Blockchain Developer Certification Course
- 25k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Self Paced
Bitcoin Blockchain is undoubtedly the buzz in the industry today. Through this blog, I will try my best to introduce you to the concepts of the cryptocurrency Bitcoin and how it created this revolutionary technology we call Blockchain. Before moving ahead, do go through our short animated video on What is Blockchain & Bitcoin.
This question often causes confusion. Here’s a quick explanation to clear your muddled head!
The following will be the storyline for our Bitcoin Blockchain blog:

Before we proceed let me brief on the history of transacting money.
When it comes to transacting money or anything of value, people have been relying on banks and other trusted third parties like banks and governments to ensure trust and certainty.
Now, these trusted parties play an important role in a facilitating digital transaction. This creates what’s known as the double spending problem.
But what if there is a way to disintermediate the flow of digital assets. Well, a technology exists today that makes this possible. 
In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto devised a peer to peer electronic cash system called Bitcoin that enabled online payments to be transferred directly, without an intermediary.
Blockchain is the underlying technology of bitcoins that overcomes all the issues of traditional banking. Let us look at these in detail.
Every single person on the network has a copy of the ledger. There is no single centralized original copy. Ledger here means the copy of all the transactions that ever happened.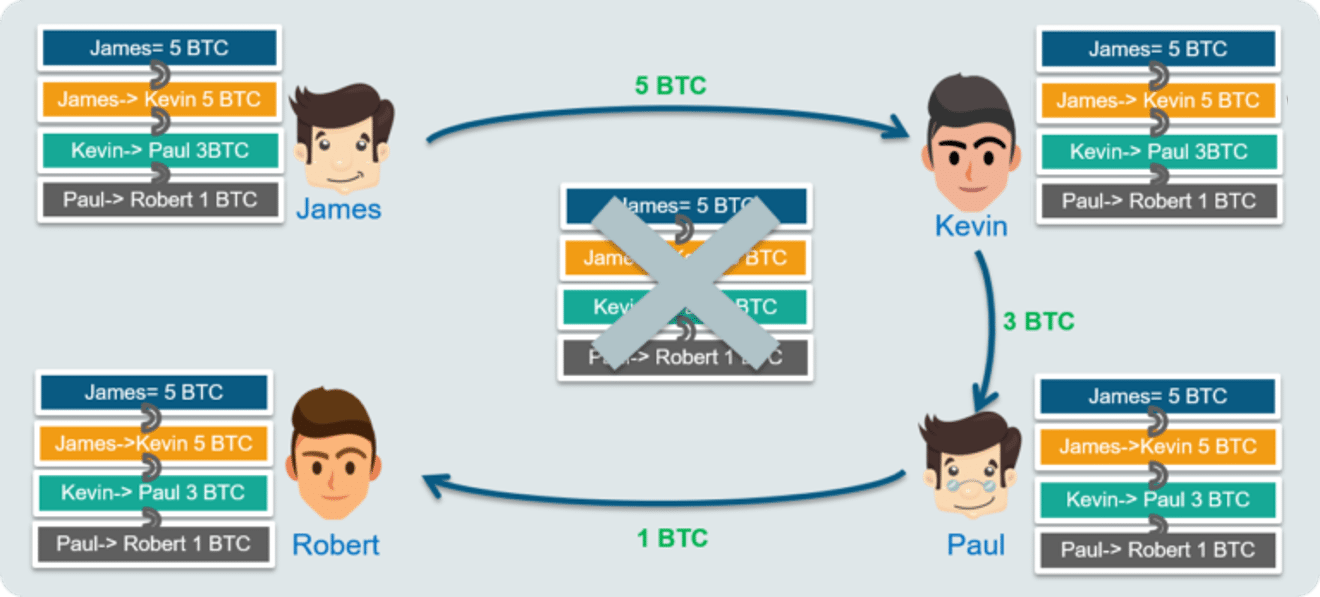
Blockchain is a distributed database that stores all the Bitcoin transactions that have ever happened in the history of Bitcoin. This ensures that no one person can make changes to the ledger because everyone else will immediately flag it as corrupt.
