Selenium Course
- 64k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
It is impossible to build a web application which is 100% bug-free. You can minimize the error, flaw, failure or fault in a computer program or system that causes it to produce an incorrect or unexpected result. This article will provide you in-depth knowledge regarding the bugs in software testing in the following sequence:
In the present world, with technology making bigger strides in every walk of like, software development needs to be precise, quick and deliver with optimum quality. A thing that is deal-breaker in the software world is a “bug” in the software being released.
A “Bug” is a most unwelcomed word in the software development process. A bug indicates a fault, error or failure in the software/system being built that produces unexpected results. A bug identified needs to be tracked and fixed to ensure optimum quality in the software/system being developed.
The journey of any error in the code to being recognized as a Bug is explained below

A bug is actually an error which would have been introduced in the due course of the software development life cycle. The most common sources of Bugs are detailed below
Every bug not only breaks the functionality it occurs in but also has probabilities of causing a ripple effect in other areas of the application. This ripple effect needs to be evaluated when fixing any bug. Lack of foresight in anticipating such issues can cause serious problems and an increase in bug count.
The impact of the Bug is measured based on Severity and Priority. Impact to business is measured in terms of Severity, whereas impact to business execution is measure in terms of Priority.
The table below is a standard definition used across the software industry for the Severities.
| Severity | Definition |
| Critical | A critical defect would create a major disruption to the business operation. A severe application problem causing considerable downtime, financial penalty or loss of integrity with customers. |
| High | A major defect would result in loss of business functionality and would require a workaround in production. |
| Medium | A defect which would have a medium impact on business functions, but could be immediately managed or worked around. |
| Low | A cosmetic only defect which would have no business or user impact |
Priority determines the impact of business execution, and subsequently, how quickly the defect needs to be fixed to ensure the project plan is on track.
The table below is a standard definition used across the software industry for the Priorities
Every reported bug follows a lifecycle till closure. A bug life cycle illustrates the journey of a bug from the time it is created to the time it is fixed and closed. A generic bug lifecycle is explained below:
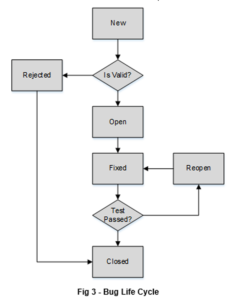
The description for each status in the lifecycle mentioned above are mentioned below
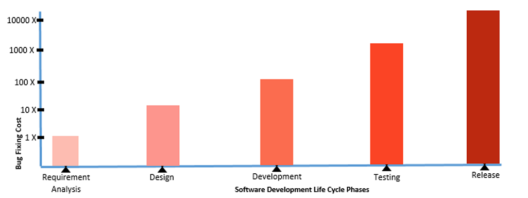
There is no set cost one can ascribe to a software bug. However, the cost of a bug goes up based on how far down the Software Development Life Cycle the bug is found. Any bug found in production the code needs to go back to the beginning of the SDLC where the development cycle can restart.
The figure below illustrates the cost of fixing a bug depending on the SDLC phase it is identified:
With this, we have come to the end of our Bug in Software Testing article. I hope you understood what are bugs, its source, and impact.
Now that you have understood bugs in SoftwareTtesting, check out the Software Testing Fundamentals Course by Edureka. This course is designed to introduce you to the complete software testing life-cycle. You will be learning different levels of testing, test environment setup, test case design technique, test data creation, test execution, bug reporting, CI/CD pipeline in DevOps, and other essential concepts of software testing.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of “Bugs in Software Testing” and we will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co