Full Stack Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
Searching Algorithms are very important as they help search data in patterns which is otherwise very difficult. In this article we will take take a look at Binary Search in C with practical implementation. Following Pointers will be covered in this article:
Let us get started with article on Binary Search in C,
A Binary Search is a search algorithm, that is used to search an element in a sorted array. A binary search technique works only on a sorted array, so an array must be sorted to apply binary search on the array. It is a searching technique that is better then the liner search technique as the number of iterations decreases in the binary search.
The logic behind the binary search is that there is a key. This key holds the value to be searched. The highest and the lowest value are added and divided by 2. Highest and lowest and the first and last element in the array. The mid value is then compared with the key. If mid is equal to the key, then we get the output directly. Else if the key is greater then mid then the mid+1 becomes the lowest value and the process is repeated on the shortened array. Else if the key value is less then mid, mid-1 becomes the highest value and the process is repeated on the shortened array. If it is not found anywhere, an error message is displayed.
Let us move further with this Binary Search In C article and see an example,
Let’s look at the code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, low, high, mid, n, key, array[100];
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter %d integersn", n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&array[i]);
printf("Enter value to findn");
scanf("%d", &key);
low = 0;
high = n - 1;
mid = (low+high)/2;
while (low <= high) {
if(array[mid] < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (array[mid] == key) {
printf("%d found at location %d.n", key, mid+1);
break;
}
else
high = mid - 1;
mid = (low + high)/2;
}
if(low > high)
printf("Not found! %d isn't present in the list.n", key);
return 0;
}
Output:
If the key is present:
If Key is not present:
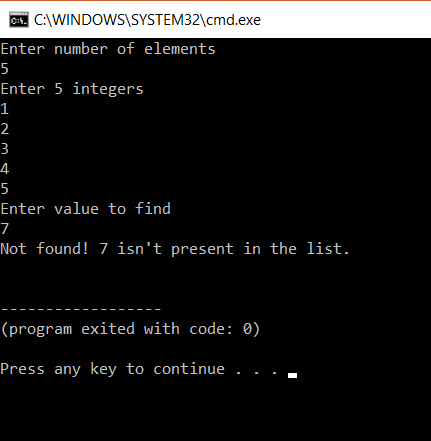
In the program above, We declare i, low, high, mid, n, key, array[100].
We first, take in the number of elements the user array needs and store it in n. Next, we take the elements from the user. A for loop is used for this process. Then, we take the number to be searched from the array and store it in the key.
Next, we assign 0 to the low variable which is the first index of an array and n-1 to the high element, which is the last element in the array. We then calculate the mid value. mid = (low+high)/2 to get the middle index of the array.
There is a while loop which checks if low is less then high to make sure that the array still has elements in it. If low is greater then, high then the array is empty. Inside the while loop, we check whether the element at the mid is less than the key value(array[mid] < key). If yes, then we assign low the value of mid +1 because the key value is greater then mid and is more towards the higher side. If this is false, then we check if mid is equal to key. If yes, we print and break out of the loop. If these conditions don’t match then we assign high the value of mid-1, which means that the key is smaller than mid.
The last part checks if low is greater then high, which means there are no more elements left in the array.
Remember, this algorithm won’t work if the array is not sorted.
Let us move to the final bit of this Binary Search In C article
Binary Search Using Recursive Function:
Code:
#include &lt;stdio.h&gt;
int binaryScr(int a[], int low, int high, int m)
{
if (high &gt;= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (a[mid] == m)
return mid;
if(a[mid] &gt; m)
return binaryScr(a, low, mid - 1, m);
return binaryScr(a, mid + 1, high, m);
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int a[] = { 12, 13, 21, 36, 40 };
int i,m;
for(i=0;i&lt;5;i++)
{
printf(" %d",a[i]);
}
printf(" n");
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
printf("Enter the number to be searchedn");
scanf("%d", &amp;m);
int result = binaryScr(a, 0, n - 1, m);
(result == -1) ? printf("The element is not present in array")
printf("The element is present at index %d",
result);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
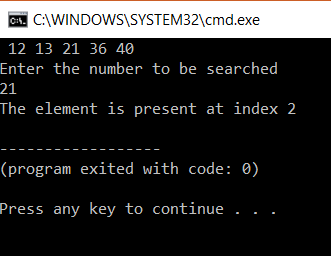
In the above program, we use a function BinaryScr to search the element in the array. The function is recursively called to search the element.
We accept the input from the user and store it in m. We have declared and initialized the array. We send the array, the lower index, higher index and the number to be searched to the BinaryScr function and assign it to result. In the function, it performs binary search recursively. If not found, then it returns -1. In the main function, the ternary operator is used. If result=-1 then not found else found is displayed.
To apply the Binary Search Algorithm in the data structure, the following conditions are:
The Binary Search Algorithm works as:
1. Initialization: Start with two pointers: ’low’ at the beginning of the array and ‘high’ at the end.
2. Calculate Midpoint: Find the middle element by calculating the index as ‘mid=(low + high)/2’.
3. Compare and Decide:
4. Repeat: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until the target is found or the ‘low’ pointers exceed the ‘high’ pointer, indicating the target is not in the array.
Initialize Pointers: Set two pointers, ‘low’ at the start (index 0) and ‘high’ at the end (index length – 1) of the array.
With this, we come to the end of this blog on ‘Binary Search In C’. I hope you found this informative and helpful. Stay tuned for more tutorials on similar topics. You may also check out our training program to get in-depth knowledge on jQuery and its various applications. You can enroll here for live online training with 24/7 support and lifetime access.
Binary search is a search strategy applied to the sorted array. It divides the array with the iterative division of the search range in half, which helps sort the arrays quickly. Binary search minimizes the time complexity to O(LogN).
Binary search repeatedly divides the search interval in half, starting with the entire list. It compares the target value with the middle element. If the target value is less than the middle element, it searches the left half; otherwise, it searches the right half. This process continues until the target is found or the interval is empty.
The time complexity of binary search is represented as O(log2n), where n is the number of elements in the array.
In binary search, the array is sorted in ascending or descending order. If it is not sorted in any particular order, then we cannot use binary search.
The binary search algorithm relies on the order of elements to eliminate half of the remaining search space at each step. So if the array is not sorted, binary search will not function properly.
Do you have a question for us? Post it in the comments section of this blog, and we will respond to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co