Everything stored on the Blockchain is encrypted. This way, everyone is able to see all the transactions but at the same time, no one will know which of those accounts belongs to you.
Isn’t this exactly what we expect a banking system to be?
Proof of Work is a concept invented in Bitcoin Blockchain wherein the miners (special users of Bitcoin) will validate transactions by solving a complex mathematical puzzle called Proof of Work. 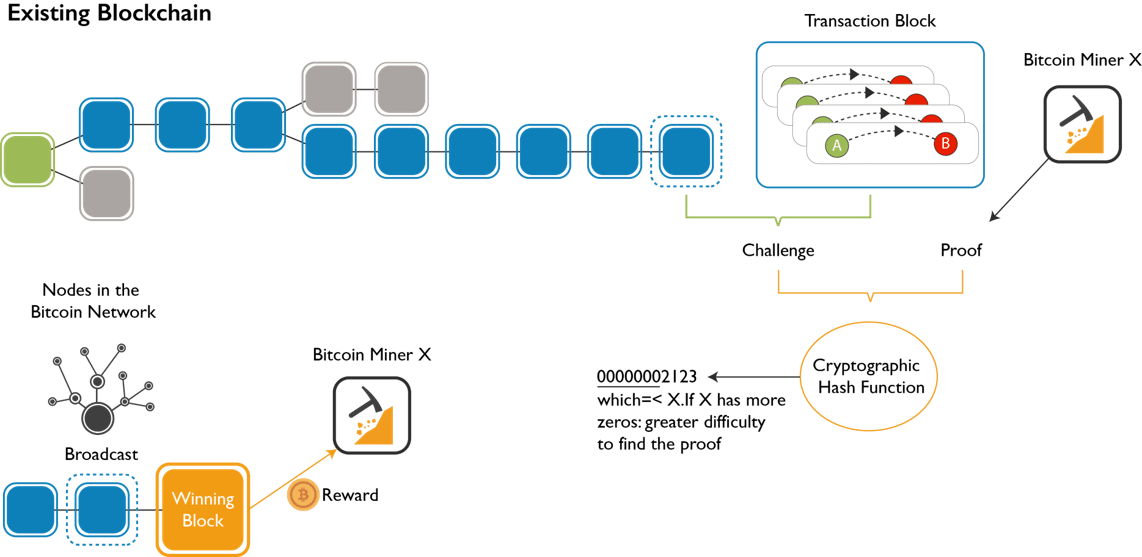
Technically, there is a hash target value designated to every block before time. Miners club together a set of unverified Bitcoin transactions (around 250) into one block, compute its hash and then begin a race to find a specific set of characters called Nonce.
The total hash obtained from the hash of the previous block, transaction data, and the nonce has to match the final pre-assigned target hash value. It is this Nonce which is computationally extensive. Only people with huge computational computing power and electricity are able to solve it in 10 minutes on average.
The most interesting part of Bitcoin is Bitcoin Mining. It is the concept in which certain users do a piece of work and are rewarded with 12.5 Bitcoins (BTC) per block. Each block takes on average about 10 minutes to mine.
This incentive is given for the efforts in computation and to cover the electricity and infrastructure costs required to achieve it. Currently, large pools control about 10-20% of global mining power and generally only these pools are successful in mining Bitcoins.
Bitcoin Mining is a process of validating transactions into a new block and adding this block to the existing Blockchain. Successful miners of Bitcoin get rewarded with a fixed amount of new Bitcoins that are mined into the Bitcoin economy. Currently, each successful miner gets 12.5 BTC (Subject to change once every 4 years or through a Bitcoin community decision) as a reward for successfully adding a block of transactions to the Blockchain.
Bitcoin wallets are generally used to transfer Bitcoins across different accounts. These are like a superset containing wallets for Bitcoin and all other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Litecoin, Dash, Ripple and Auroracoin to name a few.
All transactions on the Bitcoin network happen through one of the various Bitcoin wallets. Some of the popular Bitcoin Wallets include Jaxx, Zebpay, Blockchain.info, Electrum, Keep Eye, Exodus, and Mycelium.
