Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
A queue is an important aspect of any Programming language. Especially if we talk about Java. In this article, we will discuss the BlockingQueue Interface in Java in the following order:
A BlockingQueue Interface in Java is a queue that blocks when you try to dequeue from it and the queue is empty, or if you try to enqueue items to it and the queue is already full. A thread trying to dequeue from an empty queue is blocked until some other thread inserts an item into the queue. A thread trying to enqueue an item in a full queue is blocked until some other thread makes space in the queue, either by dequeuing one or more items or clearing the queue completely.
BlockingQueue Interface in Java doesn’t accept null values and throw NullPointerException if you try to store the null value in the queue. Java BlockingQueue implementations are thread-safe. All queuing methods are atomic in nature and use internal locks or other forms of concurrency control.
Java Queue Class Diagram
Java Queue interface extends the Collection interface. The Collection interface extends the Iterable interface. Some of the frequently used Queue implementation classes are LinkedList, PriorityQueue, ArrayBlockingQueue, DelayQueue, LinkedBlockingQueue, PriorityBlockingQueue, etc.. AbstractQueue provides a skeletal implementation of the Queue interface to reduce the effort in implementing Queue.
Stay up-to-date with the latest Flutter features and best practices through our Flutter Course.
The BlockingQueue are two types:
Syntax:BlockingQueue blocking queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque();
// Creates a Blocking Queue with capacity 5BlockingQueue blocking queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque(5);
Methods in BlockingQueue Interface
package com.journaldev.concurrency;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class ProducerConsumerService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating BlockingQueue of size 10
BlockingQueue<Message> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
Producer producer = new Producer(queue);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(queue);
//starting producer to produce messages in queue
new Thread(producer).start();
//starting consumer to consume messages from queue
new Thread(consumer).start();
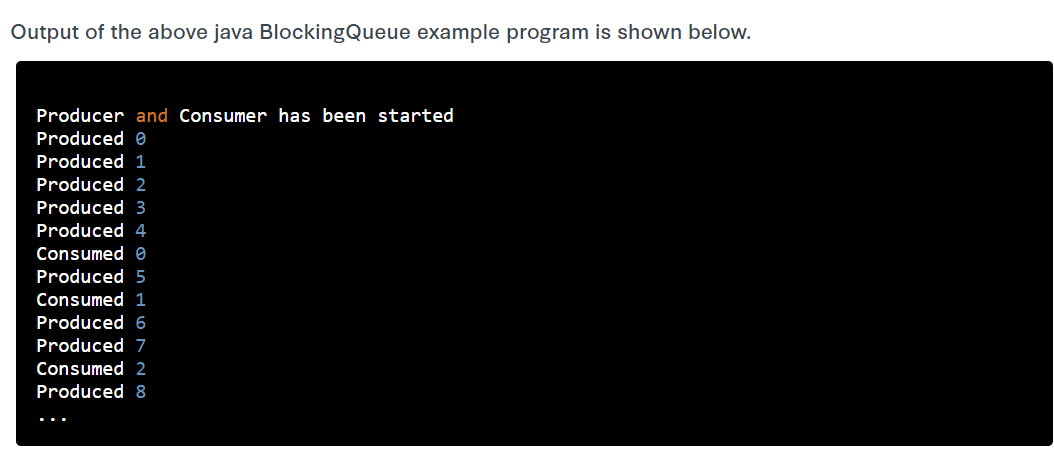
System.out.println("Producer and Consumer has been started");
}
}
With this, we come to an end of the BlockingQueue Interface in Java article. I hope all your concepts are now clear.
Check out the Java training by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe. Edureka’s Java J2EE and SOA training and certification course are designed for students and professionals who want to be a Java Developer. The course is designed to give you a head start into Java programming and train you for both core and advanced Java concepts along with various Java frameworks like Hibernate & Spring.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this “BlockingQueue Interface in Java” blog and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co