React JS Training Course
- 23k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend
- Live Class
Angular is a popular JavaScript framework for developing client-side web applications. It is a robust and versatile platform utilized by a large number of developers and enterprises globally.
As a result, Angular provides two key elements to assist developers in creating powerful applications: Angular modules and components.
In this article, we will discuss the differences between Angular Modules and Components, as well as how to use each. We will also include examples to assist you in comprehending the ideas.
 What are Angular Components?
What are Angular Components?A component in Angular stands in for a view and is in charge of managing user interactions and content rendering. A class and related templates that define the view’s appearance and layout are used to define it.
The smallest independent parts and the main building elements of an Angular application are called components. Through attributes and methods made available by the component class, they interact with the view and control particular areas of the screen.
Building dynamic and interactive applications requires the component class, which has the logic underlying the display, control user interactions, change the data model, and interact with other components or services.
Syntax:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-counter',
template: "..."
`
})
export class CounterComponent {
code...
}
Example: The HTML code for an Angular component or module is typically split into two parts: the template and the class.
counter.component.ts
JavaScript
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-counter-feature',
templateUrl: './counter-feature.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./counter-feature.component.css'],
})
export class CounterFeatureComponent {
counterValue = 0;
increaseCounter() {
this.counterValue++;
}
decreaseCounter() {
this.counterValue--;
}
}
counter.component.html
HTML
<button (click)="increaseCounter()">
Increase
</button>
<div>{{ counterValue }}</div>
<button (click)="decreaseCounter()">
Decrease
</button>
counter.component.html
HTML
<div class="container"> <h1>Edureka</h1> <h3> Difference between Component and Module </h3> <app-counter> </app-counter> </div>
app.component.ts
HTML
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'],
})
export class AppComponent {}
Explanation of the Code:
After discussing the essential elements of Angular components, let’s examine Angular Modules and their function in Angular applications.
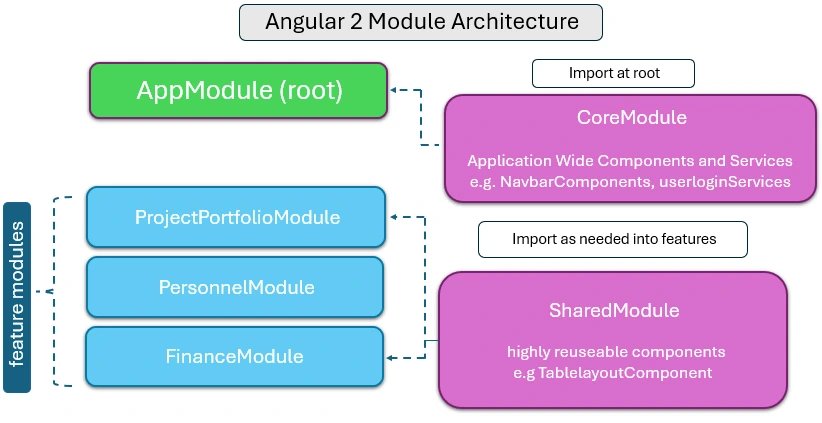
Modules are used to aggregate related components and directives, as well as the services, pipelines, and other code on which they rely, into a single cohesive unit.
They help to structure the code and make it easy to reuse components and directives throughout the application.
It is defined using the Angular NgModule decorator, which accepts an object specifying the module’s components, directives, and other code.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Components } from './counter.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [Components],
imports: [],
exports: [Components]
})
export class CounterModule { }
The module template in this instance is a straightforward HTML document. The module class defines the app-counter element, a custom element that stands in for the CounterComponent.
NgModule decorator, which accepts an object specifying the components, directives, and other code that the module includes, is used to define the module class.
In this example, the bootstrap array designates the CounterComponent as the root component that will be bootstrapped when the module is bootstrapped, while the declarations array lists the CounterComponent as a component of the module.
counter.module.ts:
JavaScript
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CounterComponent } from './counter.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [CounterComponent],
exports: [CounterComponent]
})
export class CounterFeatureModule {}
app.module.ts
JavaScript
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { MainAppComponent } from './app.component';
import { CounterFeatureComponent } from './counter/counter.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [BrowserModule],
declarations: [MainAppComponent, CounterFeatureComponent],
bootstrap: [MainAppComponent]
})
export class MainAppModule {}
Explanation of the Code:
Project Structure:
Output: The following output will be displayed for counter using component and module:
 What’s the Difference Between an Angular Component and Module?
What’s the Difference Between an Angular Component and Module?Now that we have a better knowledge of Angular Modules, let’s examine the differences between these components and modules.
| Modules | Components |
|---|---|
| A container for a group of related components and directives. | A class with an associated template that defines a view. |
| Can contain services, pipes, and other code used by the components. | Responsible for rendering a view and handling user interactions. |
| Defined using the Angular `NgModule` decorator. | Defined using a class and a template. |
| Provides a way to group related functionality and keep the code organized. | Controls a part of the screen called a view. |
| Can contain multiple components and directives. | Can interact with other components or services. |
Now that we have a better knowledge of Angular Modules, let’s examine the differences between these components and modules.
To sum up, the Angular framework’s essential components are Angular Modules and Components. While components manage user interactions and content display, modules organize linked parts and services. Developers can more easily construct reliable programs when they are aware of these distinctions.
Check out Angular JS Training Course to learn more about Angular. This course will help you design scalable applications and advance your web development career with knowledgeable professors and practical projects. Use Edureka to begin learning Angular right now!
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co