We will explore the most popular types of Blockchain Wallets based on the location of private keys, devices, and clients
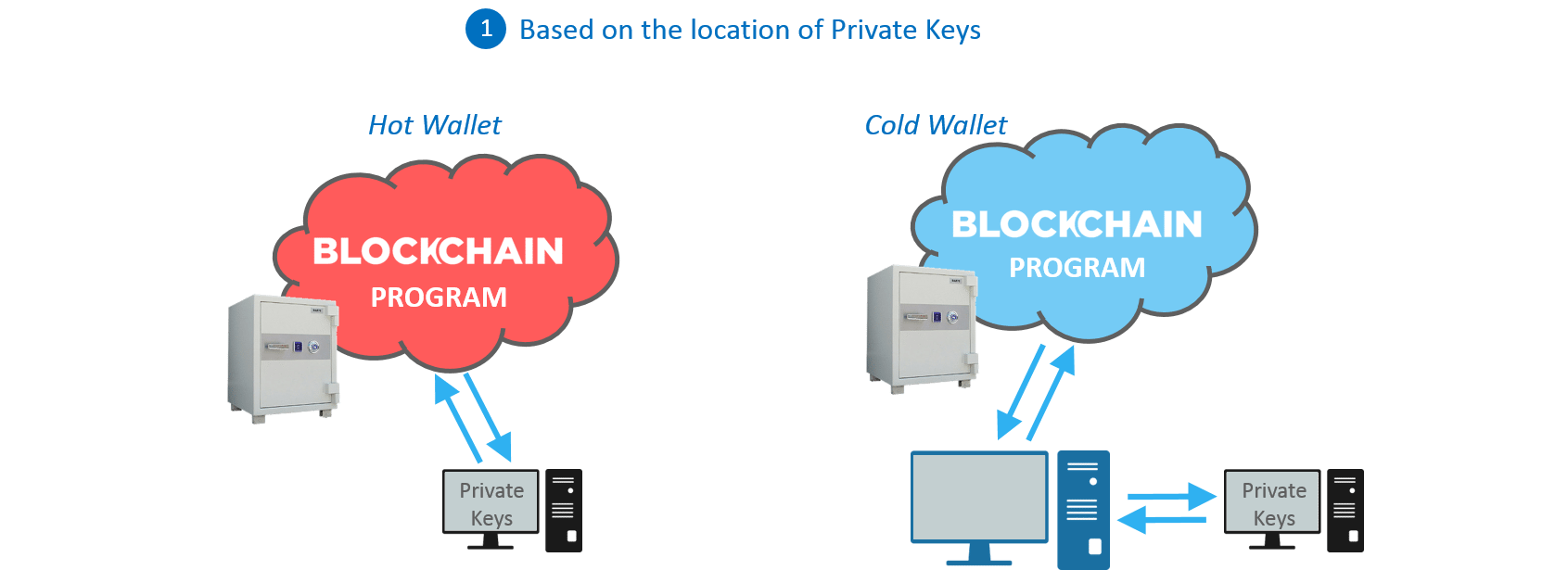 Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Hot and Cold Wallets
Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Hot and Cold Wallets
Hot Wallets are the easiest to use for transferring cryptocurrencies. There is no need to download the whole Blockchain and all private keys are stored online for fast transfers. They are less reliable when compared to cold wallets.
Cold Wallets are those where entire Blockchain is downloaded on the system and every transaction is signed offline and then published online. They are the safest way to do online cryptocurrency transfers.
