.concurrent” was introduced. This callable interface was brought in via the concurrency package that looked similar to the Runnable interface. It also can return any object and is able to throw an Exception. A Java Callable interface uses Generics, thus making it possible to return any type of object. The Executor Framework gives a submit () method to execute Callable implementations in a pool of threads. In reality, the Java Executor Framework adhers to the WorkerThread patterns.

Java Callable returns java.util.concurrent. Java Future offers a cancel () method to eliminate the associated Callable task. This is an overloaded version of the get () method, where one can specify a certain time to wait for the result. It is useful to avoid a current thread, which may be blocked for a longer period. Please remember that the get method is a synchronous method and until the callable finishes its task and returns a value, it will have to wait for a callable.
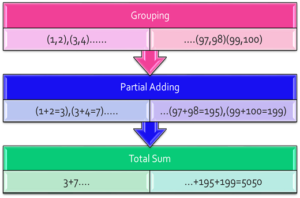
There are also “isDone()” and “isCancelled()” methods to fetch the current status of an associated Callable task. Consider the example where a sum of all numbers from one to 100 needs to be found. We can loop 1 to 100 sequentially and adding them finally. Another possibility is by dividing and conquering. In this method, we can group the numbers in a way such that each group has exactly two elements. Finally, we can assign that group to a pool of threads. Therefore, each thread returns a partial sum in parallel and then collects those partial sums and add them to get the whole sum.
Callable class is a SAM type interface and hence it can be implemented in the lambda expression.
The callable class has just one method “call ()” that holds all the code needed to execute asynchronously.
In a runnable interface environment, there was no possibility to return the result of the computation or throw checked exception. Whereas with Callable returning a value and throwing a checked exception is available.
Get () method of Future class can be used to retrieve results once the computation is done. Users can also check if computation is finished or not by using done () method.
Canceling the computation by using future.cancel () method is also a boon in some applications.
Get () is called a blocking call and it continues to block until the computation is completed.
| Callable | Runnable |
| It is part of the “java.util.concurrent” package since Java 1.5 | It is part of the java.lang package since Java 1.0 |
| A parameterized interface, such as Callable<V> | A non-parameterized interface |
| Capable of throwing a checked Exception | It cannot throw a checked exception |
| It contains a single method, call (), that returns Type V, this is same as the defined interface parameter “Type” | Here, it contains a single method, called run (), that returns void |
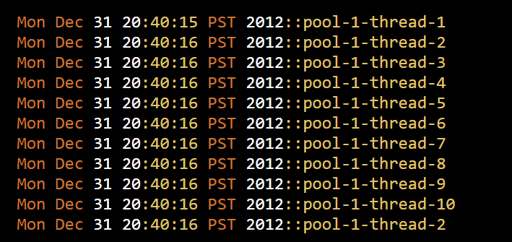
Below is a simple example of a Java callable class implemented where the code returns the name of the specific thread, which is executing the task after one second. Here we utilize the extractor framework to execute 100 tasks in parallel with Java Future to the result of the submitted tasks. The first snippet is the output and the below represents the code.
package com.journaldev.threads;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
//return the thread name executing this callable task
return Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
//Get ExecutorService from Executors utility class, thread pool size is 10
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//create a list to hold the Future object associated with Callable
List<Future<String>> list = new ArrayList<Future<String>>();
//Create MyCallable instance
Callable<String> callable = new MyCallable();
for(int i=0; i< 100; i++){
//submit Callable tasks to be executed by thread pool
Future<String> future = executor.submit(callable);
//add Future to the list, we can get return value using Future
list.add(future);
}
for(Future<String> fut : list){
try {
//print the return value of Future, notice the output delay in console
// because Future.get() waits for task to get completed
System.out.println(new Date()+ "::"+fut.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//shut down the executor service now
executor.shutdown();
}
}
The crucial and important aspect that many developers miss is shutting down the ExecutorService. The ExecutorService is vital and is created with additional thread elements. Keep in mind that the JVM stops only when all non-daemon threads are stopped. Thus simply shutting down the executor service prevents the JVM from stopping.
In order to tell the executor service that there is no need for the threads to be run, we should shut down the service.
There are three ways to invoke shutdown:
With this, we come to the end of Callable Interface in Java article. I hope you got an understanding of Future and Callable Interface in Java.
Check out the Java Online Training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. Edureka’s Java J2EE and SOA training and certification course is designed for students and professionals who want to be a Java Developer.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “Callable Interface in Java” blog and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co