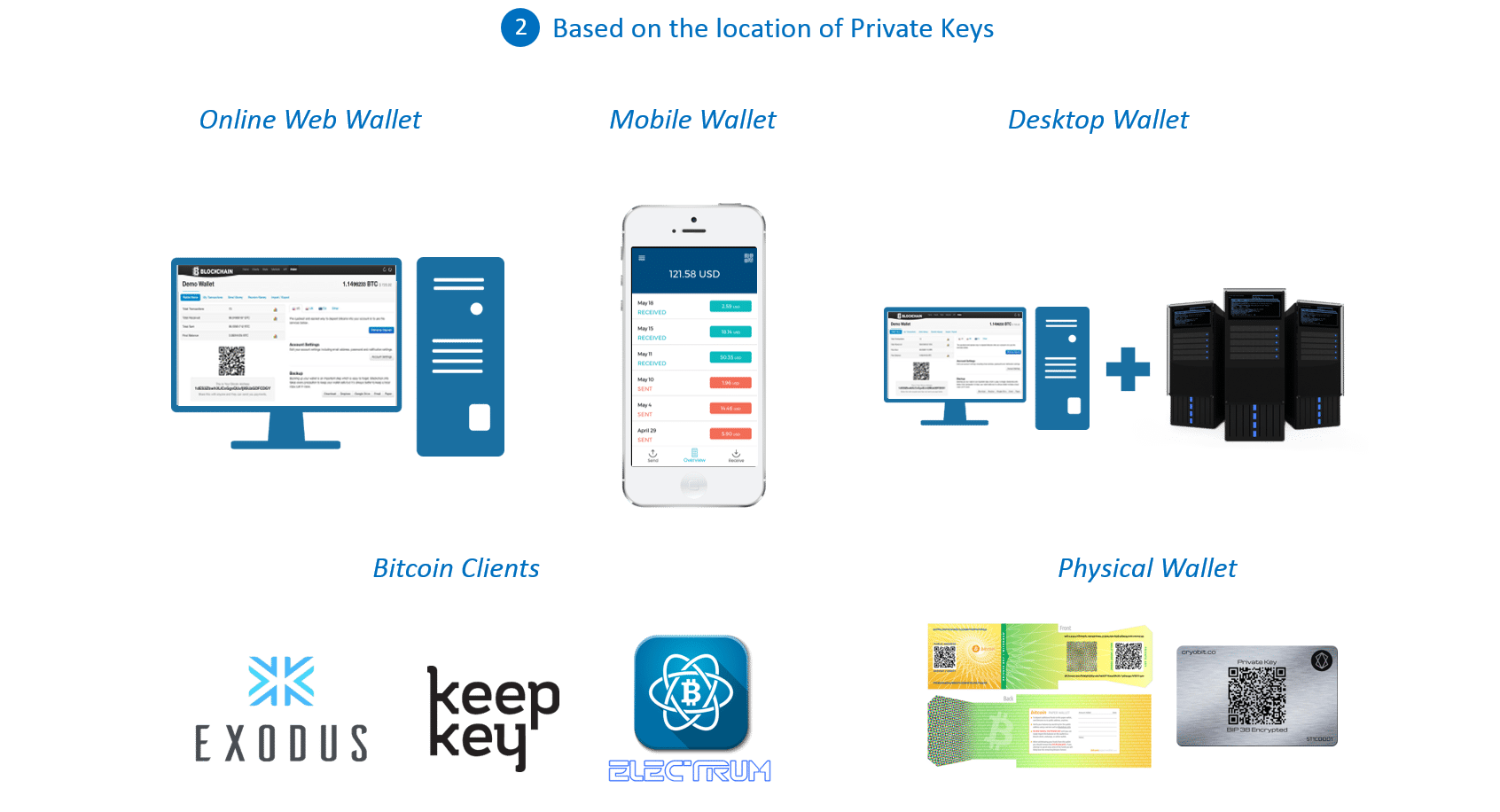 Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Wallets based on location of private keys
Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Wallets based on location of private keys
Online Web Wallet is a hot wallet where the Blockchain exists online and the user transfers using their private key and the recipient’s public address.
Mobile Wallets are similar to Online Web Wallets except they are specifically designed for mobile phone usage. Generally, mobile wallets have their own online web version too.
Desktop Wallets are cold wallets where the private keys of Blockchain accounts such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are stored on cold servers and there is a separate client machine which acts as an intermediary between the internet and the server.
Physical Wallets are those wallets where the Bitcoin (or other cryptocurrencies) details such as private key, public address and QR code are physically printed for long time usage.
Bitcoin Clients are wallets specific for Bitcoin transfers. These clients help users to process their Bitcoin transactions by charging a small fee. Some of the most popular Bitcoin Clients are Keep Eye, Electrum, Exodus and Mycelium.
Hardware Wallets can be used to directly transfer Bitcoins (cryptocurrency) from the hardware to another Bitcoin (cryptocurrency) account when it is connected to the internet. Most often, the wallets themselves contain an interface to enter the recipient’s details and the amount to be transferred.
Let us now look at how we can use Blockchain Wallets to transfer Bitcoin across multiple Bitcoin accounts. We will be using the popular wallet Jaxx for our demo.
Step 1: Download Jaxx Wallet from Jaxx.io
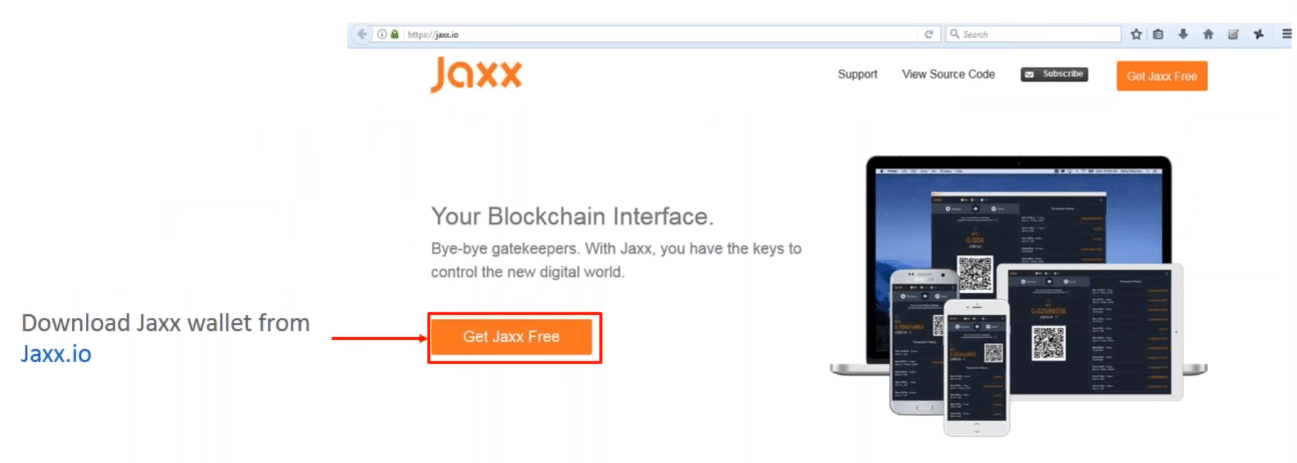 Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Downloading Jaxx Wallet
Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Downloading Jaxx Wallet
Step 2: Create your Bitcoin Wallet account on Blockchain.info
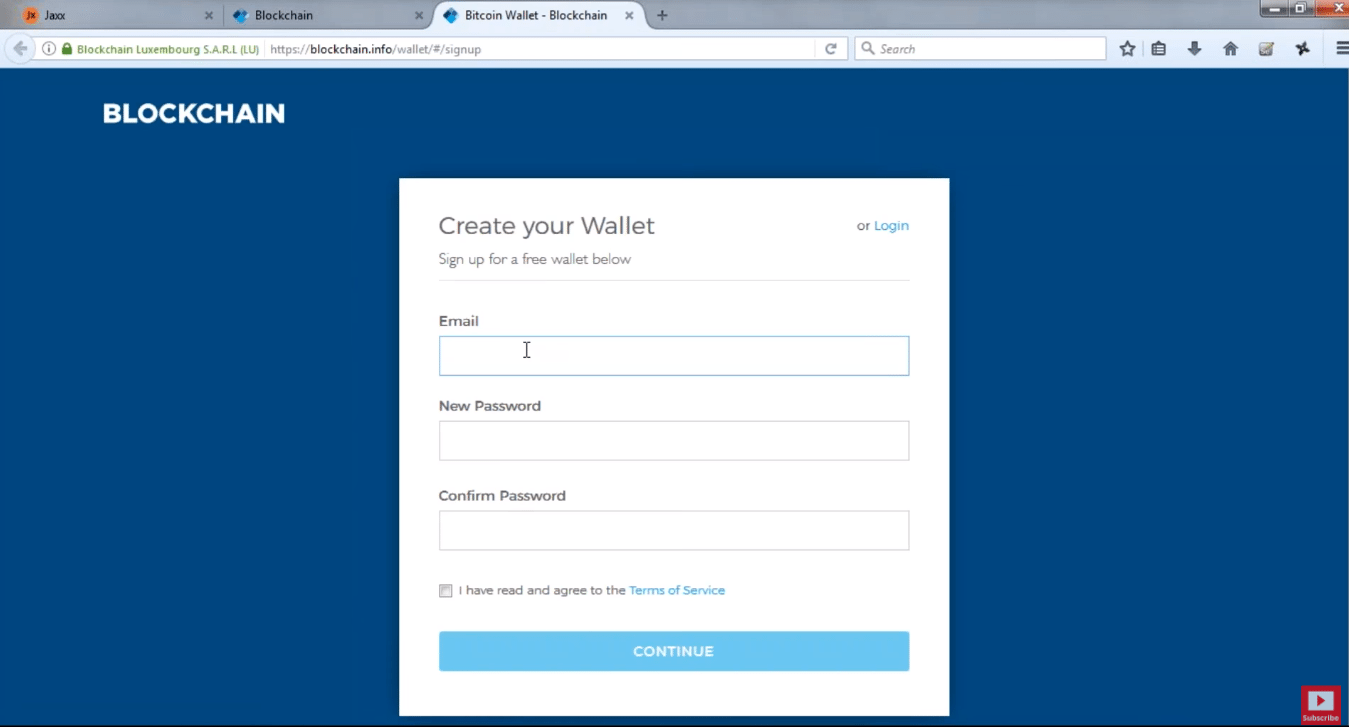 Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Signing up for a Bitcoin Wallet
Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Signing up for a Bitcoin Wallet
Step 3: Fill in the details from the Jaxx wallet. The To address can be obtained from the Jaxx wallet under Your Current Bitcoin Address field. Fill in rest of the details such as the Bitcoin amount and the optional description.
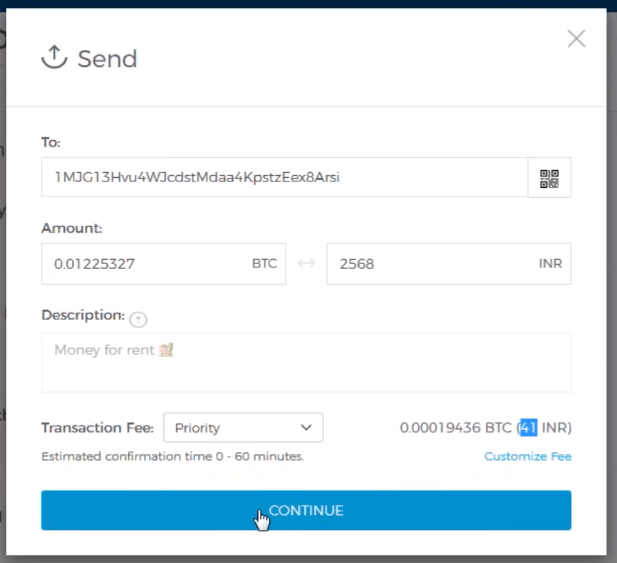 Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Sending Bitcoins from Blockchain.info Wallet
Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Sending Bitcoins from Blockchain.info Wallet
Step 4: Confirm if all the details filled are correct and click on Send Bitcoin button to confirm the transaction.
Step 5: You can now refresh the Jaxx wallet and see the updated Bitcoin balance. It takes about 30 minutes for the transaction to get a 3 block confirmation.
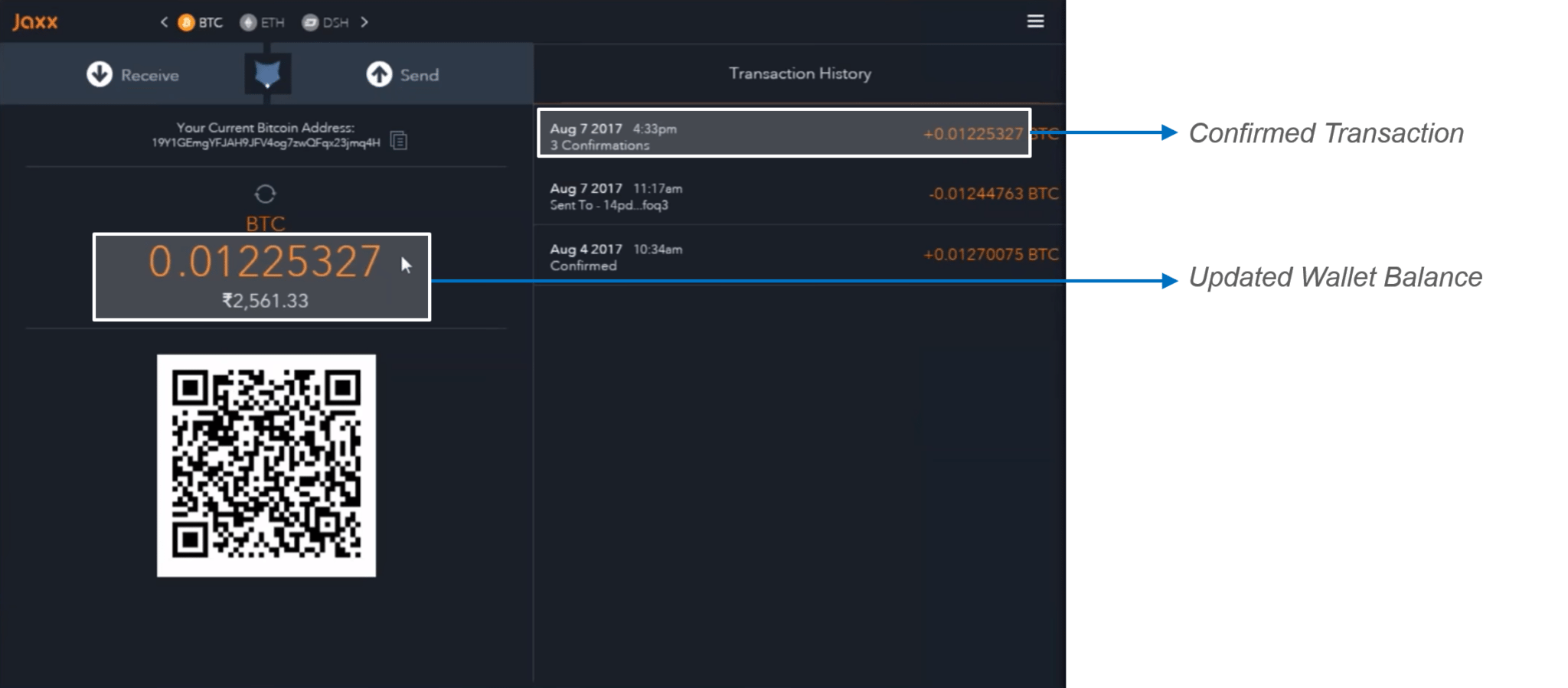 Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Confirmed transaction in Jaxx
Figure: Bitcoin Blockchain Explained – Confirmed transaction in Jaxx
I hope that I have been able to make you understand a thing or two about Bitcoin and Blockchain through this blog. I would recommend you to go through our Blockchain Tutorial and Blockchain Technology blogs to gain an in-depth understanding of Blockchain, Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, Ethereum, Hyperledger and Smart Contracts.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section and we will get back to you.
If you wish to learn Blockchain and build a career in Blockchain Technologies, then check out our Blockchain Certification course which comes with instructor-led live training and real-life project experience. This training will help you understand Blockchain in depth and help you achieve mastery over the subject.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co